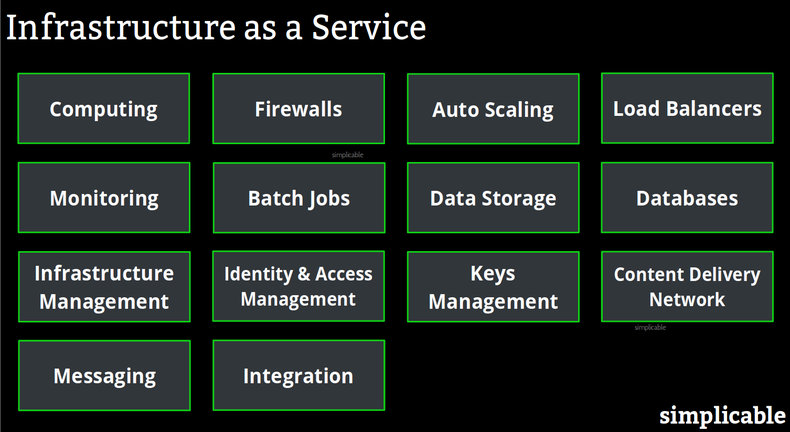
Computing
Computing instances that can be used to run websites, software as a service, automation and analysis. Instances are often virtual machines that typically support attached storage and networking. Data centers are fully managed by the provider.Firewalls
Firewalls for computing instances. For example, a firm might use a firewall to restrict access to a compute instance such that only its corporate IP addresses can connect.Auto Scaling
The ability to automatically start and stop instances in response to current demand. For example, a website that automatically adds instances when cpu utilization passes 66% for more than two minutes on an instance.Load Balancers
Load balancers to distribute work to instances. For example, software as a service that uses load balancers to distribute traffic to instances. This can be combined with auto scaling to provide a target cpu to user ratio such as a minimum of 1 cpu for every 50 users.Monitoring
Cloud infrastructure services may provide monitoring tools that allow automated responses to situations such as a server that appears to be down.Batch Jobs
Platforms for scheduling and managing batch jobs. For example, an ecommerce company might perform inventory management tasks as a daily batch job.Data Storage
Computing instances may have attached storage. It is also common to use a cloud storage service that may be more scalable, sharable and resilient than local storage.Databases
Databases including cloud-based SQL and NoSQL databases.Infrastructure Management
User interfaces and APIs for managing computing infrastructure. For example, an API that allows you to back up an instance image automatically.Identity & Access Management
Tools for managing authentication and authorization.Keys Management
Tools for managing encryption keys.Content Delivery Network
A service that delivers content and media to users from a data center that is physically close to them. For example, an ecommerce website that delivers its images and web pages from dozens of regional data centers near popular centers to reduce page load times.Messaging
Messaging platforms such as a service for delivering transactional and marketing emails.Integration
Integration tools such as publish and subscribe notifications. For example, an ecommerce site might notify all instances when a new product is added to its product database.| Overview: Infrastructure as a Service | ||
Type | ||
Definition | ||
Also Known As | Cloud Infrastructure, IaaS | |
Related Concepts | ||