Materials
Traditional crafts such as papermaking or silk making that produce a basic material. These produce high quality materials that are often used for other crafts such as bookbinding or kimono making.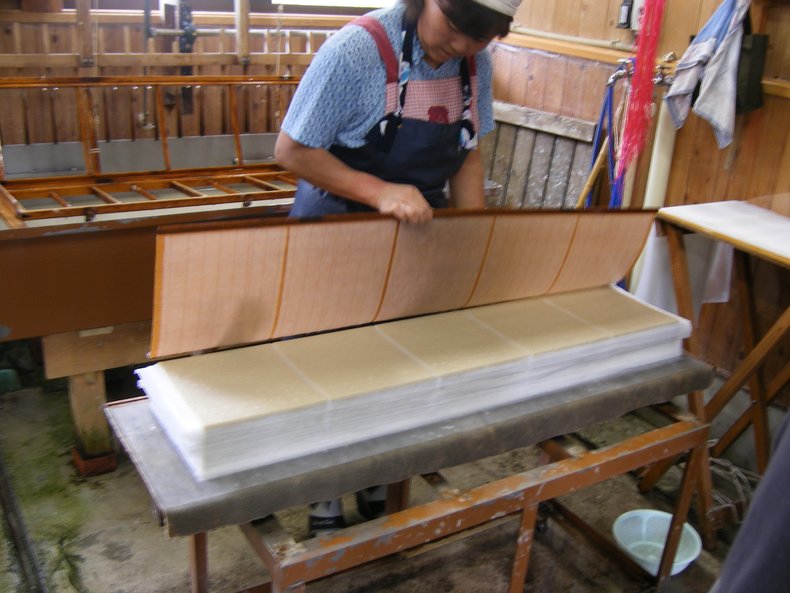
Craft Production
Craft production is the process of making products by hand. This is a common type of premiumization whereby you can make a product that is more unique and valuable than the competition with the labor of a skilled artisan. The term craft is also commonly misused as a marketing term for mass produced items.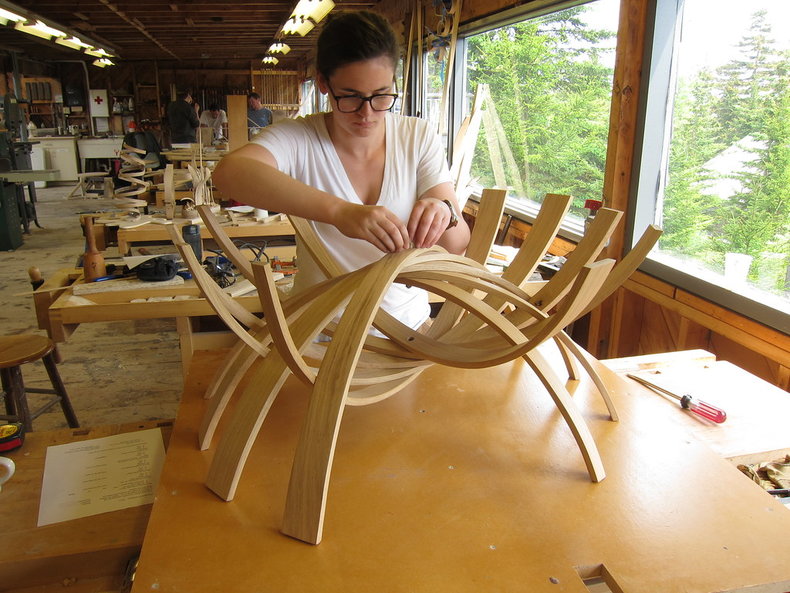
Traditional Crafts
Crafts based on long standing traditions including traditional products such as Japanese tatami mats and traditional arts such as totem poles.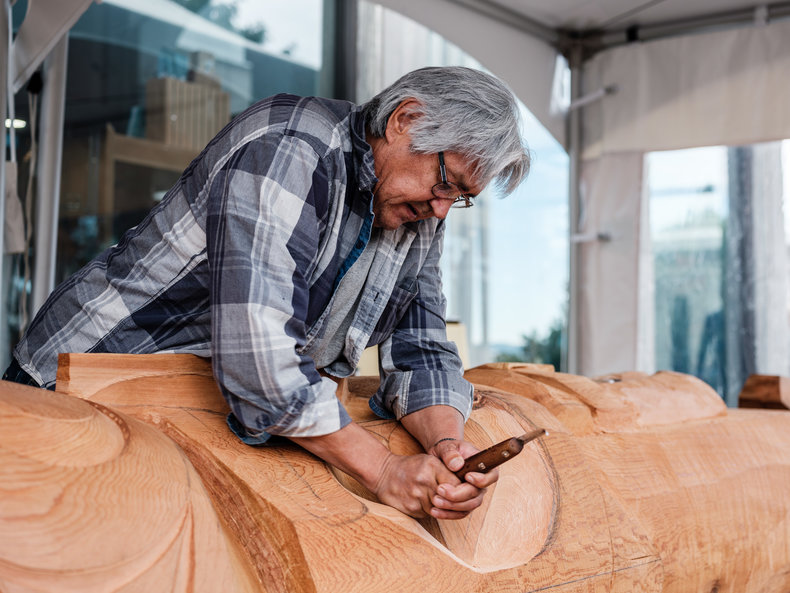
Furniture
Designing and making furniture. This is related to professions such as cabinet maker, carpenter and upholsterer.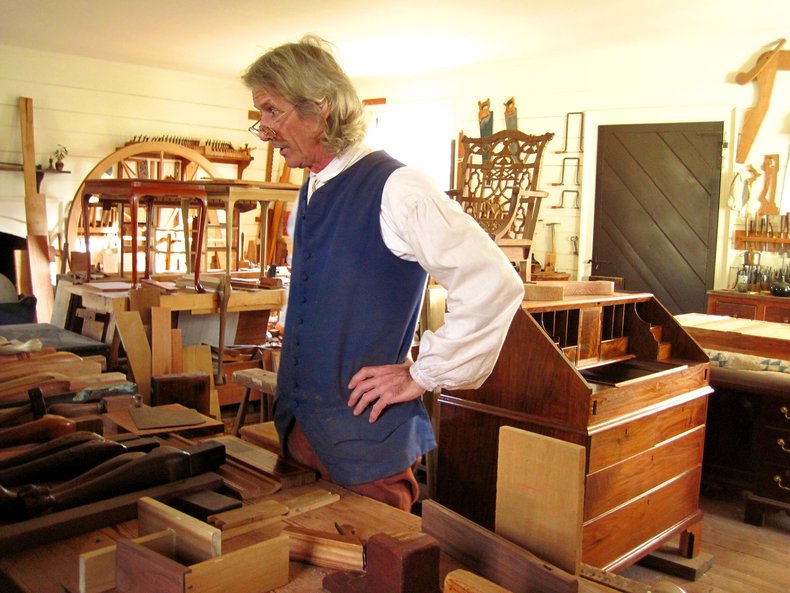
Artisanal Food
Artisanal food is a term for crops, processed food and beverage products that are produced with skill and manual labor. This is associated with high quality food produced in small batches that is sold primarily to locals. It is also widely misused as a marketing term for food produced with industrial processes. In many cases, artisanal food can be certified as an appellation such as a salt product that comes from a region known for unique salt that adheres to local standards.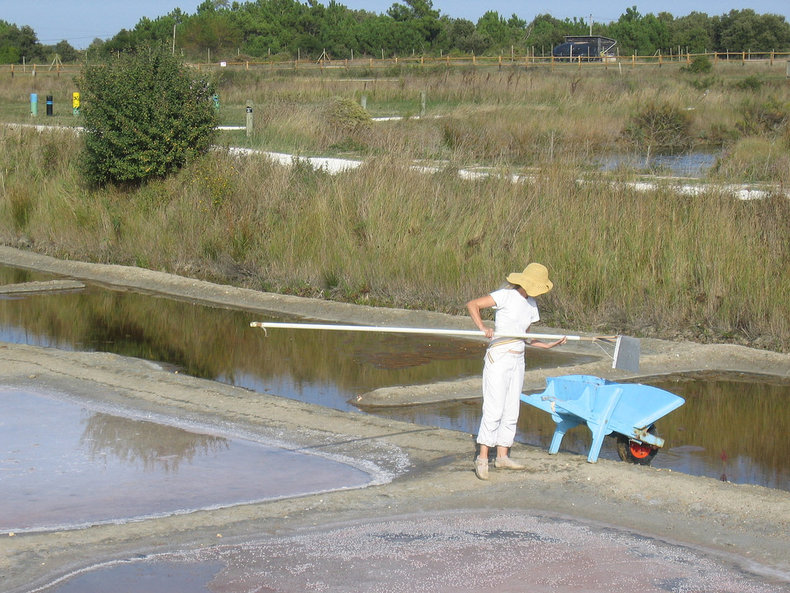
Musical Instruments
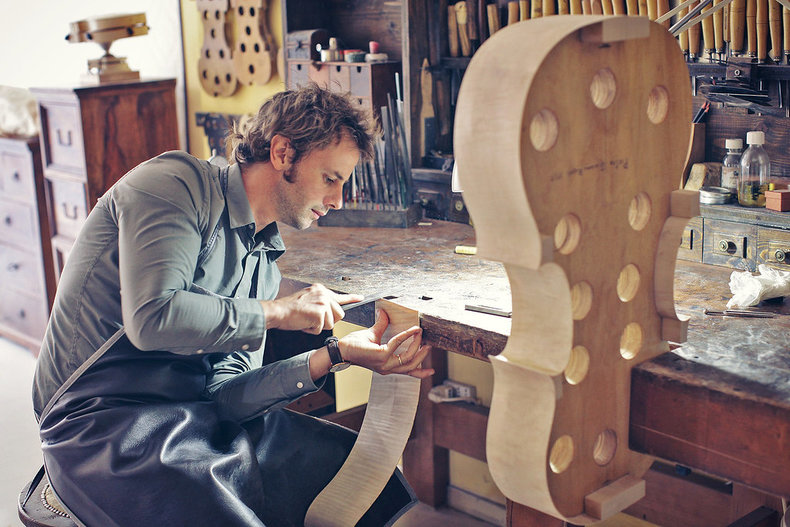
High quality musical instruments are often produced by hand. For example, an artisan who builds string instruments is known as a luthier. This generally requires an apprenticeship as it takes significant mastery to get right.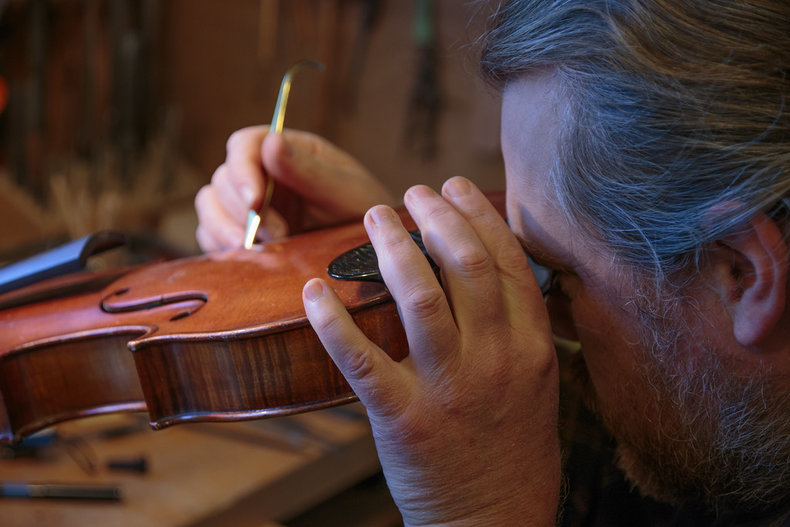
Woodworking
Wood is a flexible and natural material that has long been used for craft. This requires a variety of skills in areas such as wood carving, joinery, carpentry and woodturning. Woodworking ranges from small practical items to grand creative works that can be considered fine art.
Metalworking
Metalworking includes professions such as blacksmith, silversmith and coppersmith. Limited metalworking can be learned as a hobby without becoming a professional. This usually involves shaping, structuring and finishing malleable and ductile metals.
Jewellery Design
The design and crafting of jewellery. This is an extensive process that may begin with illustrations, computer models and wax prototypes. The crafting of jewellery requires skills such as gem cutting and metal working including fabrication, mounting, soldering, welding, casting, chasing, engraving, enameling, stone setting and polishing.
Ceramic Arts & Glassmaking
The creation of arts, crafts and the production of products using ceramic materials or glass.
Needlework
Producing clothing, housewares and decorative items with needlework such as knitting and quilting.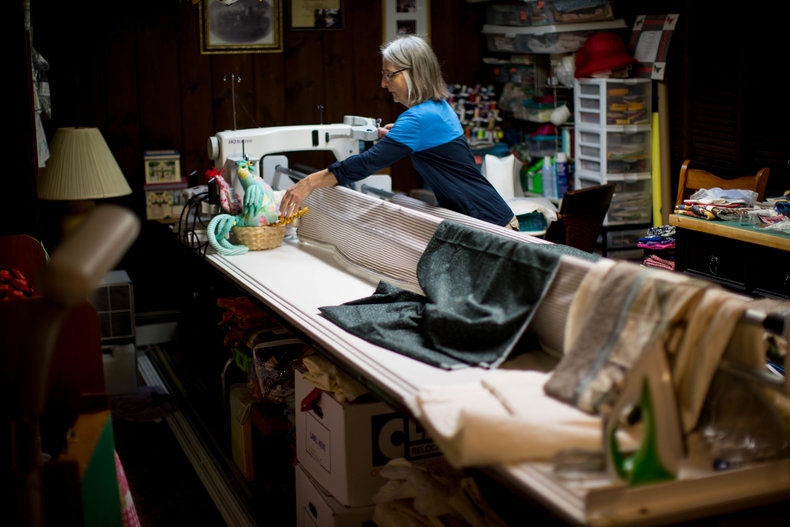
Dressmaking & Tailoring
Designing and making dresses, blouses, evening gowns, shirts, suits and other complex clothing. Dressmaker and tailor are professional designations that are also widely practiced as a hobby.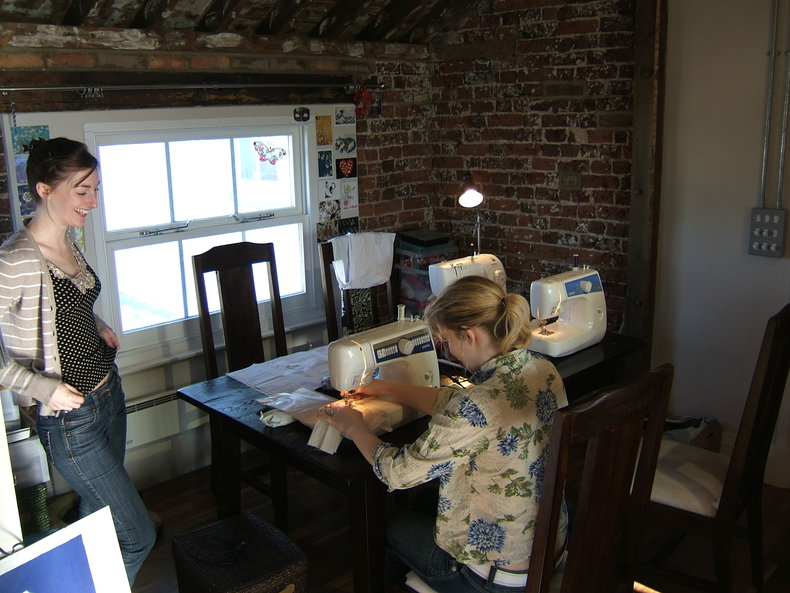
Decorative Art
Art that is produced according to constraints such as commercial requirements is often considered a craft. Fine art is produced without constraints on the creativity of the artist and is not considered craft.
Floral Design
Floral design and flower arts such as ikebana.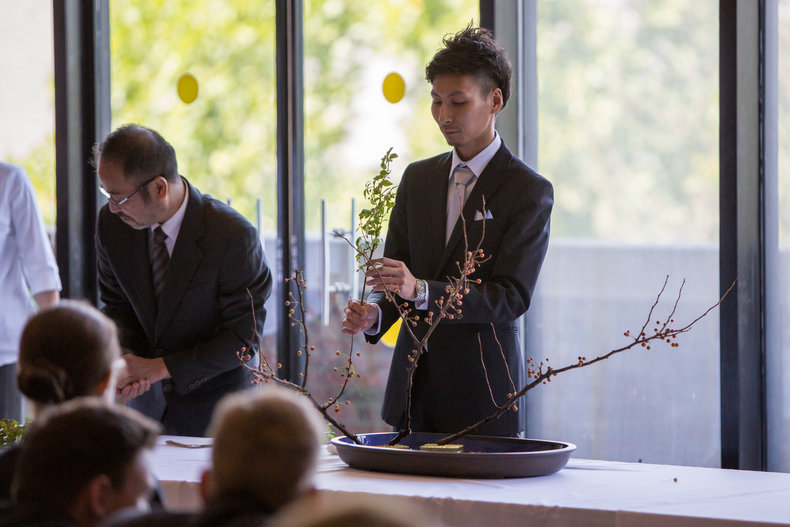
Costume Design
The design of costumes for films, theatre, performance art, festivals or hobbies such as cosplay.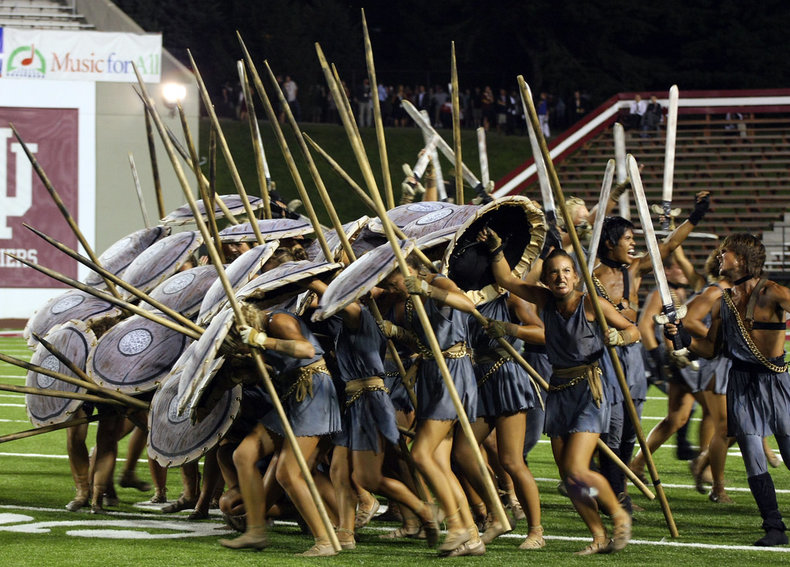
Models
It is common for design such as product design and architecture to rely on models. Such models may initially be created by hand using inexpensive materials such as paper.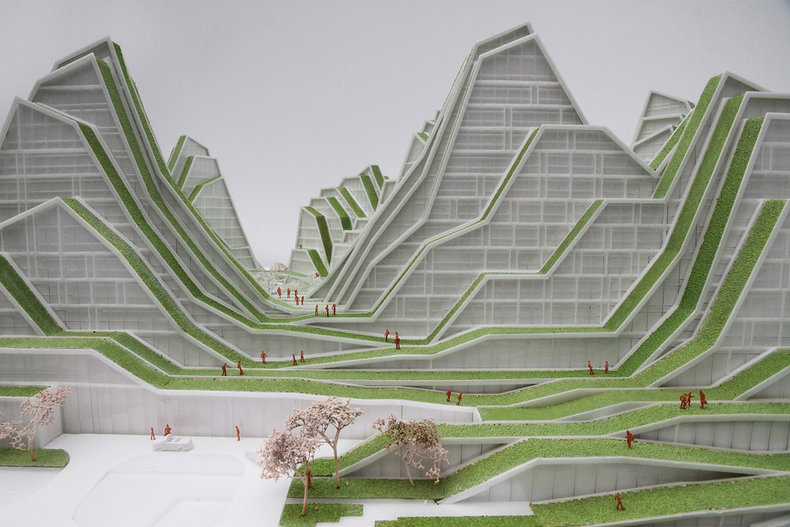
Prototypes
Prototypes are working models that implement or simulate functionality. These include throwaway prototypes that are designed to be inexpensive and evolutionary prototypes that are designed to reflect the state of the art.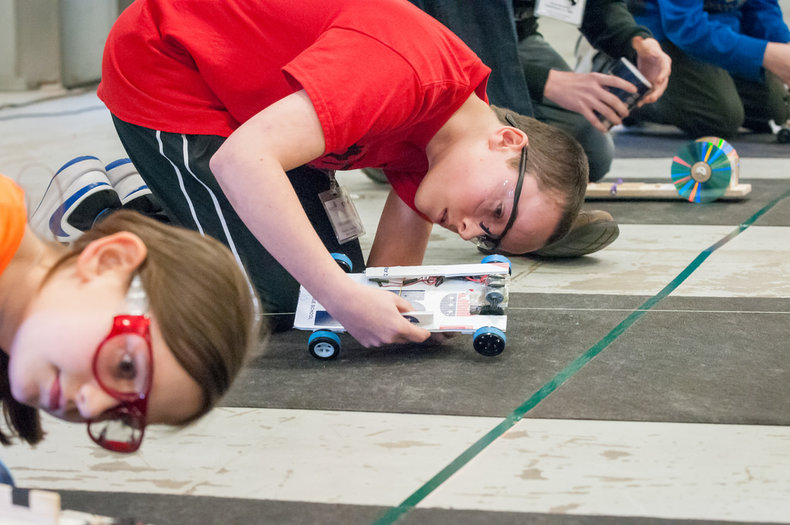
Media & Publishing
Creating physical works of media such as a scrapbook or a bookbinding for a publication.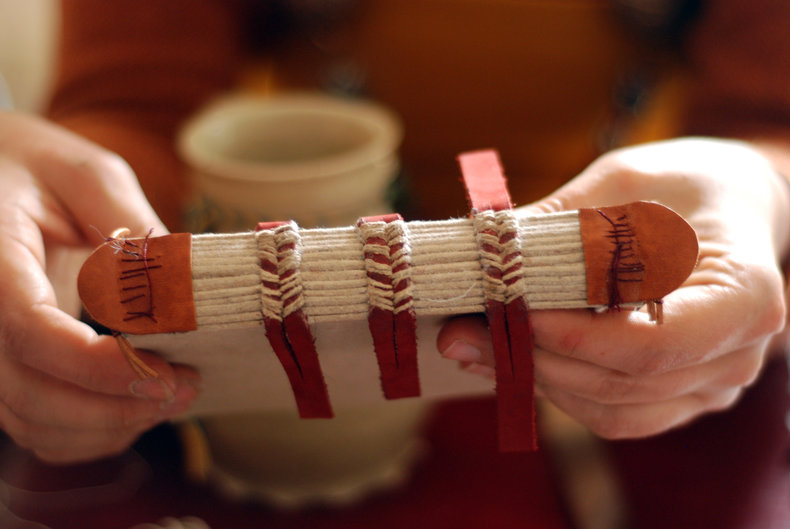
Architecture
Architecture may include crafted ornamental and decorative features created by trades such as carpenters, masons and marble setters. Historically, ornament was a pervasive feature of architecture but this went into decline in the 20th century with the popularity of modern architecture that embraced minimalism.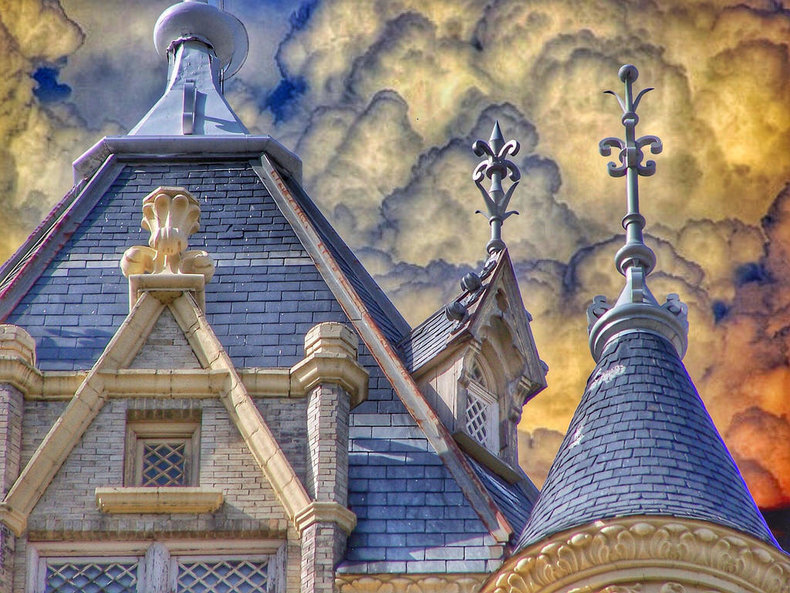
Education
Craft is often used in classes to apply lessons or as an exercise in creative expression. It is common to ask parents to donate interesting packaging to use in crafts to build an ethic of reuse in the classroom.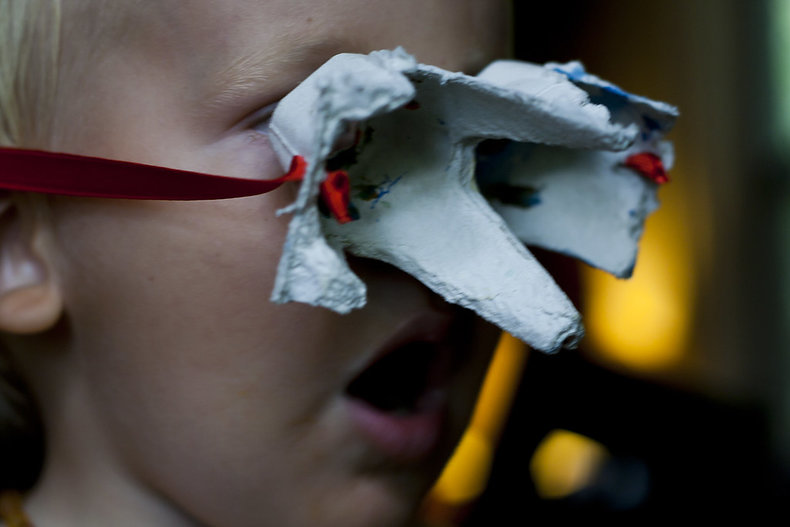
Downcycling & Upcycling
Reusing things often resembles a craft. Downcycling is the creation of something of lesser value than the original items. Upcycling is creating things of greater value. For example, making a toy out of used packaging.
Low-Tech
Information technology involves advanced manufacturing processes that can be viewed as the opposite of craft. However, the process of building new things from old components can be viewed as a type of craft. For example, low-tech enthusiasts who build their own music synthesizers.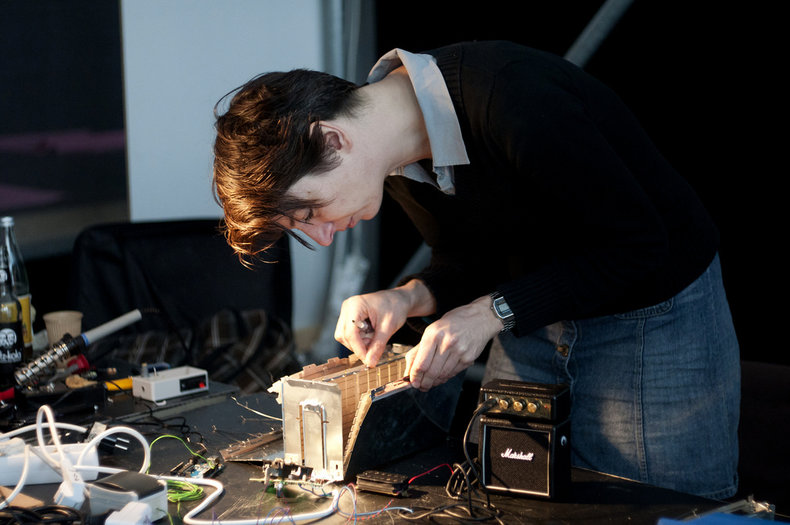
| Overview: Crafts | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Craft is skilled production or creation by hand. | |
Related Concepts | ||