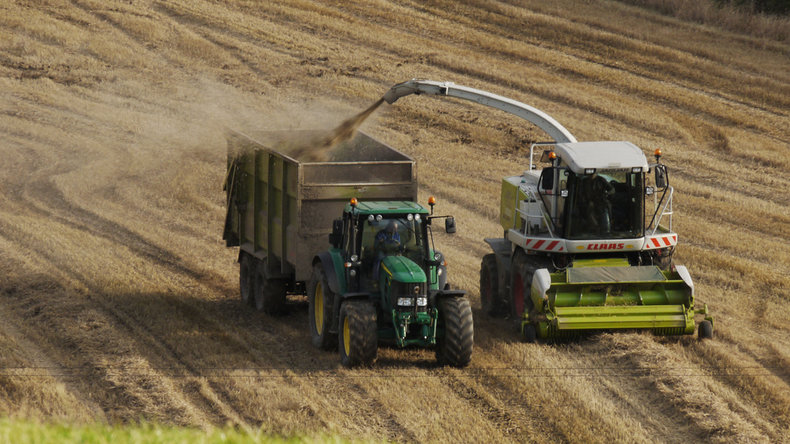
Human Capital
Human capital are the talents and health of people that allows them to produce future value. Generally speaking, people don't like to be referred to as capital. However, this is an important concept of economics that encourages investment in quality of life such as education and healthcare.Cultural Capital | Health |
Knowledge | Talent |
Relational Capital
Relational capital is the value of relationships and social structures. For example, a firm with a million loyal customers has more productive potential than a firm with zero loyal customers. Likewise, social structures and systems such as society, culture and community all increase the economic prospects of people.Community | Culture |
Investor Relationships | Loyal Customers |
Organizations | Partnerships |
Society | Talented Employees |
Natural Capital
Natural capital is any natural resource that has value. This is often destroyed due to a situation known as tragedy of the commons whereby firms and individuals don't pay for their damage to these resources.Air | Ecosystems |
Forests | Geological Features (e.g. rocks) |
Land | Minerals |
Organisms | Water |
Tangible Capital
Physical things build by humans that have productive potential.Buildings | Computers |
Equipment | Infrastructure |
Machines | Vehicles |
Intangible Capital
Non-physical things that have productive potential. This includes relational capital listed separately above.Brands | Data |
Knowledge | Patents |
Software | Trademarks |
Current Assets
The assets of a business that can be quickly converted to cash or that are intended to be sold or used within a business cycle.Accounts Receivable | Cash |
Inventory | Marketable Securities |
Prepaid Expenses | Supplies |
Financial Capital
Financial capital is cash, cash equivalents and assets with cash value. For a business, financial capital is often classified according to its source. Equity capital is cash that was raised by the investors who own the business. Debt capital are loans from creditors that are used as capital by the business.Current Assets | Debt Capital |
Equity Capital | Working Capital |
| Overview: Capital Examples | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An asset that can be reasonably expected to produce future value. | |
Related Concepts | ||