
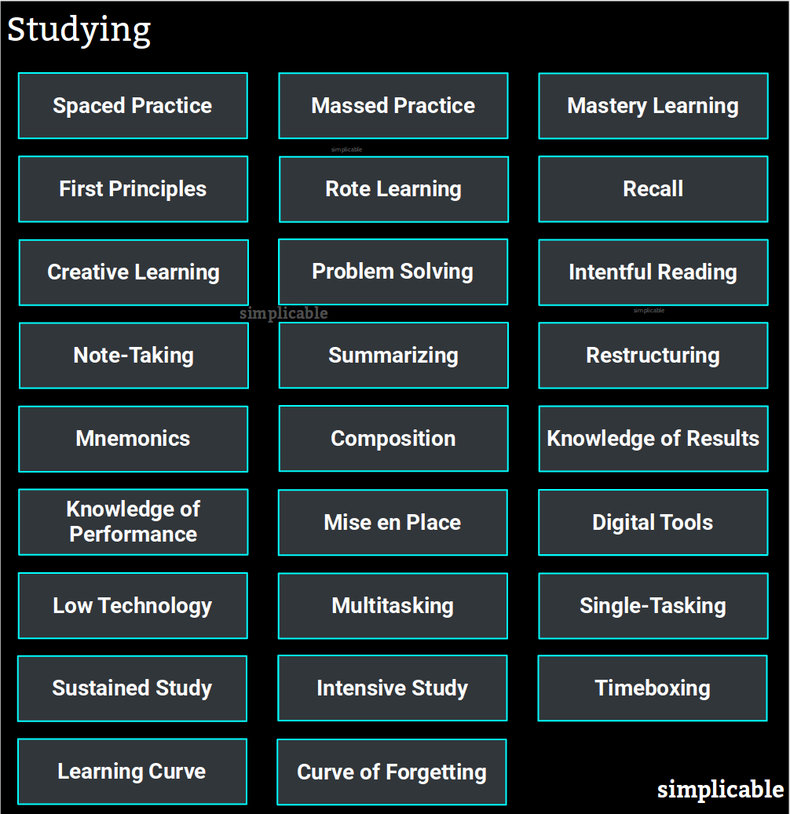
26 Types of Studying  Spaced PracticeSpaced practice is the process of studying the same materials multiple times over multiple days or weeks in order to improve retention. This is based on the spacing effect whereby people tend to remember things they have learned multiple times.Massed PracticeMassed practice, better known as cramming, is the process of trying to remember a great deal of information in a relatively short period of time. This results in shallow learning that is easily forgotten but can boost short term recall for a test. Educators often advise against cramming but may provide incentives for it in the format of tests whereby students are rewarded for regurgitating information.Mastery LearningMastery is the process of completely understanding one lesson before moving to the next. This can beat a process of pressing ahead despite low understanding.First PrinciplesFirst principles are foundational concepts that have broad explanatory power. There can be tragic consequences if you fail to understand a first principle as this can lead to a cascade of knowledge failures. As such, time spent mastering first principles is unusually productive.Rote LearningRote learning is the process of memorizing things using repetition. For example, memorizing terms with flashcards.RecallRecalling what you have learned is known to improve memory retention. For example, explaining a topic to someone.Creative LearningCreative learning is the process of developing your own non-obvious learning techniques and routines. For example, wrapping information in a story to make it easier to remember.Problem SolvingApplying what you are learning by solving problems with it.Intentful ReadingReading is a required element of study. Generally speaking, it is more productive to take this seriously and read with intent to understand as opposed to skimming through.Note-TakingThe process of capturing information from reading, class, media and other sources. This tends to increase your mental engagement and notes can become useful.SummarizingTaking what you have read and summarizing it.RestructuringRestructuring your notes using design thinking. For example, creating a timeline of events in a book to understand the story better.MnemonicsMnemonics are structures that help you memorize things such as an acronym for a bunch of terms. Developing your own mnemonics can be more effective than using existing ones.CompositionWriting about what you are learning in order to understand it or to practice for an assignment or test.Knowledge of ResultsKnowledge of results is information regarding your results at a point in time. For example, an exercise that can be scored against a list of answers. This allows you to identify what materials require further study.Knowledge of PerformanceKnowledge of performance is information regarding your performance that is independent of results. For example, a tutor who can see that you're coming close on math questions despite getting a completely wrong answer. This allows you to identify with precision what you are failing to understand.Mise en PlaceMise en place is the practice of carefully organizing your work area to improve productivity. Pundits commonly recommend a neat desk, messy desk, quiet environment or stimulating environment for study. This may come down to personal preference or perhaps variation may be most productive.Digital ToolsUsing digital tools such as a flashcard app.Low TechnologyThe use of old but reliable technologies such as paper.MultitaskingThe process of doing multiple things at the same time by switching quickly between tasks. For example, checking stock prices and studying at the same time. This reduces overall productivity due to switching costs.Single-TaskingThe process of completely devoting yourself to a task. For example, avoiding distractions such as digital media while you study. A fundamental way to increase productivity.Sustained StudyDeveloping a schedule or a habit that allows you to study at a sustainable pace to maximize performance. For example, studying 3 hours a night for 30 days instead of 90 hours over 4 days.Intensive StudyRefusing to study in a zombie-like state of disengagement. This usually involves short energetic bursts of effort followed by short breaks. With discipline or motivation these energetic bursts can also become quite long.TimeboxingDividing study time into unbreakable segments whereby you refuse to go either longer or shorter. For example, an intensive study regime with 35 minutes study sessions followed by 25 minute breaks.Learning CurveThe learning curve is the theory that learning productivity varies as you become more experienced in a topic. Generally speaking, this means that beginners learn very slowly and intermediates very quickly. When you become an expert in a topic your learning productivity peaks and no longer gets any better. The learning curve has important implications for studying as a topic may seem very difficult at first but eventually your studying productivity will improve as you begin to master first principles.Curve of ForgettingThe curve of forgetting is a theory related to the spacing effect whereby you will forget something if you don't review it fast enough. This is essentially a window of opportunity whereby a quick review of something you spent time learning pays off by preventing a tendency to quickly forget. For example, reviewing the notes from your classes each evening may be a productive use of time.StudyingThis is the complete list of articles we have written about studying.If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
HomeworkAn overview of the common types of homework.Study SkillsA list of common study skills.TrendingThe most popular articles on Simplicable in the past day.New ArticlesRecent posts or updates on Simplicable. Site Map
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited. View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page. |