Cause & Effect Analysis
Problem analysis is focused on identifying cause and effect. It can be very difficult to determine what is cause and what is effect. For example, a problem that initially looks like a human error may be a latent human error that is the result of a poorly designed user interface, system or process.Root Cause Analysis
There are often a large number of failures that can all be traced back to a handful of root causes. For example, the failure of a network device in a data center might cause thousands of processes, services and machines to fail. Generally speaking, the only way to permanently fix a problem is to address its root causes.5 Whys
Asking the question why? five times in succession to find deeper causes of a problem. For example, an almond is found in a chocolate product that is supposed to be free of nuts and the following questions are asked to reveal the cause.why?
A machine wasn't cleaned after a production run of almond chocolate.
why?
The machine's auto clean function malfunctioned.
why?
A part in the machine's cleaning unit failed.
why?
Maintenance wasn't performed on the part for more than 5 years.
why?
Maintenance processes and policies are insufficient.
It is a common theme of 5 whys that problems that initially look like machine or human error are really issues of process and internal controls. It should be noted that when two different teams perform a 5 whys analysis for the same problem they almost always come up with different paths. As such, 5 whys should be viewed as a brainstorming activity as opposed to a means to find the one root cause of a problem.A machine wasn't cleaned after a production run of almond chocolate.
why?
The machine's auto clean function malfunctioned.
why?
A part in the machine's cleaning unit failed.
why?
Maintenance wasn't performed on the part for more than 5 years.
why?
Maintenance processes and policies are insufficient.
Fishbone Diagram
A fishbone diagram is a way to visualize a problem with multiple root causes and to categorize root causes. This is often a final output of a problem analysis that can be used to make recommendations to fix various aspects of a problem in areas such as technology, process, procedure, controls, environments and culture. For example, the following fishbone diagram illustrates various root causes for a technology outage of several hours caused by a bug and failed incident management processes.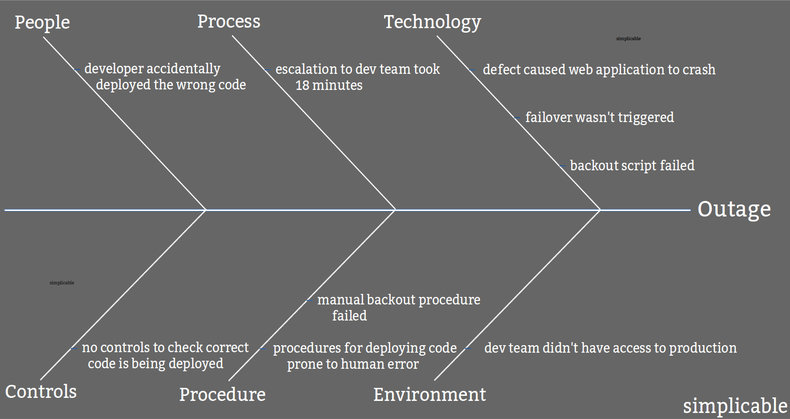
Change Analysis
Examining what changed leading up to a problem. For example, what software patches were applied to a system that is failing.| Overview: Problem Analysis | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An investigation of the causes of an incident, issue or failure. | |
Related Concepts | ||