
Aerospace technology | Agricultural technology |
Assistive devices | Audio equipment |
Biotechnology | Computers |
Computing devices | Construction equipment |
Consumer electronics | Desalination systems |
Displays | Elevators & escalators |
Energy infrastructure | Environmental technology |
Fabrics | Farm machinery |
Fashion | Firefighting equipment |
Gaming consoles & accessories | Heating, ventilation & air conditioning |
Heavy machinery | Home appliances |
Laboratory equipment | Lighting technology |
Manufacturing technology | Maritime technology |
Materials | Media equipment |
Medical equipment & devices | Mobile devices |
Nanotechnology | Navigation devices |
Network infrastructure | Printers & 3d printers |
Railway equipment | Robotics |
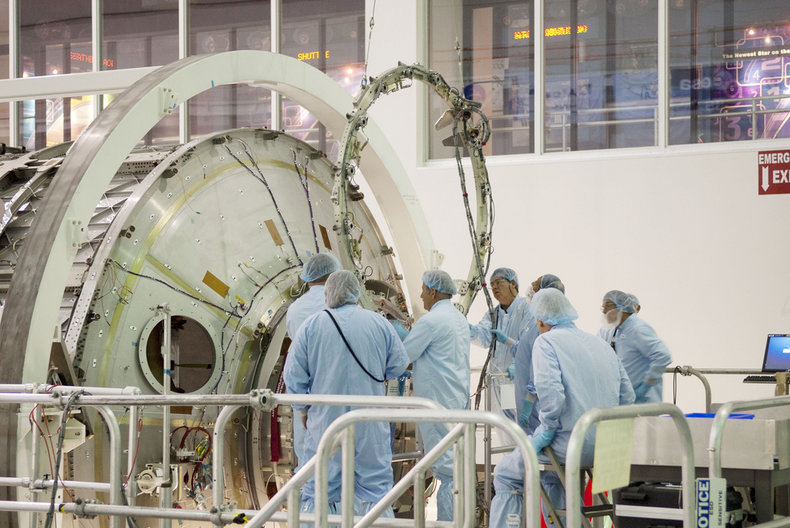
Satellites | Security systems |
Sensors | Ships & boats |
Solar panels | Spacecraft |
Sports equipment | Tools |
Transportation infrastructure | Undersea cables |
Vehicles | Virtual reality equipment |
Water infrastructure | Wind turbines |
Hardware
The physical manifestations of information technology such as computers, memory, data storage, sensors and networking devices.Machines
Machines such as an industrial drill on a production line.Materials
Advanced materials such as translucent concrete or carbon fiber reinforced plastic.Energy
Energy infrastructure such as solar panels.Transportation
Transportation infrastructure such as a high speed maglev train.Safety
Safety equipment such as a tuned mass damper that makes a large building more resilient to earthquakes.Assistive Technology
Technologies that help people with disabilities or the elderly. These are often physical technologies such as a prosthetic limb.Biotechnology
Biotechnology such as a medicine.Consumer Technology
Devices that are sold primarily to individuals such as a smart phone or television.Robotics
Robots are machines that are autonomous or semi-autonomous meaning that they can interact with the world on their own.Vehicles
Vehicles such as an electronic bicycle.Heavy Equipment
Large machines used in heavy industry, construction, mining, agriculture and other industries. For example, a crane used to construct buildings and infrastructure.Architectural Technology
Architectural technology such as a heating cooling and ventilation system.Instruments
Instruments such as a DNA analyzer used in a science lab.Printers
Devices that create physical manifestations of digital models such as a paper or 3d printer.Internet of Things
Internet of things is the practice of putting computers that are connected to the internet into every imaginable type of physical product. For example, a refrigerator that is connected to the internet such that it can regularly upgrade its software.Fashion
Modern fashion can often be viewed as a technology. For example, fashions made with advanced materials that are lighter and warmer than traditional materials.Low Tech
Technology that is far behind the state of the art that may nonetheless be preferred by consumers and businesses. Low technology may be specifically designed to remove advanced features. For example, a mechanical watch that doesn't contain a computer that is preferred by consumers who want a traditional timepiece.Nanotechnology
A broad term for any technology less than 100 nanometers. For example, most work on farms may one day be accomplished by quadrillions of nanobots that work together as swarms.Space
Technology related to space infrastructure and exploration such as satellites or spacecraft.Summary
The following are common types of physical technology: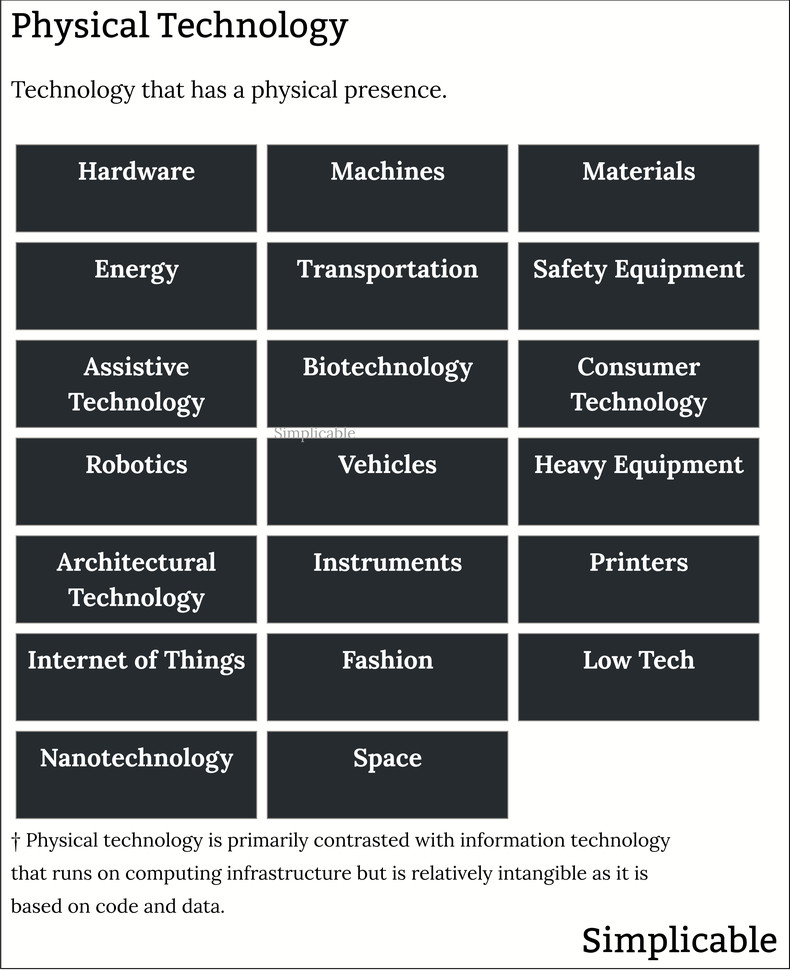
| Overview: Physical Technology | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Technology that is tangible such that it physically exists. | |
Relevance | Used to differentiate between technologies that physically exist and those that are purely code and data. | |
Synonyms | HardwareInfrastructureMachineDeviceTangible Product | |
Related Concepts | ||





























