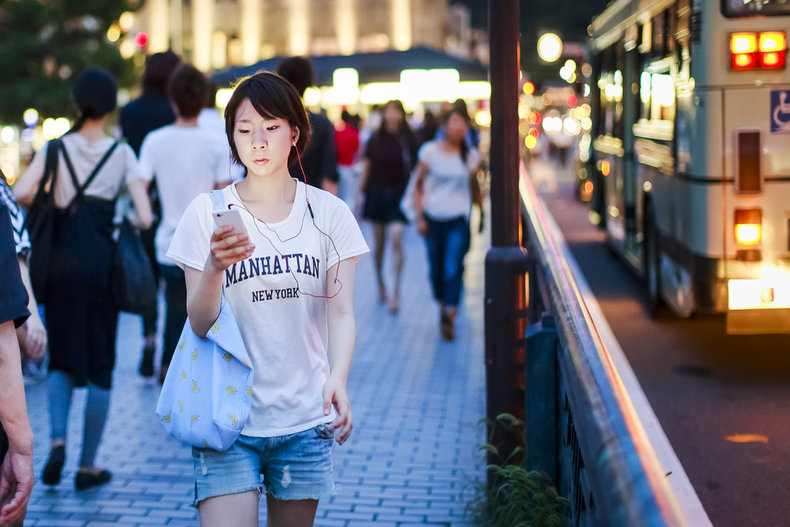
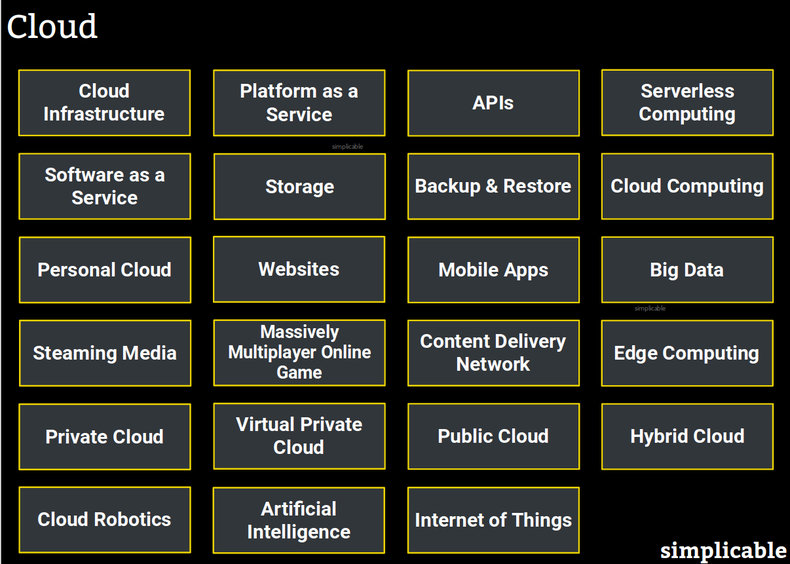
Cloud Infrastructure
Services that allow you to scale up and down the use of computing infrastructure such as servers and storage. For example, a bank website that automatically scales from 10 computers to 90 computers during peak traffic hours.Platform as a Service
Platforms for developing systems and applications that are built on top of cloud infrastructure such that they automatically scale.APIs
Services that offer computation and data. APIs may use a large number of physical computers through a single interface such that they require cloud infrastructure. For example, a national weather service that provides weather data to thousands of private companies each day using a public API.Serverless Computing
Platforms that allow you to develop software that scales without thinking about servers. Many cloud platforms allow you to automatically add or remove servers from your service. Serverless platforms abstract this concept or automatically scale without any control by systems or applications.Software as a Service
Software that runs on cloud infrastructure that is typically accessed by web, mobile app or a thin client. For example, a sales force automation tool whereby you pay per user and access the software with a mobile app without installing anything on your own servers.Storage
Platforms that allow you to store data seamlessly across many physical data storage devices with a single interface. Cloud storage is typically billed like a utility such that you are only charged for the data resources that you use.Backup & Restore
Cloud storage is often used to create backup and restore services. For example, a mobile phone that is fully backed up to storage in a data center such that it can be cloned if you lose it.Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a catch-all term for infrastructure as a service, platform as a service, software as a service and any other type of service that uses a cloud architecture whereby many physical machines are used to solve one problem or provide one service.Personal Cloud
Services that allow you to store data and media in a data center such that they work from any device you own.Websites
Large websites are almost always implemented on cloud infrastructure. For example, a web-based email service that allows users to log on from any device to read and send email. Such a service is accessed from a single URL but may use thousands of physical computers.Mobile Apps
Mobile apps can be architected such that much of their functionality is provided by services running from data centers. In this case, a mobile app is essentially a thin client that connects to a cloud platform. For example, a weather app whereby the code running on the phone itself does nothing but fetch and display information from a cloud service.Big Data
Big data is the collection and use of large amounts of data using cloud storage. For example, a mobile analytics platform that allows a video game company to discover product optimizations based on data from billions of interactions with their mobile apps.Steaming Media
Services that allow users to access media such as movies and music on demand.Massively Multiplayer Online Game
A game that allows multiple players to interact in shared environments. This requires significant computing power and is typically implemented on cloud infrastructure.Content Delivery Network
Content delivery networks are platforms that allow media to be delivered from a data center close to the user to improve performance.Edge Computing
Platforms for performing computing from a location close to where you need it. For example, an airline system that runs code from data centers close to each airport to improve performance.Private Cloud
A cloud that is built on dedicated hardware for a single organization. For example, a research facility that has its own data center architected as cloud infrastructure.Virtual Private Cloud
A cloud that is logically isolated from other networks on shared hardware. This is based on communication encryption and other techniques such as private IP subnets. For example, a virtual private cloud may communicate over the internet using a overlay network.Public Cloud
Cloud computing services that are accessible to the internet.Hybrid Cloud
Services that integrate a public cloud and private cloud, often a virtual private cloud. For example, a mobile app backend that is run from a public cloud that locates its databases in a more secure virtual private cloud that can't be reached from the internet.Cloud Robotics
Robots that get some or all of their intelligence from a cloud service. For example, a garbage sorting robot that becomes inoperative without a connection to a robot API service built on a cloud platform.Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is typically deployed to cloud such that devices in the field all share their learning data. For example, a network of self driving vehicles that share their data such that each vehicle learns from all other vehicles.Internet of Things
Internet of things is the practice of putting computers with network connectivity into everyday things such as city infrastructure or a toaster. This is typically based on cloud technology whereby each device connects to a cloud service to improve its functionality and/or share data.| Overview: Cloud | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An approach to computing that uses many resources as one. | |
Related Concepts | ||