After-school programs | Basketball courts |
Beaches | Bicycle lanes |
Bicycle parking | Canals |
Cemeteries | Childcare facilities |
Clock towers | Colleges |
Community centers | Community colleges |
Community gardens | Community kitchens |
Concert halls | Counseling centers |
Cultural centers | Disaster shelters |
Dog parks | Event spaces |
Health clinics | Historical sites |
Homeless shelters | Hospices |
Hospitals | Libraries |
Mental health clinics | Museums |
Nature reserves | Nursing homes |
Orphanages | Parks |
Pedestrian infrastructure | Performance theaters |
Picnic areas | Piers and boardwalks |
Play streets | Playgrounds |
Preschools | Public fountains |
Public housing | Public markets & farmers markets |
Public squares | Public transportation |
Recreation centers | Riverside walkways & parks |
Schools | Senior centers |
Skate parks | Sports facilities |
Sports fields | State and national parks |
Subways | Swimming pools |
Tennis courts | Train lines |
Train stations | Universities |
Waterfront promenades | Youth centers |
Social Infrastructure vs Hard Infrastructure
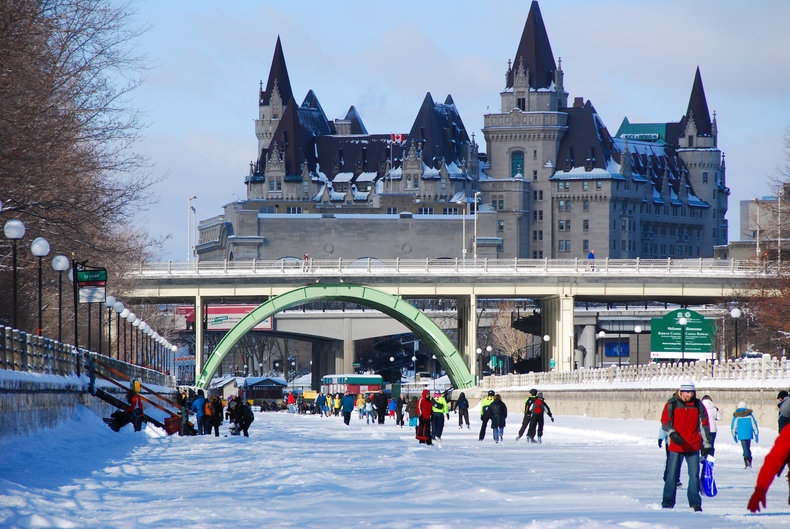
Social infrastructure is the foundation for the quality of life of a place. This is mostly high level services such as a hospital, university or museum. Hard infrastructure are the low level physical foundations of a nation or city such as roads, bridges and electrical grids. Social infrastructure relates specifically to quality of life while hard infrastructure supports both economic production and quality of life. As the term suggests, hard infrastructure is mostly physical while social infrastructure are high level systems and services.Overview
Social infrastructure are the shared spaces, facilities, systems and services that support the quality of life of a society, state, region or city. This includes areas such as healthcare, education, housing, civic institutions, safety, security, public space, recreation and culture.
Summary
Social infrastructure includes all the shared services, spaces and facilities that underlie the stability and well-being of a society. These aren't directly economic but are characteristic of highly developed nations that can found, grow and attract world-class companies. The following are common examples of social infrastructure.
| Definition: Social Infrastructure | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Foundational services and structures that support the quality of life of a nation, region or city. | |
Related Concepts | ||