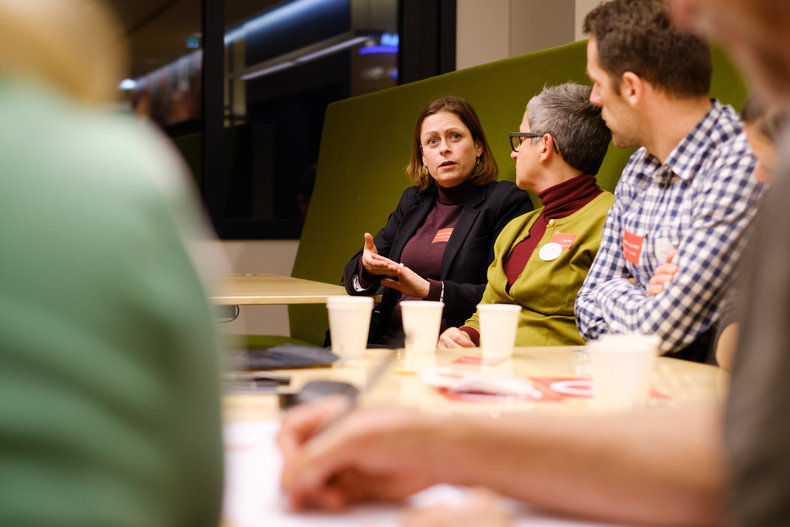
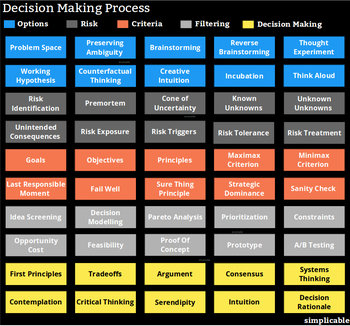
A/B testing | Argument and debate |
Beginning with a problem statement | Benefit of doubt - believing in others without being too suspicious |
Brainstorming | Breaking large decisions into smaller decisions |
Challenging assumptions | Charrette - stay in a room as a group until the decision is made |
Conceptualize - build concepts to better understand problems and solutions | Consensus decision making to try to gain general acceptance of a decision |
Consider all options | Consider ethical implications |
Consider opportunity costs | Contemplation |
Cost-benefit analysis | Counterfactual thinking - consider how the past could have been different |
Critical thinking | Decision analysis |
Decision authority - assign authority for decision to one person | Decision automation - algorithms, decision models and artificial intelligence |
Decision rationale that documents alternatives considered | Decision research |
Decision trees that work out what happens for each choice as a tree | Defensive pessimism - using optimism to generate ideas and pessimism to validate them |
Design thinking - design things to solve the problem | Develop a weighted scoring for alternatives |
Develop requirements for the solution | Divergent thinking - try to reinvent |
Do nothing strategy - a decision to do nothing, often the best strategic choice | Experiments |
Feasibility studies | Financial analysis |
First principles - use rules that you hold to be true | Focus groups |
Human factors - think in realistic ways that consider human realities | Incubation - taking time to think |
Introspection - examine yourself | Intuition - go with a gut feeling |
Keep it simple - choose the most direct and obvious solution | Last responsible moment - deferring a decision until it really needs to be made |
List pros and cons | List short and long term consequences |
List what is important to you | List your goals |
List your values | Listing what you don't know |
Listing what you know | Maximax criterion - maximize gain without concern for risk |
Minimax criterion - minimize a worst case scenario | Objectivity - try to overcome your involvement to be more realistic and grounded |
PEST analysis | Pareto analysis - the 80/20 rule |
Perform a premortem for an option by listing what will go wrong | Pragmatism - accept real world conditions and do what is most likely to achieve goals |
Preserving ambiguity - avoiding assumptions too early in the process | Principles - develop rules to be applied to the decision |
Prioritize your goals | Prototypes |
Randomization - reducing overthinking with randomization such as a coin toss | Rank alternatives |
Reframing your problem statement | Reverse brainstorming |
Risk assessments | Root cause analysis to separate cause from symptoms |
SWOT analysis | Sanity check - ask if solution makes any sense whatsoever |
Satisficing - pick the first reasonable option you find | Seek advice and consultation |
Set decision criteria | Small steps - taking small steps now and deferring big decisions |
Strategic dominance - a choice that is optimal no matter what happens | Structuring your choices |
Surveys and polls | Systems thinking to consider real world complexities such as unintended consequences |
Think aloud - speaking without filters | Think from different perspectives e.g. what do competitors not want you to do? |
Think in different modes e.g. emotional, logical, traditional | Thought experiment - simplify the problem with analogies |
Trade-off analysis | Try to identify biases in decisions |
Work to eliminate alternatives until you are down to a few choices | Working hypothesis - temporarily adopt a hypothesis to test it |