Adverse geopolitical events | Anti-competitive practices of a large competitor |
Brand identity crisis | Budget overruns |
Business model disrupted by change | Cash flow issues |
Changing customer needs | Competitive pressures |
Cost of capital increases | Customer complaints |
Customer attrition | Cybersecurity vulnerabilities |
Data breaches | Declining sales |
Difficulty in measuring marketing | Difficulty recruiting talent |
Disasters | Disengaged employees |
Disorganized processes | Economic downturns |
Employee absenteeism | Employee burnout & stress |
Employee conflicts | Employee turnover |
Environmental concerns | Ethical issues |
Exchange rate volatility | Failing products |
Failing projects | High customer acquisition costs |
Inaccurate forecasting | Inadequate asset tracking |
Inadequate training and development | Inconsistent messaging |
Increasing costs | Ineffective leadership |
Inefficient processes | Intellectual property infringement |
Interest rate volatility | International competitors |
Lack of automation | Low customer loyalty |
Legal disputes | Loss of key customers |
Loss of key employees | Loss of key partners |
Low brand recognition | Low customer satisfaction |
Low employee morale | Low internal cooperation |
Low partner performance | Low productivity |
Managing remote workers | Market saturation |
Negative customer perceptions | Negative publicity |
New competition | New laws and regulations |
Operational inefficiencies | Outdated technology |
Excess inventory | Poor inventory turnover |
Political instability | Poor customer relationships |
Poor internal controls | Poor partner relationships |
Poor reviews | Pricing pressures |
Product positioning issues | Production incidents |
Quality issues | Reputational issues |
Resistance to change | Schedule delays |
Shifting customer perceptions | Shrinkage and inventory loss |
Social instability and disruptions | Social responsibility concerns |
Stockouts | Supply chain disruptions |
Inadequate supply | Team culture issues |
Technological disruption | Trade barriers |
Unfavorable media coverage | Usability of technologies and systems |
Workplace tensions and negative politics |
Financial
Financial issues such as an inability to refinance debt due to tight credit conditions.Business Model
A business model that has been disrupted by a new way of doing things. For example, an energy company based on products that pollute the environment when cleaner and cheaper alternatives emerge.Reputation
Reputational issues such as poor customer service that receives media attention.Values
A firm that doesn't align to the changing values of a society in which it operates. For example, a business model, product or operational process that harms the environment.Regulations
Costly or burdensome regulations. This can particularly impact small businesses as it can drain limited resources.Branding
Brand issues such as a small business that has difficulty establishing brand recognition in a market dominated by widely recognized brands.Positioning
Product positioning issues such as an organic coffee that looks much the same as the other products on the shelf except that it is more expensive than the competition.Demand
Changing customer needs, preferences and perceptions that reduce demand for your products and services. For example, a cultural shift towards healthier food may negatively impact brands that produce junk food.Supply
Increased supply by your competition or a substitute product. For example, a short term property rental service that increases the supply of rooms may negatively impact hotels in an area.Price Competition
Price competition that lowers your sales and/or reduces your profit margins. This is particularly a problem if you are facing competitors with lower unit costs such that they can keep prices low and remain profitable.Costs
Rising costs such as your cost of capital, labor, materials, parts, overhead and obligations to partners.Sales
Sales problems such as an inability to recruit sales people who have many connections amongst your target customers.Customer Relationships
Customers who are unhappy with your products or services such that they are likely to cancel services and/or generate negative word of mouth.Promotion
Promotional problems such as an inability to generate demand or interest in a new product launch.Product
A new product or service that is poorly received by customers or the media. For example, a hotel that undergoes an expensive renovation only to see reviews plummet as customers feel room interiors are visually unattractive and uncomfortable.Time to Market
A product launch that is slower than you need. For example, issues setting up a production line.Time to Volume
A product launch that takes longer than expected to reach your sales targets. For example, an innovative new streaming media service that finds that their target audience are uninterested in changing their media viewing habits.Know-how
A firm that lacks the knowledge to get something done well. For example, a high speed train manufacturer with product reliability issues due to a lack of reliability engineering know-how.Technology
Technology issues such as a costly service outage due to a failure of IT infrastructure.Information Security
Information security attacks or vulnerabilities.Change
An inability to change such as a project failure or business transformation that fails to achieve its objectives.Employee Performance
Employees who lack motivation, talent, diligence or professional standards. For example, a retail location with poor customer satisfaction due to poor management and employees who aren't friendly, helpful or reliable.Organizational Culture
The habits, norms and expectations that have evolved in your organization over its history. For example, a call center where employees openly complain that customers have negative traits such that negativity towards customers is commonplace.Productivity
Low output in an hour of work. For example, an office where people are spending as much time on personal social media as working.Efficiency
Low output for a unit of input. For example, a factory that produces 200 units an hour with $1 million in equipment versus a competitor that produces 2500 units an hour with $1 million in equipment.Measurement
A firm that isn't able to detect problems because their measurements and benchmarks fail to detect significant underperformance. For example, a firm that aggressively reduces unit cost without properly measuring quality or product ratings. This may result in quality failures and a loss of brand reputation and market share.Quality
A firm that can't achieve its target level of quality. For example, a firm wants to release a hot chocolate mix that is perceived as higher quality than a major competitor. They have tested dozens of formulations and packaging designs but all score poorly with customers.Customer Experience
Problems with your end-to-end customer experience. For example, a mobile device brand that customers perceive as visually unappealing, difficult to use and unreliable.Distribution
Problems reaching customers with your products and services. For example, a restaurant chain that runs out of critical ingredients across an entire region due to a supply chain disruption.Operations
Business process issues such as a single point of failure on a production line that is causing expensive downtime.Summary
The following are foundational types of business problem.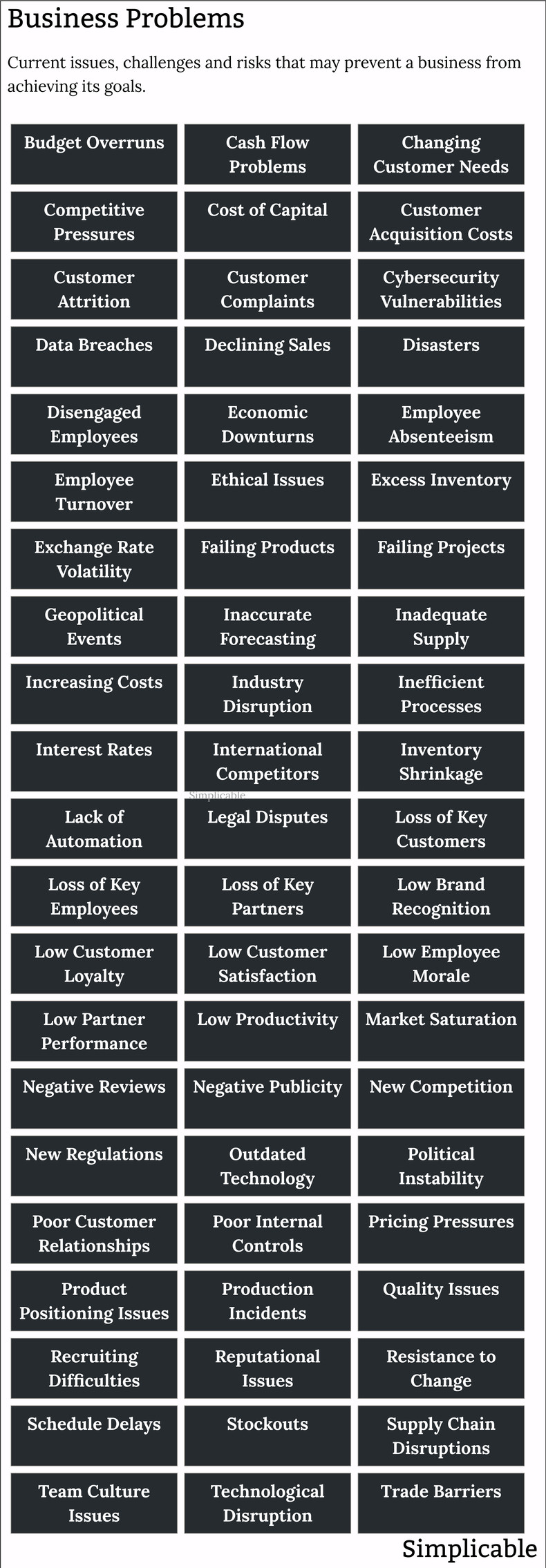
| Overview: Business Problems | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Current or long term challenges and issues faced by a business. | |
Related Concepts | ||