
Interest Rates
Interest rates greatly influence the cost of capital of all businesses. This influences capital spending and competition. When interest rates go down, businesses may expand. When they go up, businesses may contract or fail at higher rates.Credit Conditions
The willingness and ability of banks to lend. Credit tends to go through a cycle of easy lending followed by tightening. This is driven by the liquidity of banks and their perceptions of risk.Business Cycle
The rise and fall of supply in an industry. Most industries go through a cycle whereby supply increases, leading to intensive competition and falling prices. When prices fall too low, supply falls as businesses cut back on capital and labor.Business Confidence
How the managers of businesses feel about future opportunities and risks. Optimism eventually brings capital spending and increased competition. Pessimism brings cut backs and divestiture.Consumer Confidence
How consumers feel about their economic future. Confident consumers spend more, save less and take out more debt. Pessimistic consumers save, pay down debt and spend less.Debt & Savings
The debt levels of governments, businesses and consumers. High debt levels can constrain spending and lead to the bankruptcies of businesses and individuals. At the government level, it can shake confidence in the currency of a nation.Inflation & Deflation
A sustained increase or decrease in general price levels. Moderate inflation can be positive because it encourages businesses and consumers to spend as everything is always getting more expensive. High inflation can be damaging to markets as businesses and consumers begin to hoard goods. Deflation discourages spending as everything is always getting cheaper.Labor Market
Salaries and the availability of skilled employees.Trade
The ability to trade with foreign markets without barriers such as tariffs. This varies with time due to factors such as a trade war.Growth
The growth of an industry or the economy in general. This includes periods of negative growth such as recessions and depressions.Taxes
Business taxes in a particular country or region. Generally speaking, a high tax rate and administrative burdens such as collecting value added taxes discourage entrepreneurship and business investment.Demographics
The demographics of a population have a large impact on consumption, labor and competition. For example, a country with a large population of educated young people entering the job market may experience superior growth rates.Economic Security
The political and economic stability of a nation or region. For example, a nation where supply chain disruptions are rare.Competition
The current level of competition in a market. In some cases, difficult financial conditions such as a recession reduce competition levels and represent an opportunity for a new entrant. This is particularly true if you have a drive to innovate where nobody else is making investments. For example, General Electric, IBM, Microsoft and Apple were founded during recessions.Summary
The following are common examples of economic conditions: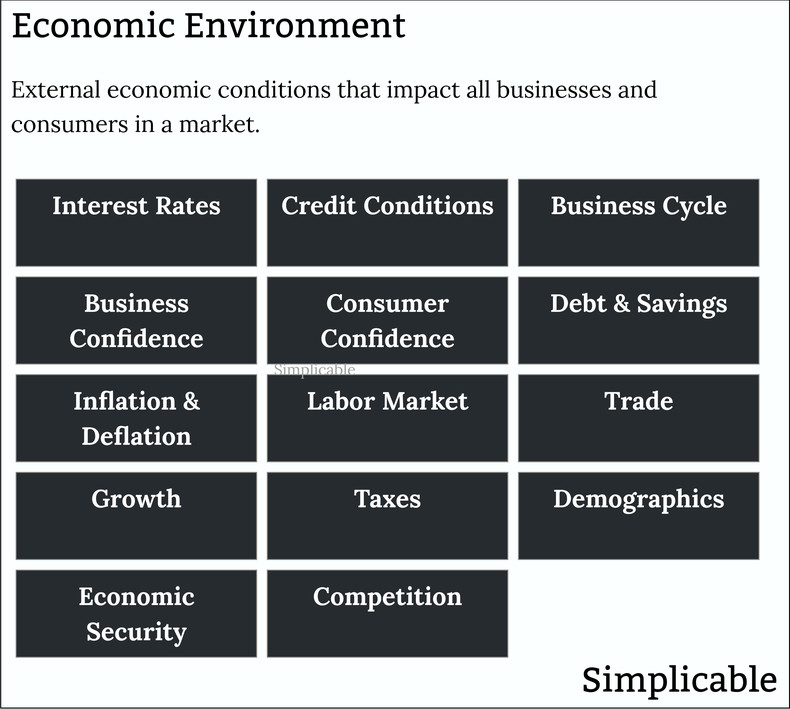
Summary
The external economic conditions that influence the economic life of consumers and businesses.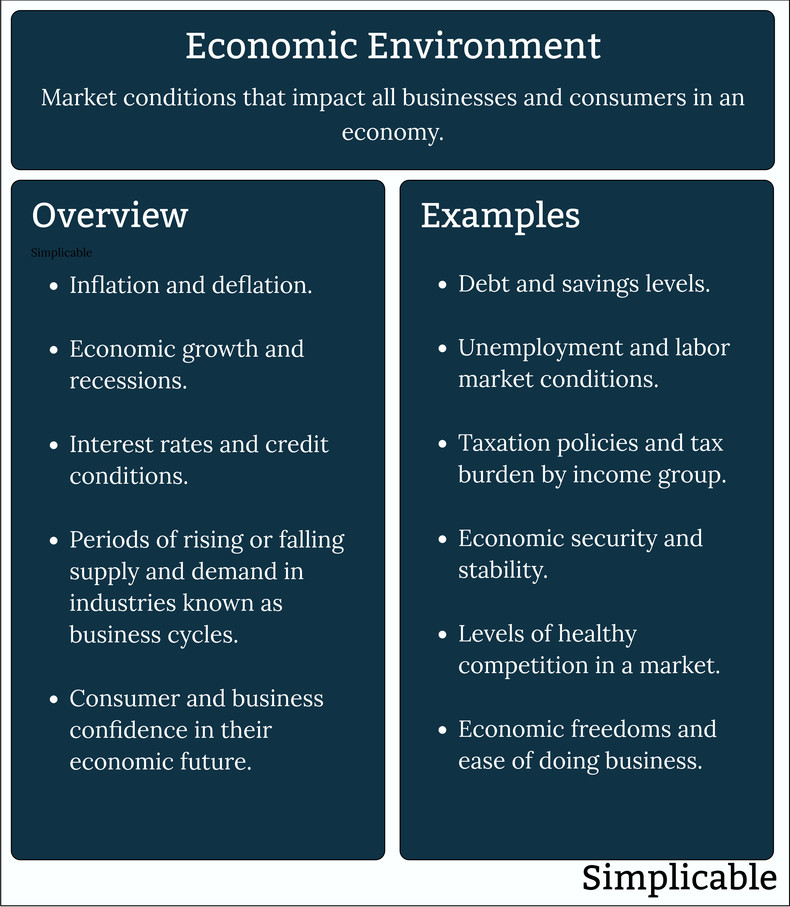
| Overview: Economic Environment | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A set of external economic conditions that impact all businesses and consumers in a market. | |
Related Concepts | ||


































