Emergence
Culture emerges as opposed to being centrally planned or designed. As such, it is difficult for those with power and authority to change culture. Culture is owned by those who live it.
Interaction & Influence
Cultures are in a constant state of interaction whereby they influence each other.
Identity & Belonging
Cultures serve to unify the members of a group by providing a sense of common identity, purpose and belonging.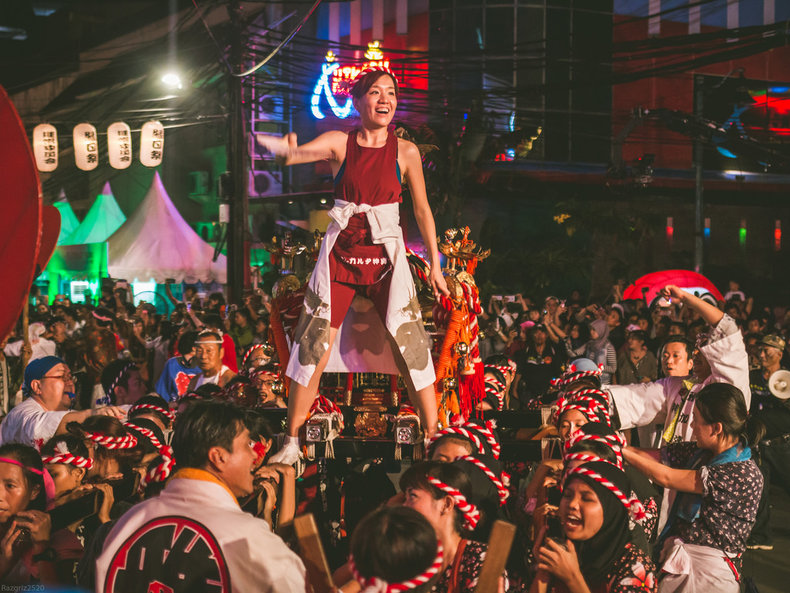
Norms & Expectations
Belonging to a culture is based on conformance to a set of norms and expectations. This is equally true of a counterculture that rejects mainstream norms but replaces these with an alternative set of norms.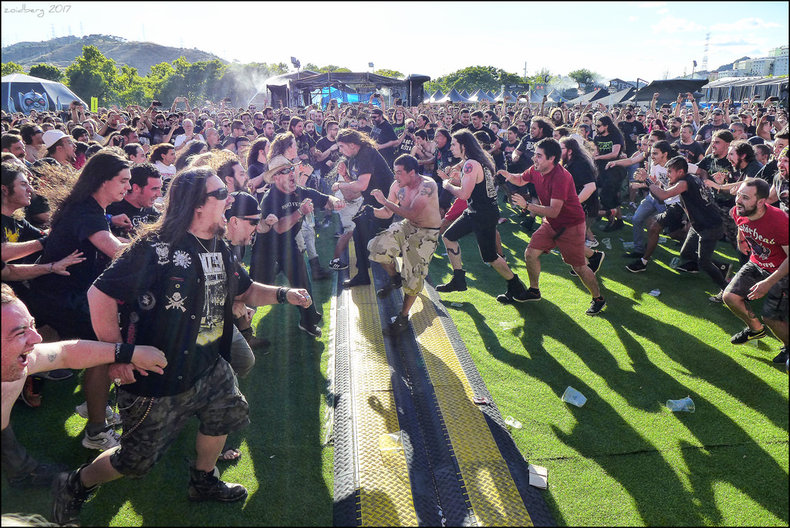
Freedoms
In addition to norms that restrict behavior, a culture may defend freedoms. Where governments may protect the interests of boring types who want to regulate every aspect of behavior, culture may defend the interests of those who are a little more lively.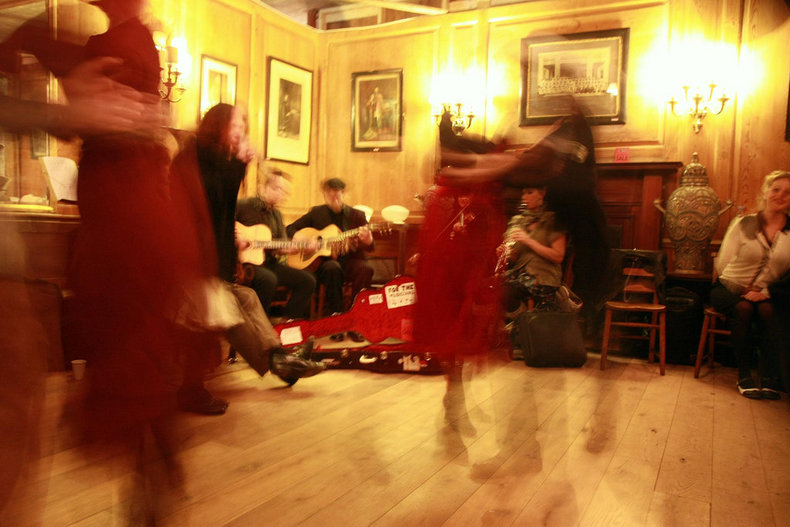
Rational
Culture is rational but not necessarily logical. It can be explained with emotion as opposed to numerical analysis.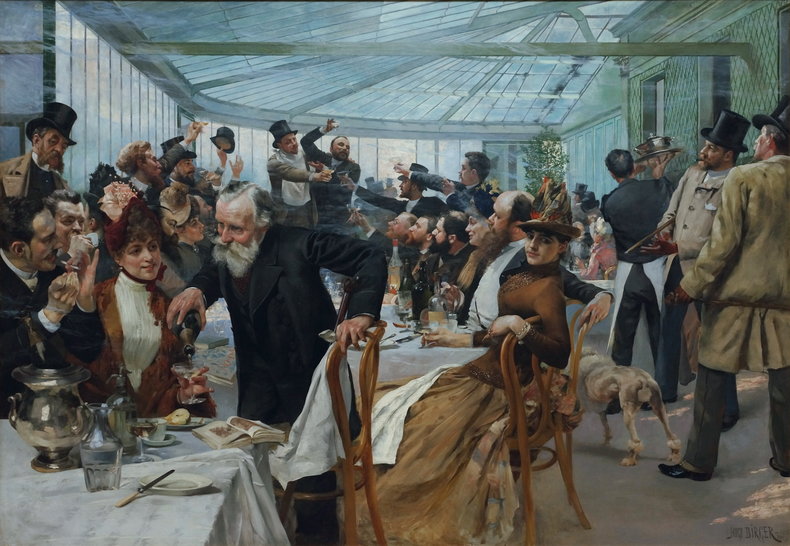
Sacrifice
Culture can include elements of sacrifice. Preserving a tradition may involve doing things the old way without modern conveniences. Culture can also include hardships that create a sense of accomplishment and allow members of a group to bond. For example, the Japanese tradition of carrying mikoshi through the streets at festivals that can weigh several thousand kilograms. This requires pain, endurance, risk and precision teamwork.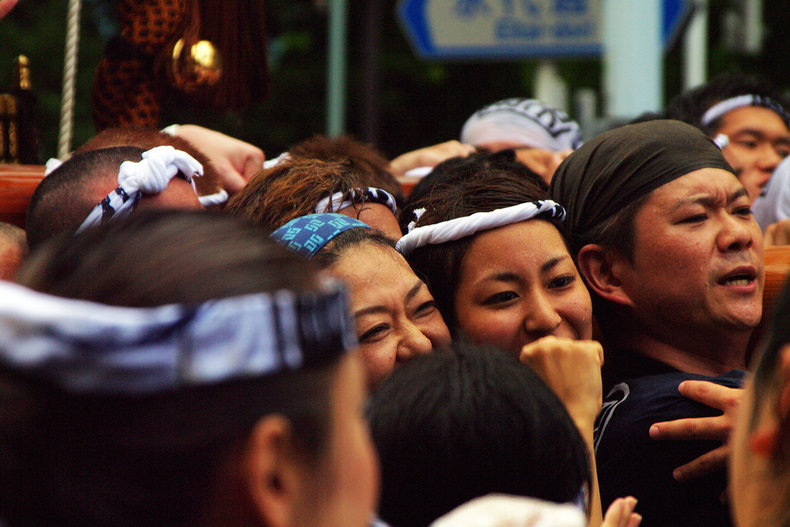
Competition
As with other domains, culture can be intensely competitive such as the competition between sports teams. This may be driven by a human desire for competition with the associated thrill of winning.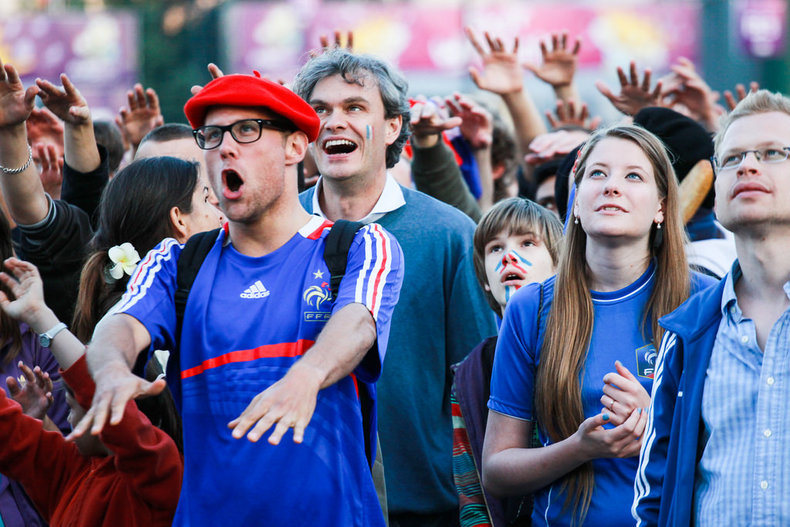
Creativity
Any profession or hobby that includes high levels of creativity and imagination is considered an element of culture. This includes art, music, architecture, performance art, film, cuisine and any other creative pursuit that embraces the principle of art for art's sake.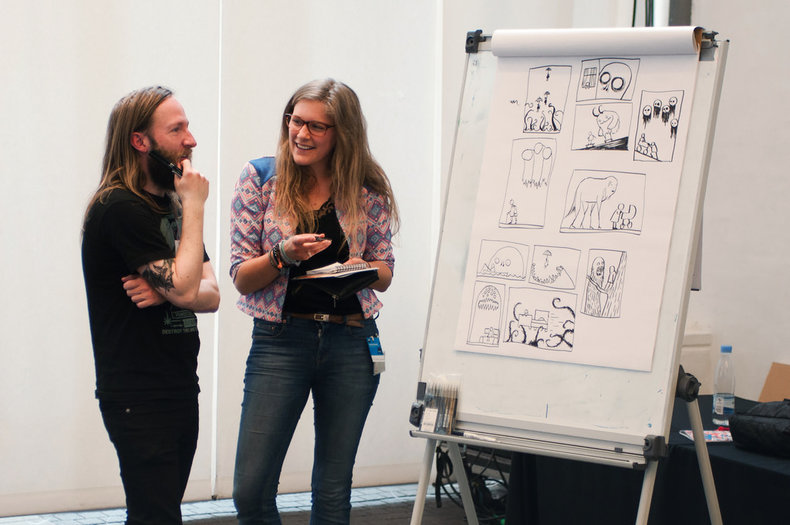
Refinement
Culture may seek perfection of an art, craft or practice with mastery education. This differs from economic pursuits that may seek to cut every corner in the name of productivity, efficiency and expediency.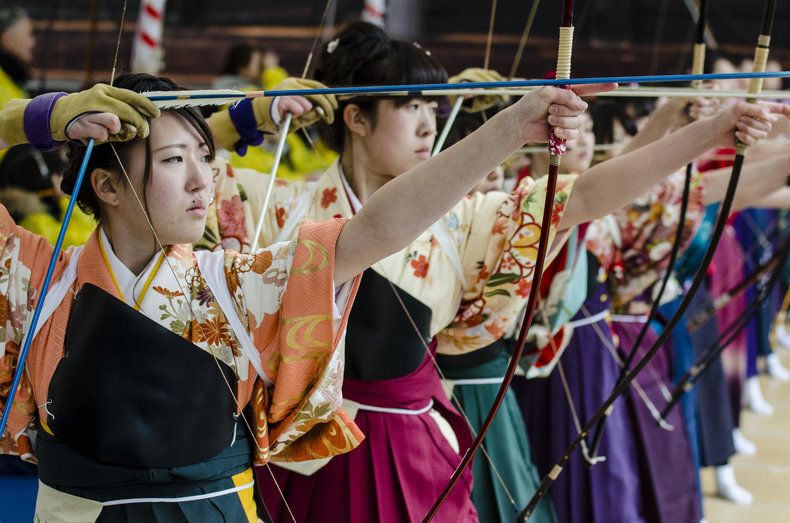
Aesthetics
Culture may be highly visual including colors, fashion and aesthetics that are embraced as symbols of a culture.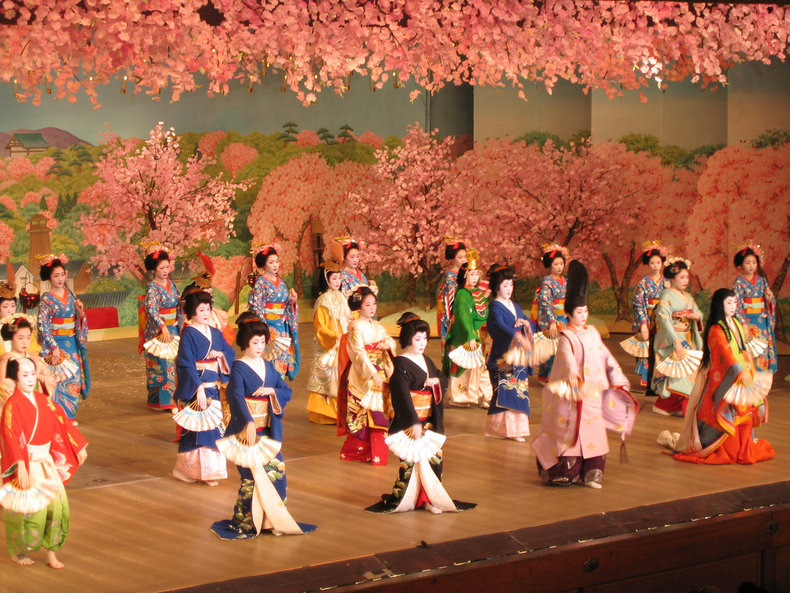
Social Status
People may compete for respect within a culture and evaluate themselves and others based on notions of social status that can be unique to a culture.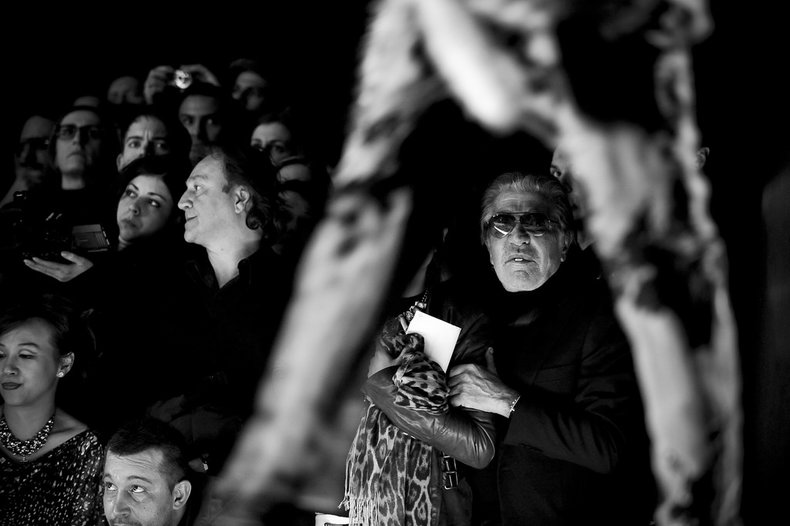
Multiculture
Culture exists at the level of a civilization, society, nation, region, city, ethnicity, organization, group and family. Cultures can transcend borders and include people based on their interests. As such, almost everyone belongs to multiple cultures that overlap in countless ways.
Change
Traditional cultures provide a stabilizing influence whereby culture remains much the same in the face of constant social change. Other cultures, such as organizational culture or youth culture may drive aggressive change.
History
Cultures may be based on a long history of a people or group that provides a rich source of traditions, stories and experiences.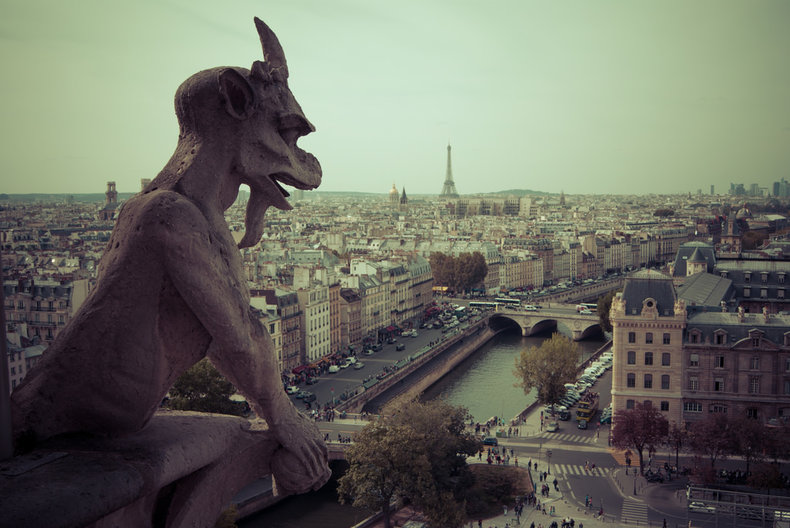
Storytelling
Myth, legend and storytelling allow culture to extend into the realm of the imagination to create rich meaning and symbols.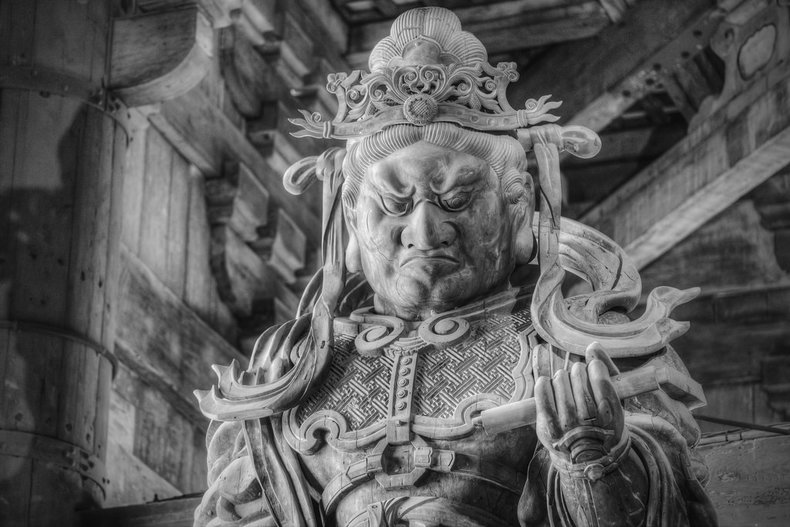
Traditions
Traditions are ways of doing things that are passed down from long standing members of a group to new members. In the context of traditional culture, this often involves a transfer of knowledge from an older generation to a younger generation.
Pastimes
Culture includes many of the things that people choose to do with their leisure and travel time including things like films, festivals and sports. Many holidays are also attached to a set of cultural practices.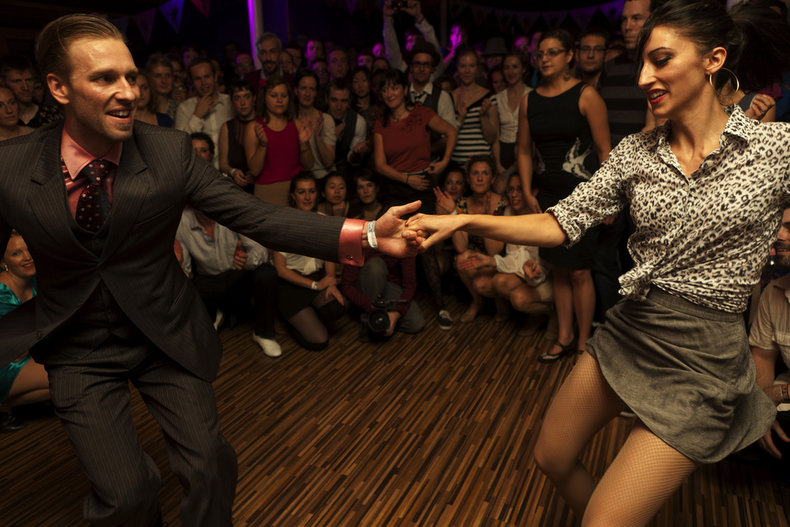
Lifestyle
Culture influences your daily life from your choice of breakfast to how you get to work. For example, a city with a lively culture of bicycling as compared to a culture centered around automobiles.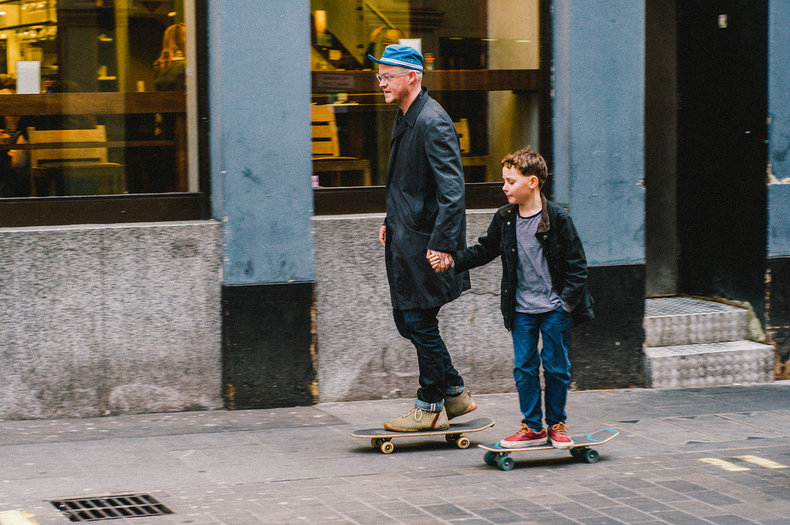
Social
Culture is often a means of socializing.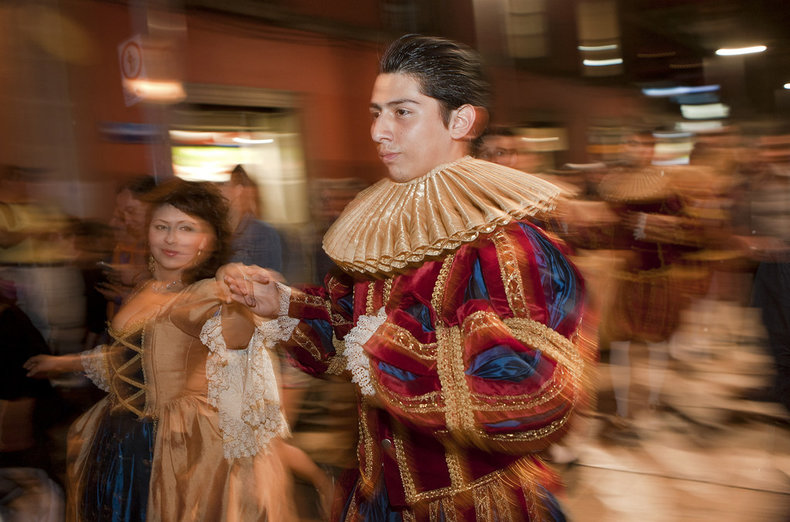
Community
Shared elements of culture help people to engage their neighbors and form communities based on mutual respect. For example, a city may have a culture that includes norms of politeness that help people to remain courteous to each other. Other elements of culture may help people to get along wherever they are on a global basis. For example, a super culture that transcends national boundaries.
Language
Language is defined by culture and continually emerges within traditional cultures, subcultures and super cultures.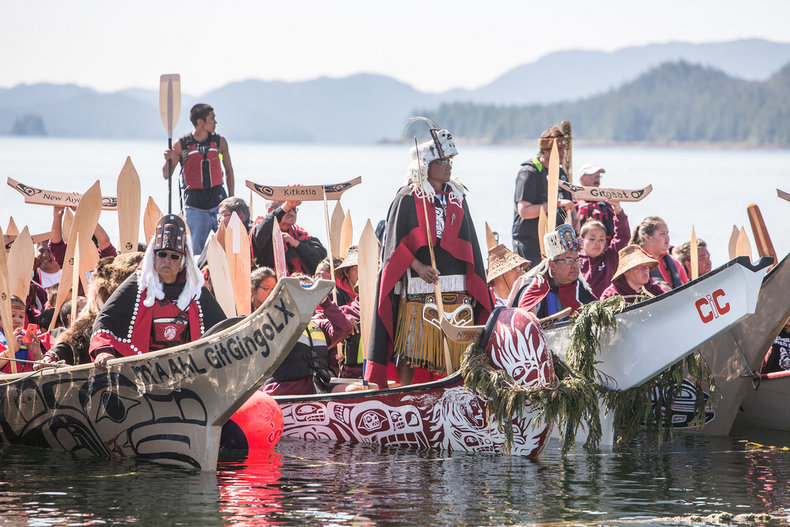
Politics
A civilization may view the many layers of culture that exist within a society as competition and seek to create a unified culture by interjecting into every aspect of life.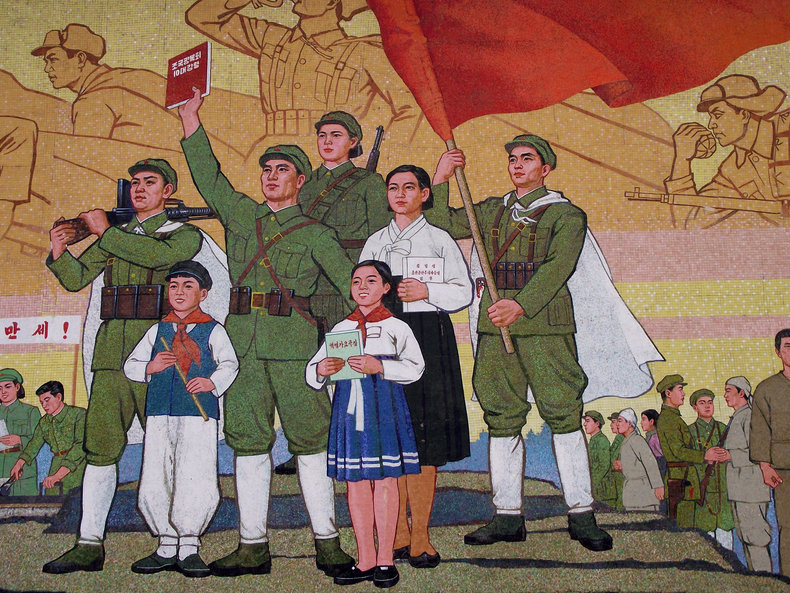
Epic Meaning
Culture is a means of seeking meaning and purpose in life beyond the bland realities of politics and production.
Anomie
Anomie is a society, community, place or individual who lacks culture such that behavior is not bound by any sense of shared experience and belonging. This is typically described as a state of confusion and isolation. In other words, culture is widely considered a human need.
| Overview: Culture Characteristics | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Traditions, symbols, meaning, norms and expectations that emerge as the result of the shared experiences of a group. | |
Related Concepts | ||