Physics
The path of least resistance is often used as a rule of thumb or heuristic in physics. For example, the rule of thumb that lightning is most likely to strike large grounded objects that are closest to the base of a thundercloud such as a tower or tree.Principle of Least Effort
The principle of least effort is a rule of thumb in marketing and design that customers or users will almost always do things the easiest way. For example, if there is a pub in the basement of an office tower, teams in the offices above will be likely to socialize there as opposed to walking 5 blocks to the next closest pub. This may hold true even if the further pub has far better food.Principle of Least Astonishment
The principle of least astonishment suggests that a design should do things the way the user expects unless there is a very good reason to change. For example, a user of a remote control expects a big red button at the top to be the power button. If you get creative and make this button the mute button, users won't be happy.Desire Path
A desire path is the way that people naturally want to do things, usually because it's the easiest way. This is an important concept in design as going against a desire path can result in a design failure. For example, users of a microwave just want to hit a button and have their food heated to some reasonable temperature without answering a lot of questions. A microwave that makes it any harder than this could fail on the market.Keep It Simple Stupid
An approach to problem solving that suggests that the simplest, most obvious solution is often the best. For example, a single switch that allows a pilot to quickly disable all automatic pilot functions of an aircraft if they are malfunctioning as opposed to 20 different multi-step procedures to disable 20 different automated functions.Low Hanging Fruit
Low hanging fruit is an analogy that suggests it is best to accomplish easy things before proceeding to harder things. This may or may not be a good idea depending on the value of each task. For example, it is common for executives to focus on easy to understand tasks such as an office interior design project and avoid difficult tasks that have far more value such as reinventing their business to stay competitive.Pareto Principle
The pareto principle is the theory that 80% of a result is achieved with the first 20% of effort. For example, a student who can get an 80% score on a test with 3 hours of study but would need to study for 15 hours to get 100%. In this case, the path of least resistance is to do the 20% of work that gets you the 80% result.Pragmatism
Pragmatism is a philosophy that considers something true if it is true for all practical purposes. For example, if people commonly believe flowers are beautiful, then they are beautiful.Ethical Failure
Taking the easy way, even if it is ethically wrong. For example, continuing with a business that is obviously destroying the planet because you are getting paid.Bread & Circuses
The observation that populations are often content with basic sustenance and entertainment. This can be seen in modern consumer behavior that often prioritizes entertainment, comfort, convenience and safety. This can be construed as a dark and uninspiring condition whereby people have given up on self-actualization as they prefer an easy and safe life.Sour Grapes
Sour grapes stems from a myth about a fox that sees grapes that are out of reach so he assumes they are sour. This is an analogy to a common human behavior whereby it is easier to reduce our expectations than to achieve what we really want.Lowering The Bar
Lowering the bar is when a society, organization, group or individual lowers their standards over time to make things easier. For example, a culture that begins to accept low quality food because its cheap and easy.Overview
The path of least resistance has both positive and negative connotations. Where it often makes sense not to overcomplicate things, it can also be a mistake to lower the bar by always choosing the easiest and most convenient option.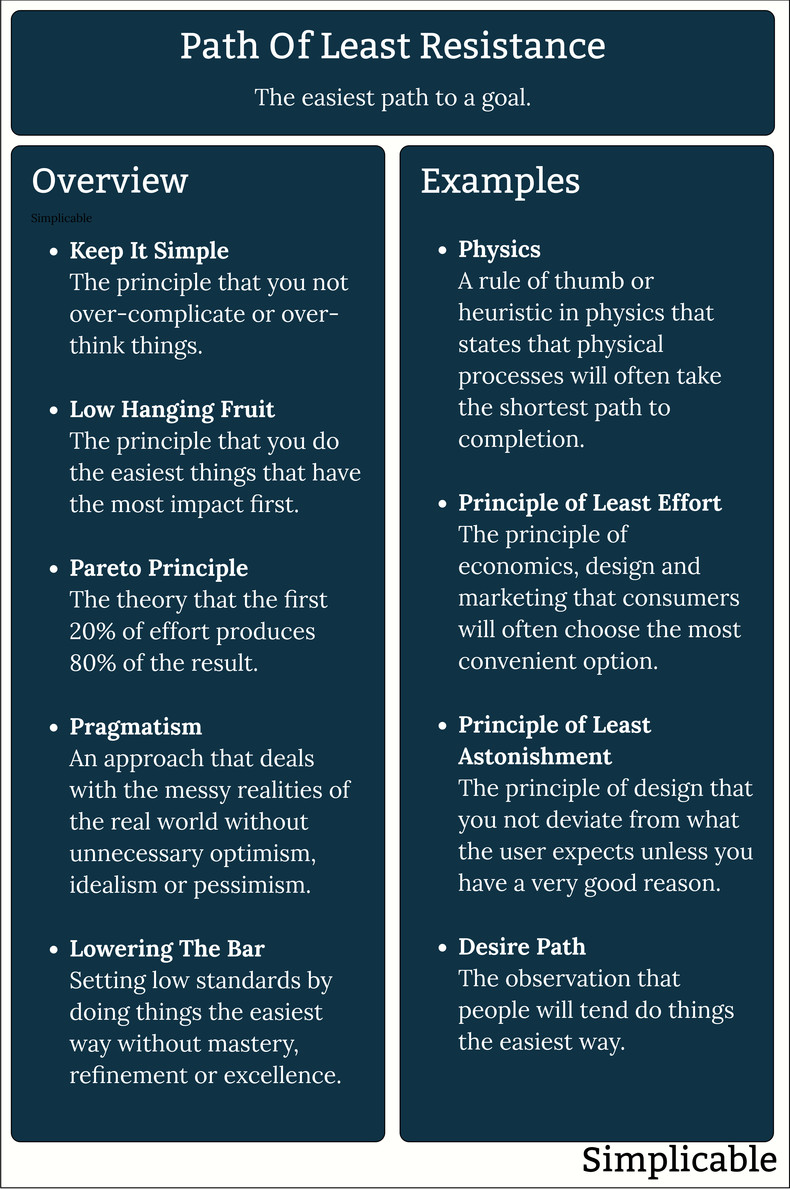
| Summary: Path Of Least Resistance | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The easiest path to a goal. | |
Related Concepts | ||