Switchover
Switchover is the correct term for a manual failover whereby a human needs to be involved to replace a failing resource. For example, a failing virtual server on a cloud platform that needs to be released with a new instance launched from a backup using a management console.Heartbeat
A form of automated failover whereby a resource sends out a regular heartbeat message to let another resources know it is still alive. If a number of heartbeats for a resources are missed, a failover is triggered. A heartbeat is a push from a resource outwards.Health Check
A health check is a pull operation that verifies the health of a resource from the outside. For example, a load balancer may provide a health check on a server by monitoring for a failure to reply to client requests. Alternatively, the load balancer may make requests of its own to check if a resource is up.Load Balancing
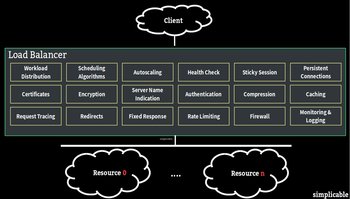
A load balancer is a tool for distributing workload to servers and other resources. These support failover using health checks or heartbeats. A load balancer may effectively achieve failover by removing a failed resource from its pool of active resources. A load balancer may also start new resources to replace the failed resource using autoscaling capabilities.Peer Failover
Peer failover is any architecture where resources failover for each other as peers as opposed to having a centralized controller such as a load balancer perform the failover. For example, two servers can send each other heartbeats and take over the other server's work when a heartbeat fails. This can also be orchestrated across a large number of peers to create highly resilient services.Standbys
Standbys are resources that perform no work until they are needed to replace a failed resource. A hot standby is a running resource with data mirrored in real time such that failover can be achieved quickly. A cold standby is a resource that is not running. In many cases, data needs to be restored from a backup to prepare a cold standby for launch.Cloud Failover
Cloud infrastructure allows resources to be scaled up and down on demand and is ideal for performing automated or manual failovers. Cloud platforms typically provide failover functionality with load balancing services, management platforms, autoscaling tools and API gateways.Disaster Recovery
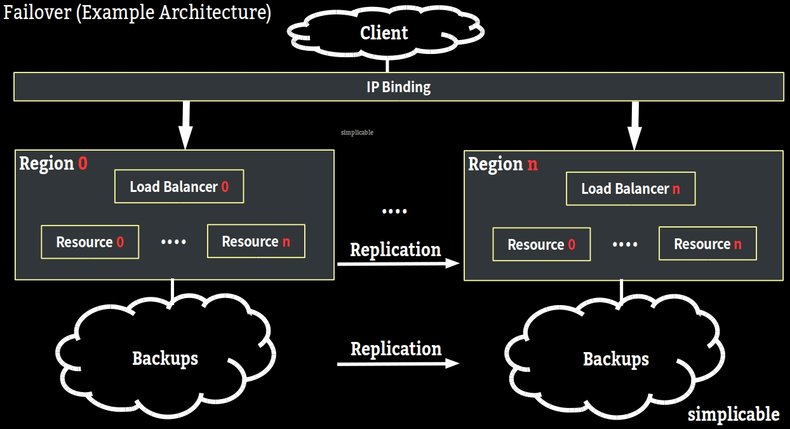
Disaster recover is the process of managing the risks of large failures due to disasters. Disasters may take entire data centers out of operation as opposed to single resources. As such, disaster recovery often requires architectures that can failover all the resources in an entire region. This can be achieved with cloud architectures that allow load balancing across multiple regions. Alternatively, it can be achieved with a hot or cold site and switchover procedures for a disaster.Failback
Failback is the process of repairing a failed resource and putting it back to work. This is the reverse process of failover.| Overview: Failover | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The process of replacing a failing computing resource with a healthy resource. | |
Related Concepts | ||