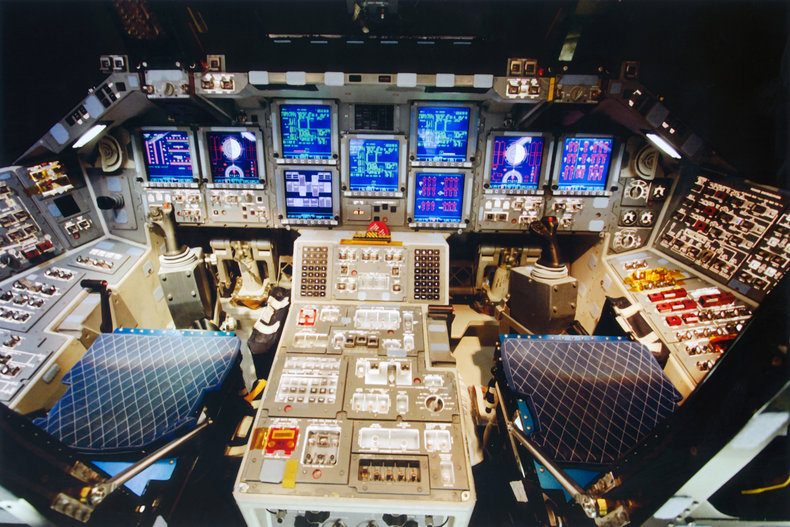
Space Shuttle Example
The Space Shuttle program is often used as an example of Moore's Law. The first Space Shuttle launched in 1981 featured computers capable of 480,000 instructions per second. Common smart phones are now capable of billions of instructions per second. The Space Shuttle Atlantis, the last shuttle to launch in 2011 only had a small percentage of the computing power of a laptop at the time. The computers weren't upgraded to current standards because they were valued for their reliability.Limits to Moore's Law
It can't continue forever. The nature of exponentials is that you push them out and eventually disaster happens.~ Gordon MooreSome observers claim that Moore's Law has begun to break down due to the high cost of R&D, manufacturing and test costs. This is not viewed as a technical limitation, although it is anticipated that miniaturization of current technologies may reach limits around 2030 as transistors approach atomic size.
Selected Examples
The following are a few examples of processor capacity that demonstrate Moore's law. Keep in mind that this list includes both supercomputers and processors for relatively inexpensive consumer devices.| System | Year | Million Operations Per Second |
| IBM 7030 (supercomputer) | 1961 | 1.2 |
| Intel 4004 | 1971 | 0.09 |
| Cray 1 (supercomputer) | 1975 | 160 |
| Intel 8080 | 1974 | 0.145 |
| IBM System 370 (mainframe) | 1977 | 0.730 |
| Intel 8035 | 1980 | 6 |
| Intel 286 | 1982 | 1.28 |
| ARM2 | 1986 | 4 |
| Motorola 68030 | 1987 | 9 |
| Namco System 21 (arcade system) | 1988 | 73 |
| Intel i486DX | 1989 | 8.7 |
| ARM7 | 1994 | 40 |
| Intel Pentium | 1994 | 188 |
| Intel Pentium Pro | 1996 | 541 |
| Intel Pentium III | 1999 | 2,054 |
| ARM Cortex-M3 | 2004 | 125 |
| Intel Core 2 Extreme | 2006 | 49,161 |
| Intel Core i7 920 | 2008 | 82,300 |
| Intel Core i7 2600K | 2011 | 176,170 |
| Intel Core i7 5960X | 2014 | 298,190 |
| AMD Ryzen Threadripper | 2020 | 2,356,230 |
| Apple A12 | 2019 | 5,000,000 |
| Apple A14 | 2020 | 11,000,000 |
| Fugaku (supercomputer) | 2021 | 442,000,000,000 |
| Overview: Moores Law | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | The prediction that the speed of computer processors doubles every 18 months. | |
Definition (2) | The prediction that the number of transistors on commercially available processors doubles every 2 years. | |
Related Concepts | ||