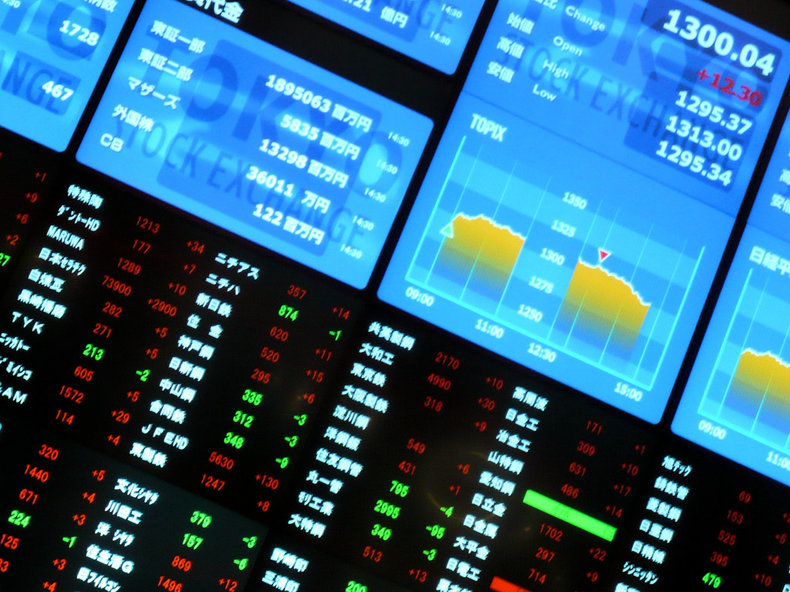
Stocks
A market for buying and selling stocks that represent ownership interest in a business. Stock markets also typically trade certain types of securities such as exchange traded funds that implement a variety of investment strategies.Bonds
Markets for issuing new debt or buying and selling existing debt securities. Many bond markets are over-the-counter meaning that they rely on a dealer network as opposed to an exchange.Derivatives
A financial market for trading contracts such as futures, options and credit default swaps. Includes both exchanges and over-the-counter markets.Foreign Exchange Market
A decentralized market for trading currencies. The largest market in terms of trading volume with mostly large financial institutions participating.Commodity Market
Markets for commodities such as energy, metals and agricultural products. It is common to bet on the prices of commodities without taking delivery with a variety of derivatives.Money Market
Trading in short-term debt instruments such as treasury bills, commercial paper, certificates of deposit, bills of exchange, repurchase agreements, federal funds and asset-backed securities.Real Estate Market
The market for real estate primarily involves agents that represent buyers and sellers.Reinsurance
A market for insurance purchased by insurance companies. A method for transferring risk.| Overview: Financial Market | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A platform or system of economic exchange. | |
Value | A fundamental basis of economic activity. Performs functions such as funding governments and businesses, storing wealth, conducting trade and managing risk. | |
Related Concepts | Investing EconomicsKeynesian Beauty Contest Wealth Preservation SpeculationArbitrageEfficient Market Hypothesis | |