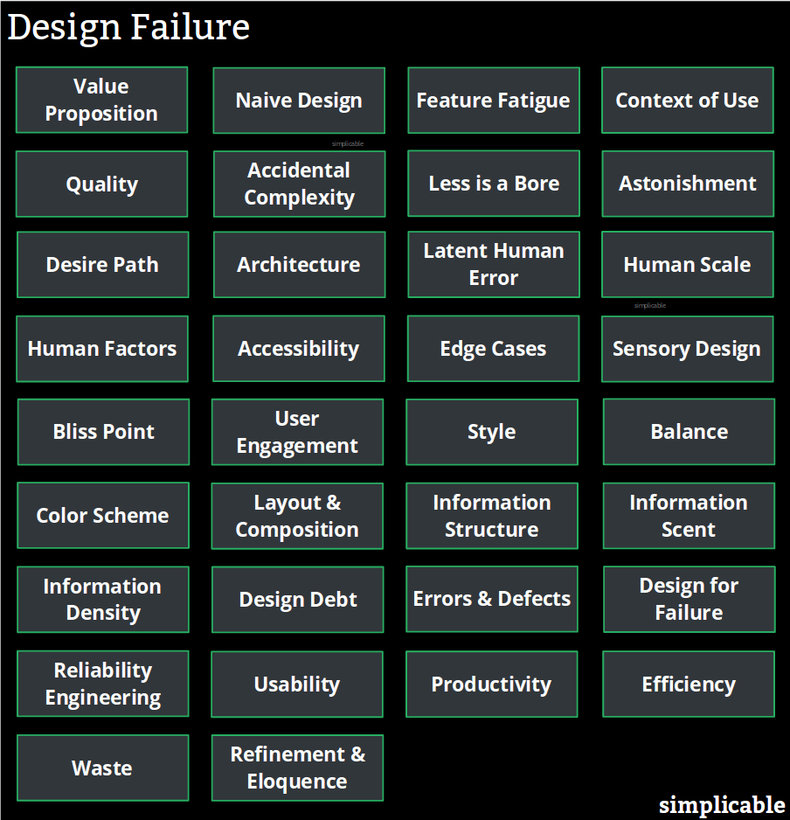
Value Proposition
A design that customer's don't need. For example, mobile devices that replicate the functionality of a smart phone or tablet that are less easy to use.Naive Design
Designers who don't use their own product or who are disconnected from the customers, context and culture that surrounds their products. For example, a designer of a playground who has no experience around children such that they misunderstand how kids play.Feature Fatigue
Including functions and features that customers dislike or that make your design difficult to use.Context of Use
A design that performs poorly in certain conditions such as wheels of a baby stroller that work great in the lab but are terrible on many real world surfaces.Quality
A design that isn't fit for purpose such as a snowboard that is too bendy or not bendy enough from the perspective of the customer.Accidental Complexity
Accidental complexity such as software designed around a bunch of needless abstract concepts that serve to make things big, slow and confusing.Less is a Bore
The idea that some designs go too far to avoid complexity such that they are perceived as low value. For example, a building that goes too far with minimalism and truth to materials such that is is perceived as brutally boring.Astonishment
Needlessly reinventing user interfaces in ways that users find counterintuitive, unpredictable and difficult to learn.Desire Path
Forcing users down paths that don't come naturally to them.Architecture
Structural problems such as a bridge built from both sides of a river that doesn't align in the middle.Latent Human Error
Designs that are likely to lead to human error such as a dangerous product in packaging that looks like a food product.Human Scale
Failure to build things to human scale such as a door that is too narrow for many people.Human Factors
Failure to consider human factors such as the use of hard brick on a jogging path that is likely to harm the health of joggers.Accessibility
Failure to consider the full range of human characteristics and abilities such as an elevator that is unusable for many people with disabilities.Edge Cases
A failure to consider important edge cases such as an aircraft design that fails to consider severe storms that are rare but possible.Sensory Design
Poor sensory design such as a product that makes a beeping sound that many users find unpleasant.Bliss Point
A design that fails to achieve a bliss point by giving the customer too much or too little. For example, a chocolate bar that is too small to be satisfying or too large such that customers regret eating it.User Engagement
Poor user engagement such as a game that is perceived as boring.Style
A product that lacks visual appeal such as a pair of shoes that fails to invoke the interests and passions of customers.Balance
A design that isn't visually balanced such that it is perceived as low quality and unstable.Color Scheme
A color scheme that fails to communicate. For example, a blue life jacket that is difficult to spot in the water.Layout & Composition
A poor arrangement of elements such as a navigational tool that customers perceive as disordered.Information Structure
The structure of information such as a deep website based on sparsely populated categories that make information and tools difficult to discover.Information Scent
User interfaces that fail to communicate where things can be found. For example, cryptic icons based on abstract concepts that customers find nonintuitive.Information Density
The amount of information per square inch on a user interface. Users tend to prefer information density that is similar to a book and may become frustrated by sparse information or environments that pack too much into a screen.Design Debt
Selling out the future to save time or money now. For example, a city that emerges as tightly packed buildings and narrow streets such that the future needs of the city are difficult to meet.Errors & Defects
A design that doesn't work such as software that is buggy due to its design.Design for Failure
A failure to design for failure. For example, a web browser that allows a poorly designed web page to crash it.Reliability Engineering
Failures of reliability engineering such as a bridge in an earthquake prone area that can't endure a large earthquake.Usability
User interfaces that are unpleasant from the perspective of users such as a touch screen that often fails to register touches as the user intended them.Productivity
Designs that fail to make users productive such as software that requires users to jump through dozens of hoops to complex a task that could be much simpler.Efficiency
Designs that consume too many resources per unit of output such as an inefficient engine that consumes more fuel and generates less useful energy than the competition.Waste
A design that is wasteful such as an over packaged snack. This can be viewed as a failure of sustainability.Refinement & Eloquence
Refinement and eloquence are commonly used to describe the artistic prowess of a design. In some cases, a design can follow all the rules of design and meet customer needs but still be a failure simply because it lacks refinement such that it is perceived as unattractive.| Overview: Design Failure | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A design that is low value or that destroys value. | |
Related Concepts | ||