Operations Outage
A production line goes down for three shifts due to a failed machine. A root cause analysis determines that the machine had multiple design issues. Such problems weren't detected or mitigated by maintenance processes. When the machine needed to be replaced, several issues complicated the process making the outage longer.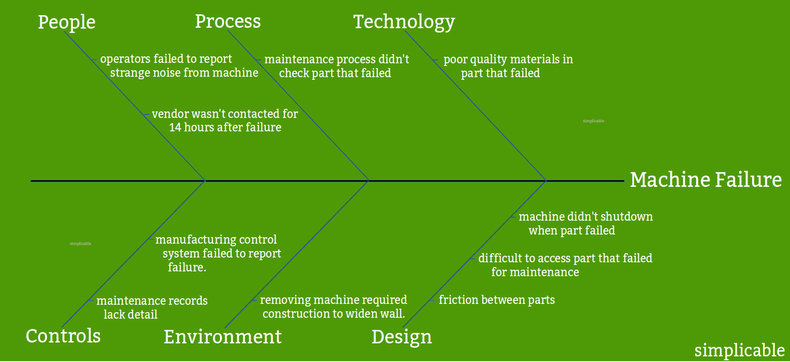
Service Outage
A software service experienced an outage after a bug that was missed in testing was launched to production. The procedures required to fix the problem did not go smoothly as backout procedures failed and developers had trouble accessing environments due to issues with security keys.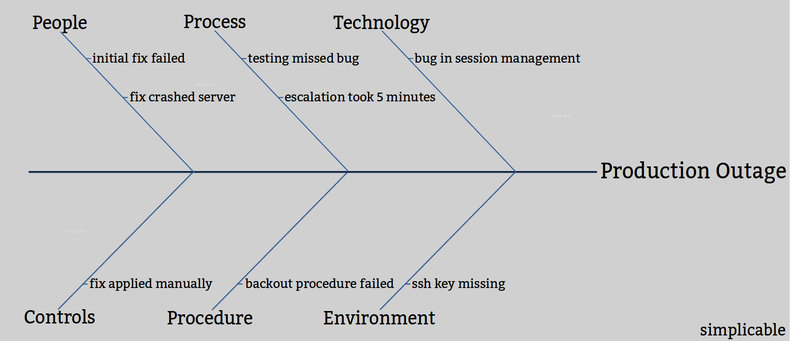
Quality Failure
A customer finds a problem with a product that had passed quality control. A quality assurance investigation reveals that a machine error caused the defect. Quality control tests and processes failed to detect the problem.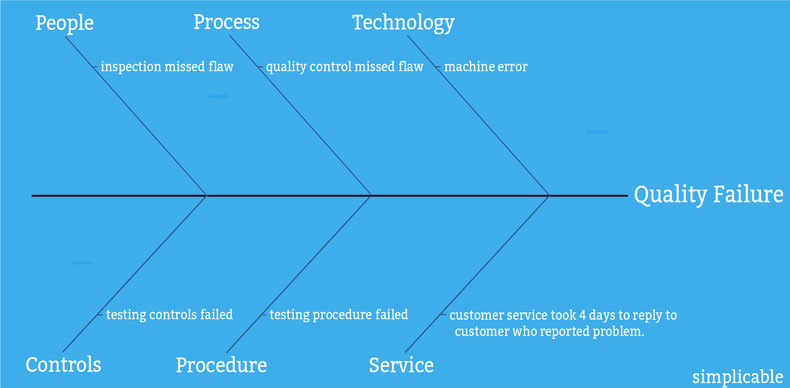
Security Incident
A worker loses a laptop filled with company data at a bar. The incident investigation discovers a lack of policy and procedure to prevent such problems. Root cause analysis also reveals technical shortcomings such as weak encryption, a poor password policy and lack of an audit trail for data.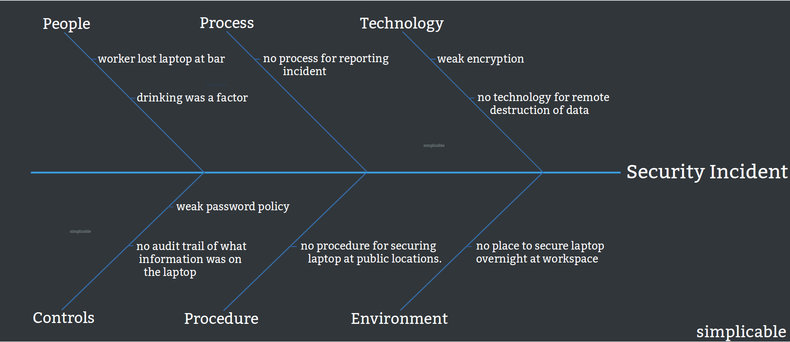
| Overview: Fishbone Diagram | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A visualization of the causes of a problem. | |
Also Known As | ||
Invented By | Kaoru Ishikawa | |
Related Concepts | ||