The spread of languages such as English on an international basis. | International sporting events that draw participation from most nations. |
World cuisine such as an Italian restaurant in Tokyo. | International cooperation between nations. |
Studying or working in a foreign country. | International flights and travel. |
Corporations that operate in multiple countries. | Exchange of knowledge across borders. |
International trade and trade agreements. | International diplomacy between countries. |
Playing online video games with players across the globe. | Interacting with people on a global basis in social media. |
Interconnected financial markets and trading across borders. | Religions that span multiple countries. |
The tendency for cultures to influence each other. | International nonprofit and political organizations. |
Universities that accept students from practically every country in the world. | Global fast food chains that operate in a large number of countries. |
Global brands and retail chains. | The diffusion of new technologies over borders. |
News organizations that instantly report events on a global basis. | The internet and global computer networks. |
The international postal system. | The ability to telephone anywhere in the world. |
Global supply chains that exchange goods between nations. | Foreign exchange and the global flow of money. |
The ability to invest in foreign companies or government bonds. | Global media organizations that distribute media in many countries. |
A city that accepts millions of international tourists each year. | Transportation systems that are interconnected across borders. |
War and international conflict. | Products that are sold in multiple countries. |
Movies that run in foreign countries. | Streaming media of foreign series, films and documentaries. |
The ability to use IT services physically located in a foreign country. | Outsourcing business processes to a firm in another country. |
Opening manufacturing facilities in a foreign country. | Subcultures such as cosplay that exist globally. |
Volunteering in a foreign country. | Humanitarian aid between developed and developing countries. |
Trade
The exchange of goods and services between nations. Trade is a feature of ancient societies that has expanded due to improvements in transportation, political stability and cooperation.Immigration
The ability to live, work or go to school in a place other than the place where you happened to be born. Immigration is a pervasive feature of history that is nothing new.Travel
The ability to travel and experience other places and cultures.Communication
International systems of communication began with mail services that were impressively global by the late 19th century. Telephone services were more or less global by the early 20th century. This made the world feel like a smaller place as you could instantly talk to anyone anywhere in realtime.Transportation
International systems of transportation such as shipping and air travel.Knowledge
Knowledge has always spread from country to country with word of mouth and written texts. This occurs almost instantly now due to the internet.Media & Entertainment
Media and entertainment such as movies and magazines are commonly distributed in multiple countries.Culture
Cultures have always influenced each other due to the spread of knowledge and people. This process is accelerated in the modern age. Culture can exist at many levels such as a nation, region, city, neighborhood, subculture or superculture. It is also possible that a global culture will emerge. Culture by its nature does not change quickly and can vary greatly even within one nation. As such, global culture would likely complement national cultures as opposed to replacing them.Law
Legal agreements between nations such as trade agreements or environmental regulations. Modern globalization is associated with multilateral agreements whereby many countries agree to a single agreement as opposed to a complex web of bilateral agreements between nation and nation.Environment
The planet has common resources. In theory, these can be completely used up or destroyed by a single nation. As such, international cooperation and law is seen as a hope for avoiding declines in quality of life due to environmental mismanagement. Unfortunately, globalization has a bad track record of allowing firms to shift production to nations with low environmental standards in order to avoid local regulations.Human Rights
Without trade, the international community has less leverage over issues such as human rights within the borders of a nation. Trade sanctions are commonly used to respond to human rights issues. Immigration of refugees is another capability of globalization that allows nations to aid those who face inhumane treatment.Political Stability
Forums for resolving international disputes and establishing international cooperation.Capital
Integrated banking systems allow capital to flow over borders. For example, a retiree in Spain who can instantly buy and sell stocks in an Australian company.Science
International programs of science such as joint space programs.Types of Globalization
Globalization includes systems, culture, knowledge, trade and international politics. The following are common types of globalization.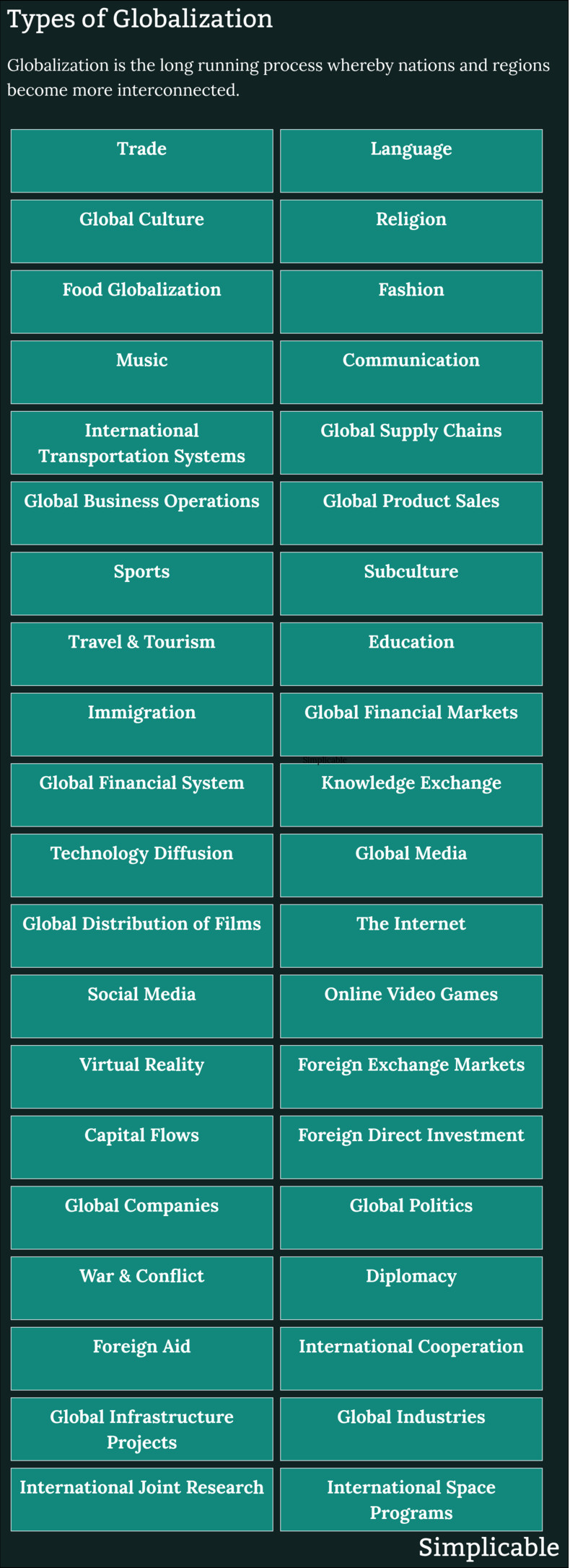
Summary
Globalization is a long running process that has accelerated in modern times due to technology that allows transportation, communication and trade to be scaled across the globe.
| Overview: Globalization Examples | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The process whereby systems expand from being regional or national to encompass the entire planet. | |
Also Known As | Globalisation | |
Related Concepts | ||