Individualism
The belief that you are an independent person who is defined by your own qualities as opposed to your memberships in groups. Individualists tend to identify with other individualists and aspects of society and culture that are individualistic.
Family
Your immediate and extended family.
Friends
Identifying with your friends and social circles.
Language
Language is the foundation of thinking and is an extremely pervasive element of identity. This may not be obvious when you are surrounded by your native language but becomes apparent when you're immersed in a foreign language. For example, if you go on vacation in Tokyo but don't speak Japanese you may suddenly strongly identify with anyone who can speak English.
Philosophy
Identifying with a way of thinking about the universe such as pragmatism.
Personality
Elements of your personality that you feel define you or give you things in common with others. For example, an optimist who identifies with other optimists.
Religion
On a global basis, around 86% of the world's population belong to a religion.
Race
The perception that there are groups that have related genetic ancestry that are labeled with broad terms such as "Asian."
Ethnicity
A shared background such as nationality or culture.
Nationality
Belonging to a nation.
Birthplace
A hometown or nation where you were born.
Culture
Culture is identity based on shared experiences and traditions. This exists at many levels such as national culture, subculture and super culture.
Community
Identity based on a sense of place such as your hometown or neighborhood.
Disability
A sense of solidarity or connection to the disability community.
Class
Socioeconomic class such as working class or middle class.
Social Status
Elements of social status such as appearance, wealth, style, personal presence and youthfulness.
Consumer Culture
It is common for products and services to attempt to sell elements of identity such as social status or peak experiences. For example, an individual who views a collection of shoes as an element of their identity.
Politics
Political views and affinity for a political party. Some nations are sharply divided along political lines such that this becomes a pervasive part of identity.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle such as an urban or rural way of living.
Gender
Masculine and feminine characteristics.
Sexual Orientation
The gender or genders to which an individual is attracted.
Profession
Your profession such as Engineer or Artist.
Hobbies
Hobbies such as someone who strongly identifies as a surfer.
Memberships
Memberships such as a student who belongs to a university.
Accomplishments
Accomplishments such as graduating from university.
Media
Identifying with people you've never met and fictional characters. For example, identifying with a hero of film such that you view yourself as having similar qualities or aspirations.
Experiences
Experiencing something can cause you to identify with it. For example, playing hockey can cause an individual to identify with the sport.
Concept
Creative Expression
Identifying with creative expressions such as art or music that captures how you feel.
Digital Identity
The ability to assume an identity in digital environments that may differ from your own. For example, the ability to become a character in a game that somehow feels part of your actual identity.
Types of Identity
The following are common types of identity.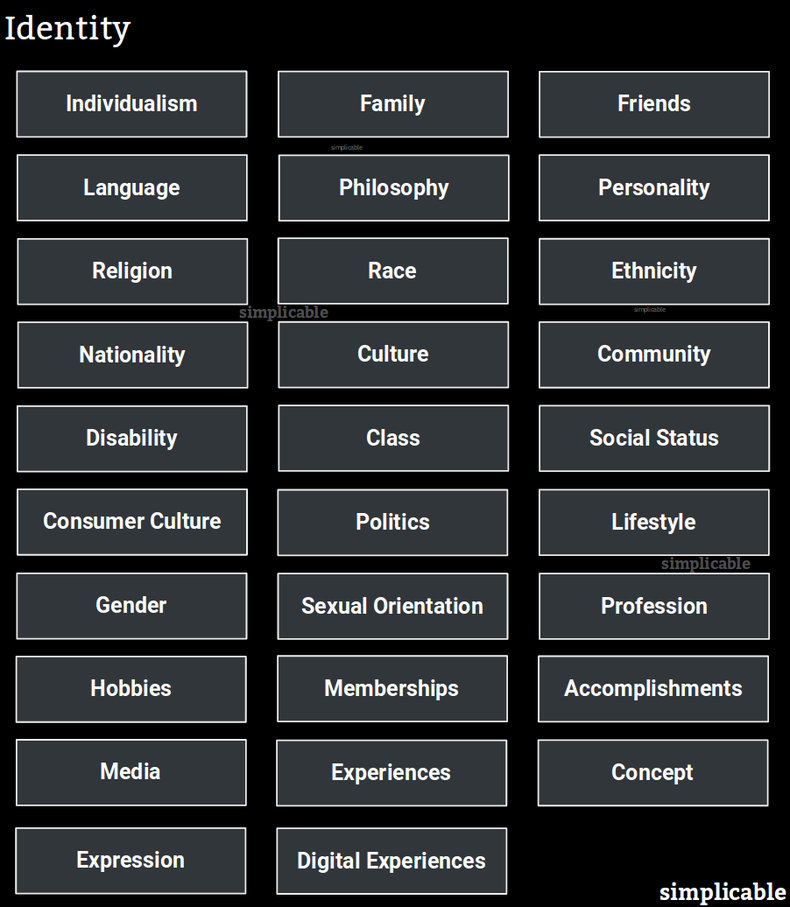
Summary
Identity includes your personal identity related to your characteristics and your social identity related to your group memberships.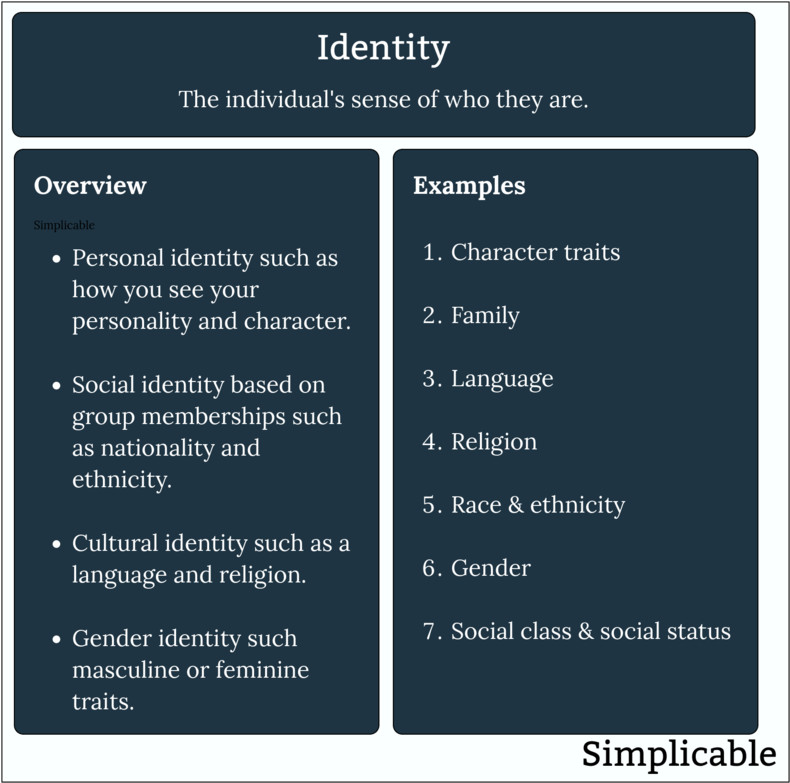
| Overview: Identity | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The characteristics that you believe define you as an individual. | |
Related Concepts | ||