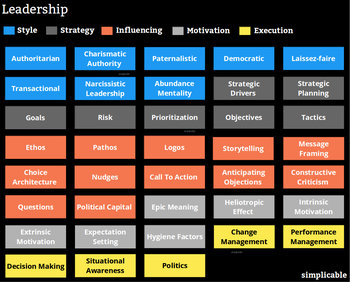
Abundance Mentality | The belief there is enough for everyone. Builds others up. |
Affiliative Leadership | Builds group cohesion, harmony and comradery. |
Authentic Leadership | Based on candor, transparency and keeping it real. Typically talented with no fear of challenge. |
Authoritarian Leadership | Controls based on authority. May use secrecy and other negative tactics to increase control. Fears competition, disorder and charismatic individuals. In some cases, authoritarian leaders don't have all that much authority but may reference other authorities such as rules to try to increase their power. |
Autocratic | Indicates a leader in a position of power and authority who uses this power without concern for what others think. |
Bureaucratic | A leader who believes in strict adherence to processes, rules, procedures, roles and responsibilities. In many cases, these leaders have simply adapted to life in a bureaucratic organization. |
Charismatic Leadership | Idiosyncratic leadership based on the personal presence and style of an individual. Often inconsistent but commands respect and may get things done. |
Coaching | A leader who views themselves as a coach or mentor who is focused on giving feedback and advice to improve performance. |
Command And Control | Issuing orders that are to be followed with precision without question. Important to some types of work that require precise coordination of effort. |
Contingency Leadership | Changes their style to match the situation. For example, giving low performers supervision while allowing high performers do as they please. |
Creative Leadership | Implements processes for non-obvious value creation such as experiments. Encourages a culture of brave ideas, positivity and bias for action. |
Democratic | A leader who doesn't set any direction but views themself as the facilitator of democratic processes. Prone to mediocrity and inaction based on the characteristics of group decisions such as the abilene paradox. |
Directive Leadership | Provides clear instructions and deadlines. Clears issues and expects results. |
Ethical Leadership | Leads according to principles that they view as fair. Important to roles that have some ethical aspect such as fiduciary duty. |
Humble Leadership | Uses the power of humility whereby a leader recognizes how much they depend on others. Viewed as grounded and helpful such that they can establish credibility. |
Laissez-faire | Laissez-faire leaders stay out of the way and allow teams to do what they do. They give people freedom but little support and direction. Works well where teams know what they are doing. |
Participative Leadership | Views leadership functions such as strategy and decision making as a participative process. Generally won't make decisions and prefers extensive social processes such as frequent meetings. |
Paternalistic Leadership | Manages for the good of the team as opposed to for the good of stakeholders. Common in collectivist cultures. |
Path-goal | A broad term for leaders who provide clear directives and goals. |
People-oriented | Socializes a lot. Gives out work assignments in an informal way. Socializes decisions and issue clearing. |
Progressive Leadership | Embraces aggressive change without necessarily being able to articulate its value. Tends to follow trends. |
Servant Leadership | Adds value by supporting team. May lack much of a strategy or vision. Prone to mediocrity such as allowing low performers to drift. |
Situational Leadership | Adapts their style to the situation. Another term for contingency leadership (above). |
Strategic Leadership | Focused on strategy. Provides strategies and goals as opposed to direction and support. Some employees will thrive under these conditions while others may find it difficult. |
Supportive | Another term for servant leadership (above). |
Task-oriented | Focused on clearing the latest tasks. Reactive. |
Seagull Leadership | A laissez-faire leader who provides no direction or support. Swoops down to suddenly push people when there is an issue. This is also known as management by exception. |
Assertive Leadership | A gritty leader who isn't afraid to engage in political battles with anyone. Has a fearsome personal presence and is typically competent in their roll. Defends their team if they are loyal. Doesn't fit in where the culture values group harmony. |
Transactional Leadership | Follows a generic process of setting goals, monitoring, clearing issues and evaluating performance. Can manage anyone competently but isn't into strategy and pushing for their team. |
Transformational Leadership | A leader who is looking to shake things up -- to disrupt complacency and push for high performance. |
Transitional Leadership | A leader who is concerned with a project or initiative as opposed to a sustained team and organizational function. Common in matrix organizations. |
Visionary | Concerned with the future and uninterested in details of operations that aren't exciting enough. Often a founder who owns many shares. |