Strength of Memory
The forgetting curve isn't a single curve but differs by person, topic and learning experience. Vivid learning experiences may be fully retained as we regularly access these memories. Less interesting memories aren't recalled and can begin to fade within seconds. The degree to which a new memory is retained is known as strength of memory. For example, Ed and Sue attend the same cocktail party and are introduced to the same people. Ed is a people-person and experienced salesperson who remembers most names after the party. Sue finds people uninteresting and quickly forgets their names.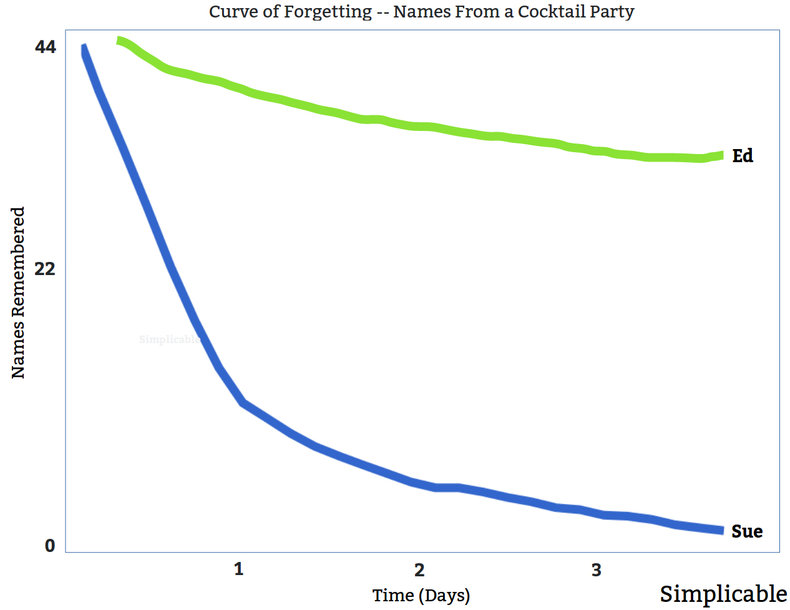
Spaced Practice
Spaced practice is the process of studying a topic repeatedly with a short span of time, usually a day, between each repetition. This is designed to strengthen memory and overcome the forgetting curve. Each repetition serves to flatten the curve such that knowledge becomes more and more durable.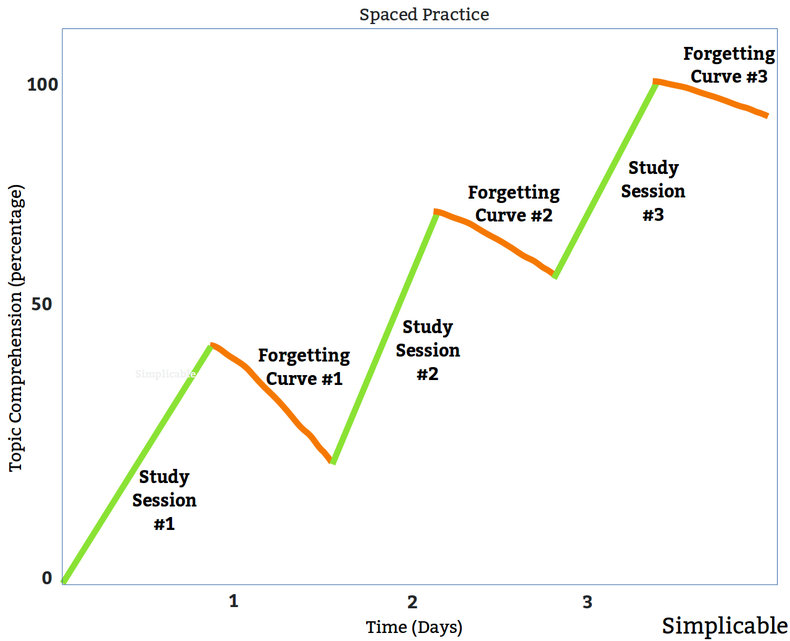
Cramming
Cramming is the process of studying just before information is required. This allows you to absorb information and regurgitate it on a test or in a job interview. However, it results in a very steep forgetting curve as you try to absorb a great deal of information in a short period of time with no reinforcement later. Education systems that encourage cramming tend to produce low knowledge retention.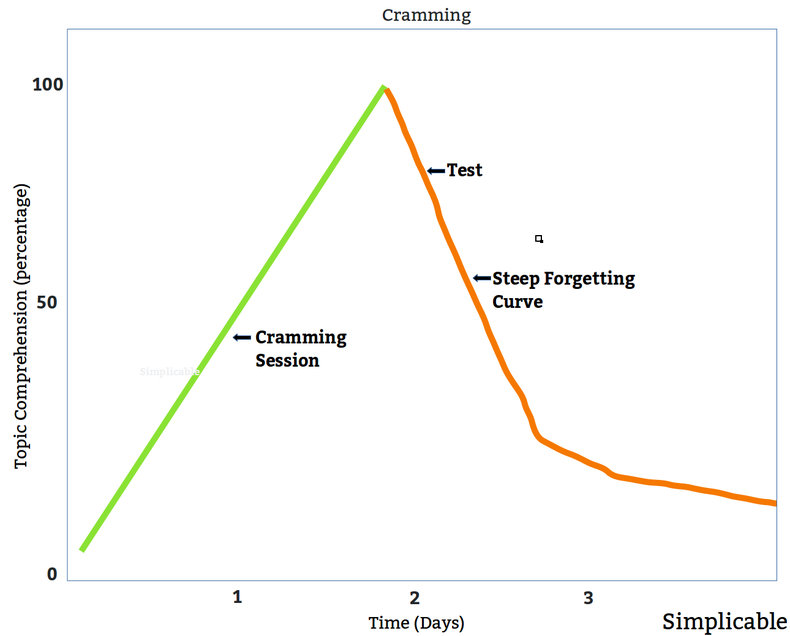
| Overview: Forgetting Curve | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | A model that maps out how much knowledge is retained over time after a learning event. | |
Definition (2) | The degree to which knowledge is lost with time. | |
Also Known As | Curve of Forgetting | |
Attributed To | Hermann Ebbinghaus | |
Related Concepts | ||