|
| |
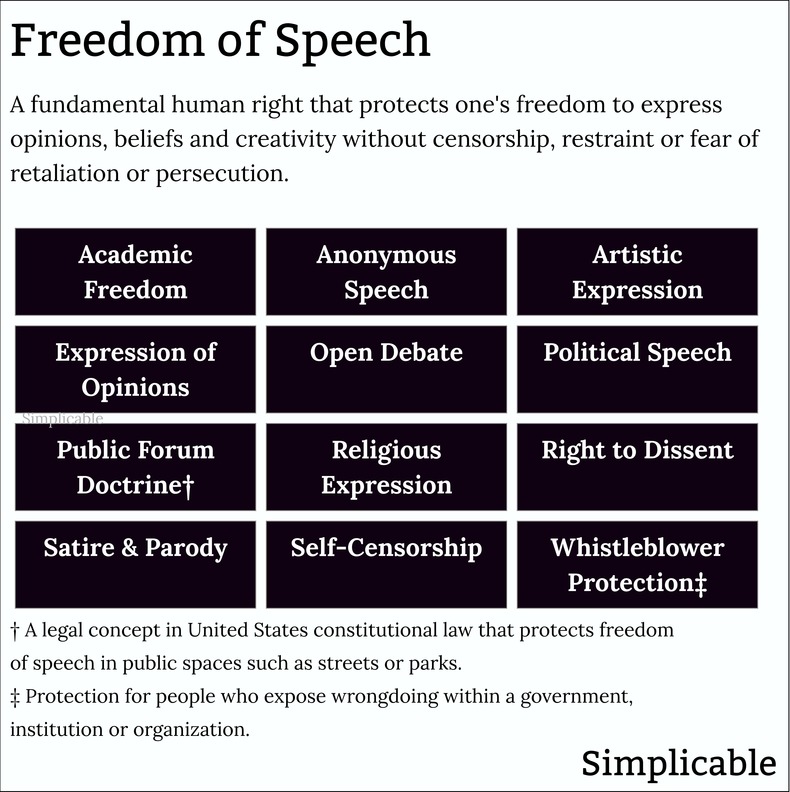
Democratic rights are fundamental freedoms and entitlements that are required to sustain a democratic society. These include basic human rights, civil liberties, legal rights and political rights as follows.Freedom of SpeechThe right to express ideas, theories, options, dissent and creativity without fear of retaliation or persecution. Freedom of speech is the cornerstone of democracy whereby a true democracy can't exist without it. This extends to things such as academic works, media, conversation, debate, protests, publications, performances, comedy and visual works such as art.
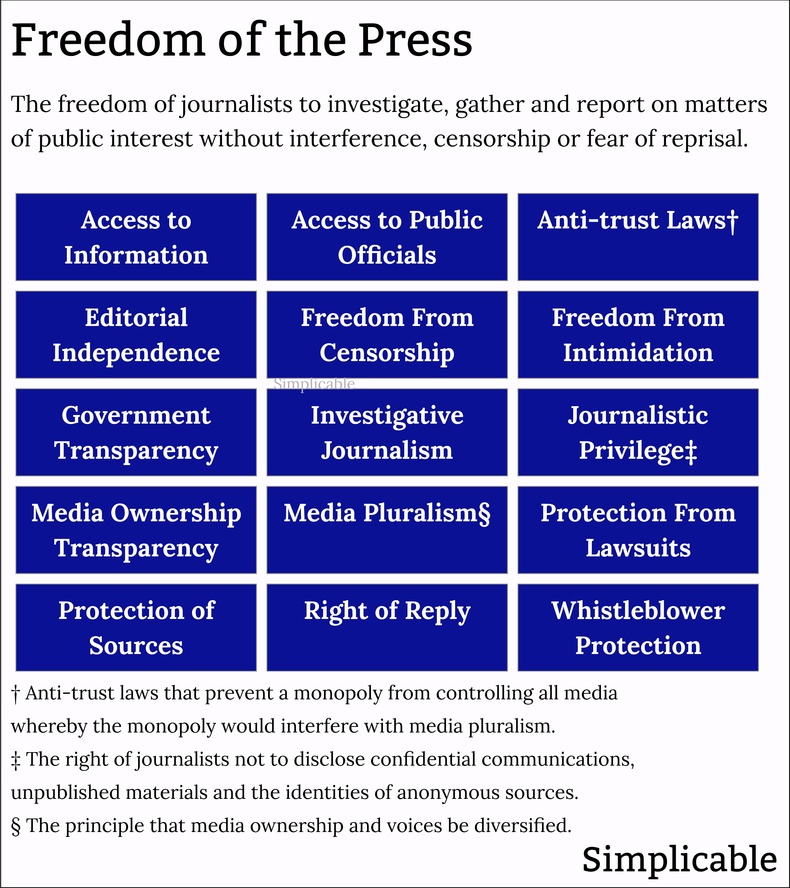
Freedom of The PressSpecial protections, beyond freedom of speech, regarding the use of media to publish information of public interest in areas such as news, politics and social issues. Freedom of the press includes the principle of media pluralism whereby the media should support diverse perspectives and voices as opposed to having concentrated ownership or control by a government, elite or monopoly. For example, a government that provides equal access to government officials with no special privileges for a media outlet that aligns to its agenda.
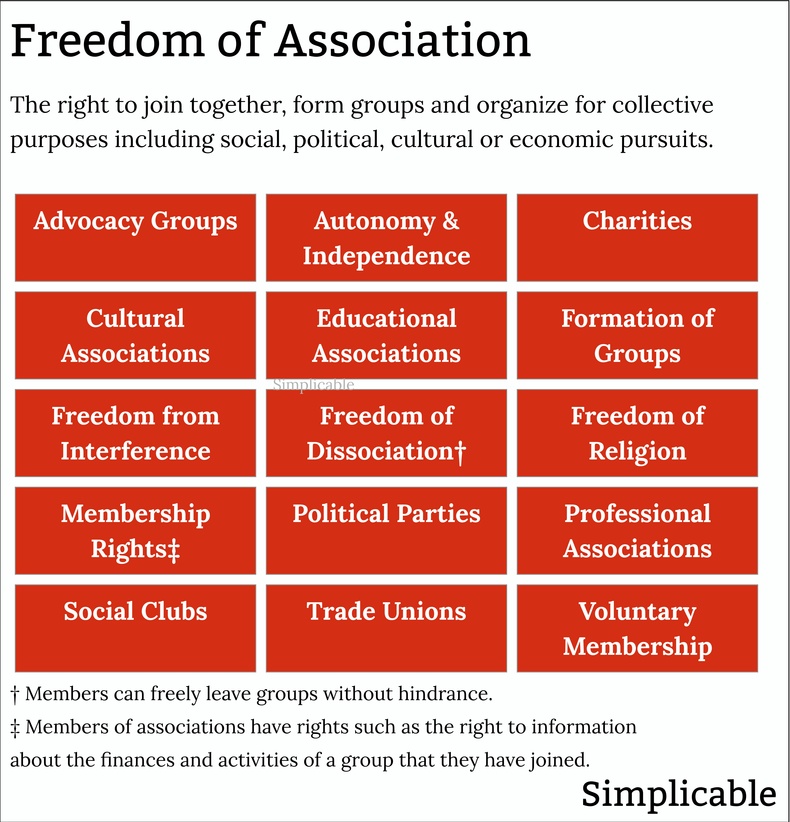
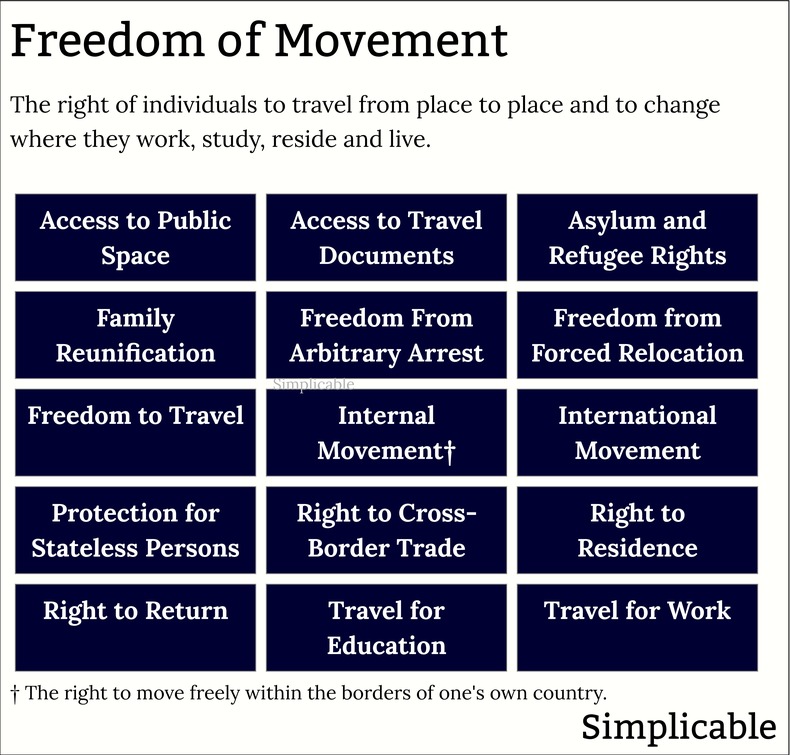
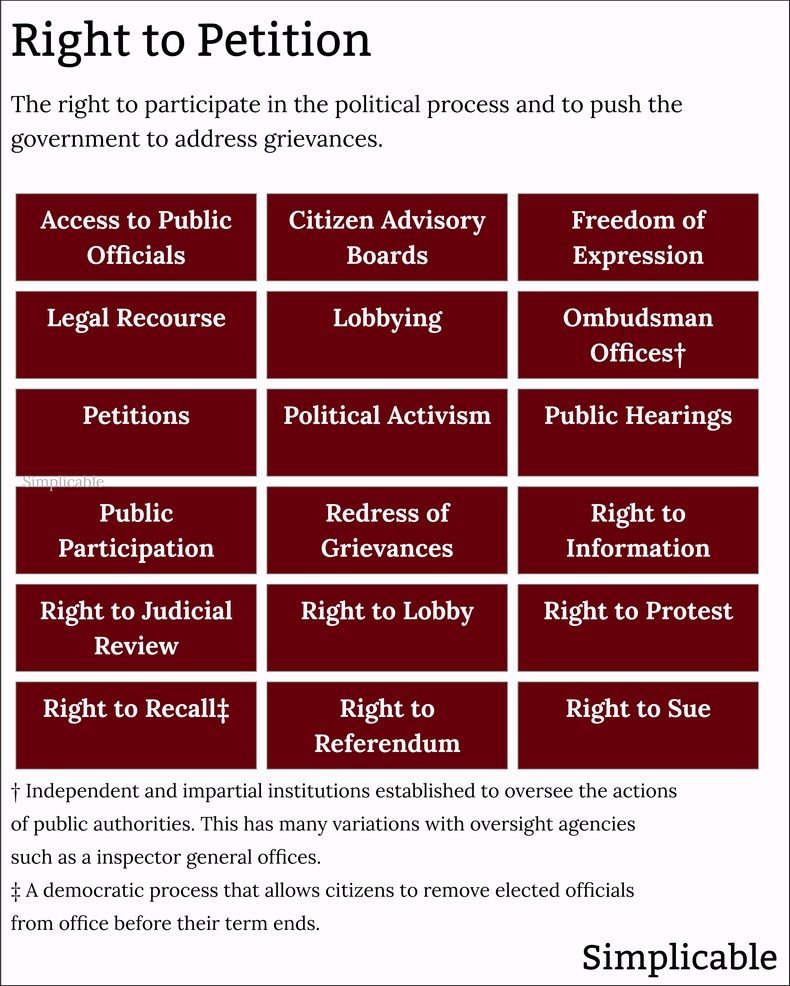
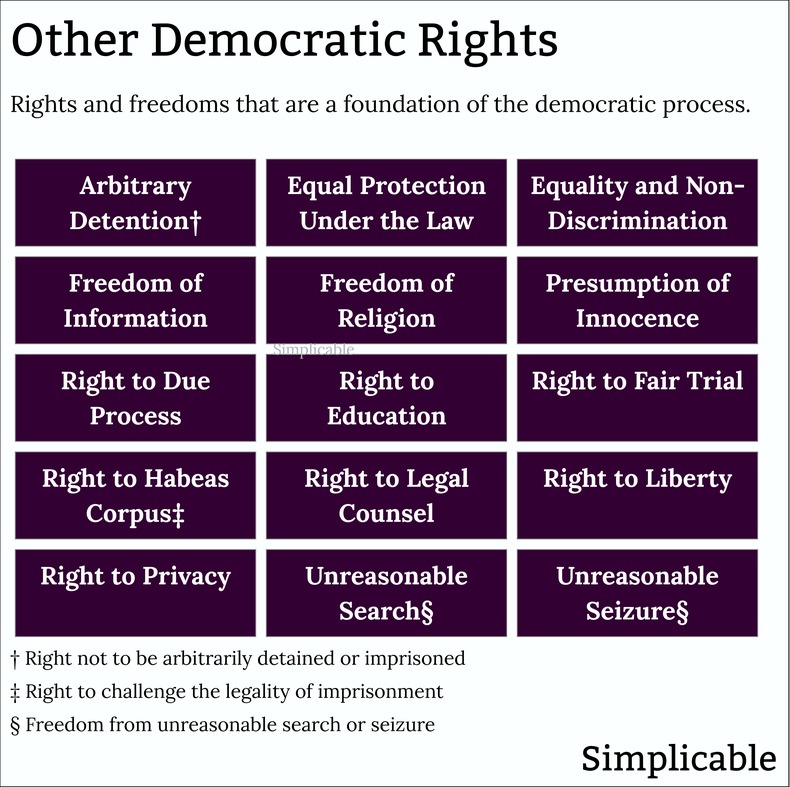
Freedom of AssemblyThe right to gather with other people without interference, provocation or reprisal from the government. Freedom of assembly is a key right that guarantees the right to protest, express your culture, practice your religion or organize as workers. This is closely tied to other freedoms such as freedom of association, freedom of movement and freedom of speech.Freedom of AssociationThe right to join together into organized groups to pursue common interests without undue interference or restrictions. This can apply to a variety of areas such as economic, social, political and cultural endeavors. Freedom of association provides protection for institutions such as religions, trade unions and political parties. This only applies where members have appropriate rights such as the right to leave the group without hindrance. Freedom of MovementThe right to move from place to place. At its most basic, freedom of movement includes the right to access public space and to move where you like within the borders of your own country. Freedom of movement also includes the right to choose where you will live, work and go to school. Another key type of freedom of movement is the right to international travel and interaction such as trade. Right to VoteThe right to cast a vote in elections that has equal weight. This can include elections for legislative bodies such as congress and executive officials such as presidents. The right to vote also applies to referendums that give voters a voice regarding specific issues or proposals. The right to vote includes principles of non-discrimination and ease of access to elections that are fair and open.Right to Run for Public OfficeThe right to seek election to an elected position in government. This typically includes eligibility requirements and a nomination process designed to show that you have some support amongst voters. However, this right should not be influenced by financial resources or political connections. For example, a candidate with ample support from voters is entitled to equal access to resources, debates and fair presentation on the ballot.Right to PetitionThe right to participate in government decisions and policy and to hold the government accountable. For example, the First Amendment to the United States Constitution, grants the right to "... petition the Government for a redress of grievances." The right to petition calls for government transparency, citizen oversight and public participation in policy making. Other Democratic RightsFoundational rights that provide a foundation for the democratic process. For example, a right to education can be viewed as a democratic right because knowledge empowers people to participate in political life. Likewise, basic legal rights such as the Right Not to be Arbitrarily Detained or Imprisoned are democratic rights because they prevent a government from using its power for political reasons.LimitationsRights are seldom absolute and are often limited in some way. This is because rights and freedoms often conflict such that some balance needs to be struct between them. For example, your right to freedom of speech can conflict with another person's right to safety and security. As such, issuing threats against others isn't typically protected by freedom of speech. ProtectionDemocratic rights are typically enshrined in the constitution of a democratic nation. Over time, this can be extended with amendments to a constitution such as the Bill of Rights of the United States. Democratic rights are further protected by laws, legal challenges, an independent judiciary, judicial review, checks and balances, oversight bodies, democratic institutions, civic institutions, public awareness and participation, activism and international treaties and standards such as human rights protections.Challenges & IssuesPower structures such as a political, corporate or wealthy elite can be hostile to democratic rights as this limits their power. As such, there is an ongoing process whereby the elite try to find ways to limit rights or bypass democratic processes. This can take many forms such as passing laws or instituting policies that have a chilling effect on the democratic process. The following are common challenges and issues that may threaten or limit democratic rights.Chilling EffectsIn some cases, governments or other power structures try to create fear around freedom of speech in order to reduce it. For example, a government may implement vaguely worded defamation laws in an attempt to create ambiguity around what you can and can't say.
Rights
This is the complete list of articles we have written about rights.
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|