Standard Elements
Use of standard native elements such as the buttons of html. Avoids attempts to override the look and feel of such elements.Practical Color
Solid colors that are selected for practical reasons such as contrast for visibility. Typically gradients and ornate textures are avoided.Sans-serif Typography
San-serif fonts are selected for their readability on a range of screens.Grid Layouts
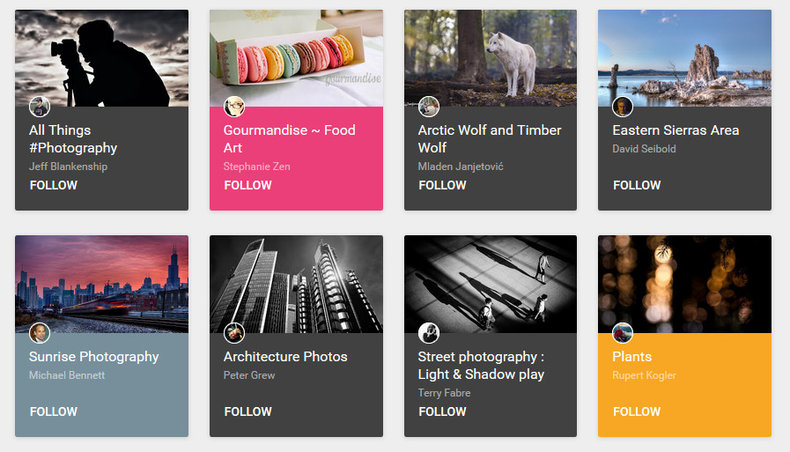
Grid layouts that lend themselves well to resizing. Also simplifies the generation of interfaces from a platform.Symettrical
Flat designs tend to rely on symmetry for balance. Although asymmetrical elements may appear in a grid there is rarely much attempt to use sophisticated asymmetrical balance techniques.Native Dimensions
Tends to avoid 3D looking icons and effects on a 2D screen.Mechanical over Organic
Flat designs rely on geometrical shapes with no attempt to make designs soft, curvy or organic.Decorations are Functional
Flat designs are decorative in the sense that they often make heavy use of icons over text. They also commonly use photographs. Flat design avoids illustrations that have no function such as a decorative background.Skeuomorphs
Skeuomorphs are avoided. Seams and shadows may be used to provide cues to users about what is touchable. These could be considered skeuomorphs except that they are used for a functional purpose.Philosophy
Flat design is more of a philosophy and style than a strict set of rules. As a philosophy, it embraces form follows function and doesn't decorate without a reason. As the name suggests, it makes no attempt to look multidimensional and produces interfaces that look much like a flat poster.| Overview: Flat Design | ||
Type | Design Style | |
Definition | A modern minimalist style for information oriented user interfaces that embraces form follows function, simple native elements and practical design choices for a wide range of devices. | |
Value | Inexpensive designs that look good across a range of devices.Easy to generate dynamically.Focuses on content and function over superfluous decoration. | |
Related Concepts | ||