Domino Theory
A prominent theory in the cold war that each country that falls to communism leads to another country falling until an entire region or the world is completely communist. This was used to justify American involvement in the Vietnam War.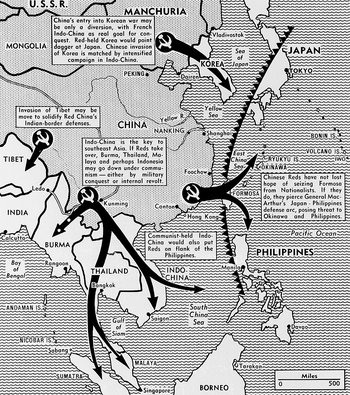
Habits
It is often suggested that a minor bad habit can lead to a far more severe problem. This was a common argument of the temperance movement that lead to a prohibition on alcohol in the United States from 1920 to 1933.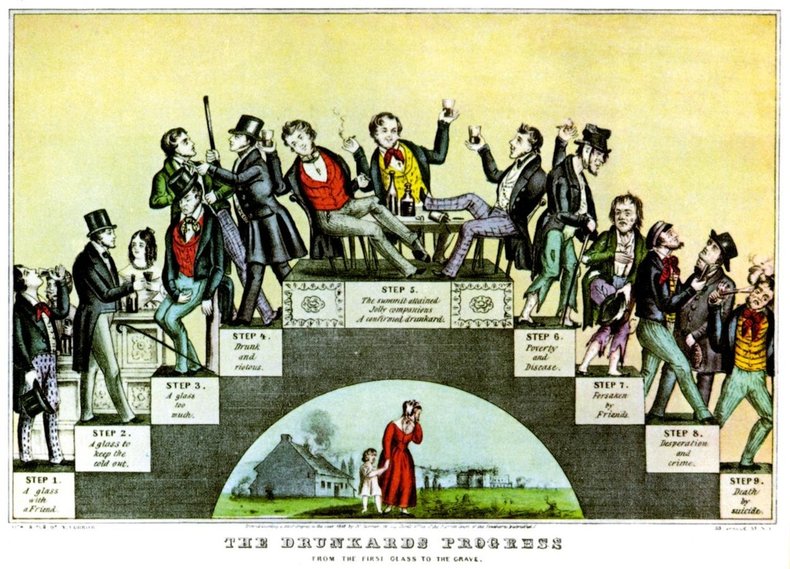
Vicious Cycle
A vicious cycle is a progression where negative results feed into a process that causes even more negative results. This occurs in a repeated cycle that is difficult to escape. For example, poverty that creates obstacles, risks and health problems that all lead to worsening poverty.
Slippery Slope as a Fallacy
Any "slipping" to be found is only in the clumsy thinking of the arguer, who has failed to provide sufficient evidence that one causally explained event can serve as an explanation for another event or for a series of events.~ T. Edward Damer, Attacking Faulty ReasoningSlippery slopes do exist. As such, an argument that a position is a slippery slope isn't necessarily a fallacy. However, it is difficult to prove or disprove the potential for a complex chain reaction. Slippery slope arguments are commonly accused of being fear mongering or propaganda. For example, a slippery slope argument may be used to portray a reasonable or moderate position as being extreme and dangerous.
| Overview: Slippery Slope | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A seemingly reasonable or relatively harmless state, action, behavior or rule that causes a chain reaction of negative consequences. | |
Related Concepts | ||