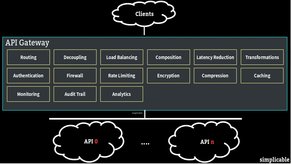
How does it work?
Edge computing works by processing close to users, devices or integration points to reduce latency and distribute computation to many instances. Each data center where you have an instance is known as an edge. The trick is to have users, devices and services connect to the edge closest to them. There are various ways of doing this. For example, you can develop a system of returning different IP addresses to different DNS servers so that a URL maps to different IPs from different regions. For example, return an IP in your Hong Kong data center when a DNS server is located in Hong Kong. This is far from a perfect solution because DNS servers aren't necessarily regional but it is nonetheless a common way to implement edges. It is also possible to implement edges by redirecting requests to different URLs based on region.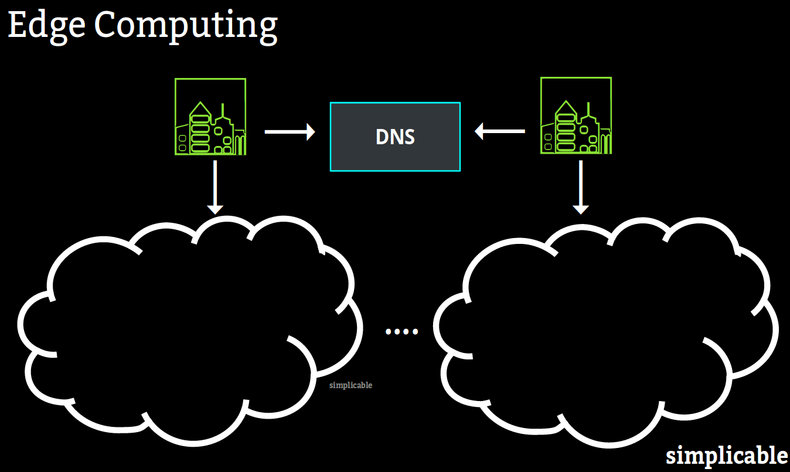
What is an edge?
An edge is the closest data center instance you have to a user, data source, device or service. In other words, it is the closest computing instance to the work to be done.Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
Edge computing is often based on cloud computing. Cloud computing is a class of technology for scaling a service to many instances. The same can be said of edge computing. Both edge computing and cloud computing are methods for achieving horizontal scale. Edge computing often uses cloud computing and the two techniques can be viewed as complements.Edge Computing vs Content Delivery Network
A content delivery network is a service that serves static files such as video, images and html from edges. This is extremely similar to edge computing. As such, content delivery networks may offer edge computing capabilities. Edge computing is computing from the edge, a content delivery network is static content from the edge.Edge Computing & IoT
Edge computing is often mentioned as being related to internet of things, commonly known as IoT. This is due to the large scale processing requirements that may be required if you start connecting everyday things such as bicycle tires to the internet. Such connected devices may generate a great deal of data that can be summarized at the edge before transmission across the internet. This may dramatically reduce processing and the global internet bandwidth required to implement IoT services.Example
A mobile app with a large number of users depends on a backend service that is run on cloud infrastructure from 28 regional data centers. Users get a different IP for the service depending on the location of their DNS server. This isn't always accurate, so the service also does redirects when a user happens to connect to an edge that is physically distant from their current location. Edges are used to improve the reliability of the service with a technology that can bypass any edge that is down by redirecting users to another edge.| Overview: Edge Computing Definition | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The practice of handling requests, data, events and transactions relatively close to where they occur by scaling code to multiple geographical locations. | |
Related Concepts | ||