Internet Latency
Internet latency is the time it takes for a client such as a mobile phone to get an initial response from an internet service such as a website. Internet latency impacts the speed of messaging, voice over IP, email, websites and some mobile apps.Low Latency
Low latency describes a fast response time. Generally speaking, a latency of less than 10 milliseconds is considered low.High Latency
High latency describes a slow response time. The biggest factor impacting latency is the geographical distance between the client and server. If you are in a remote location such as Antarctica you will have higher latency than if you're in California using services that are also located in California. Slow, unreliable or overburdened network infrastructure also increases latency. For example, a telecom company that regularly upgrades equipment may have lower latency than its competitors.Internet Backbone
An internet backbone is a high capacity data route on the internet that connects different networks. Generally speaking, you will have lower latency if you are close to an internet backbone or multiple internet backbones. This is a common consideration in the selection of locations for data centers.Packet Loss
Packet loss is a message between you and a host that is lost in transit. Networks experiencing problems may drop all or some of your messages. This may appear to the user as high latency as software may automatically retransmit failed packets but things become slow.Ping
Ping is a tool available on many computers to test your latency to a host. For example: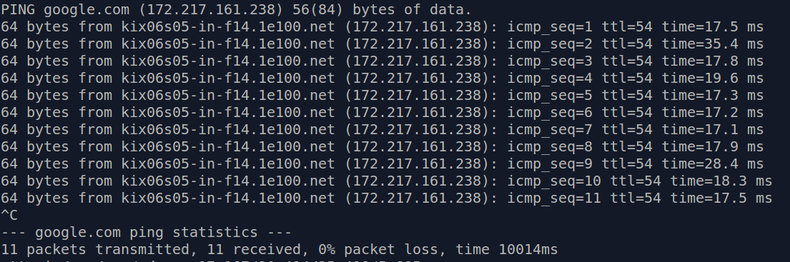
Traceroute
Traceroute is another common tool for testing latency that provides more details than ping. It lists the hops that a message takes from client to server.Wired vs Wireless
Generally speaking a fiber optic connection provides lower latency than wireless communications. Signals in a fibre optic cable travel at approximately 186,282 miles per second, the speed of light.Latency vs Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the total amount of data that can be theoretically transferred in a second based on the technologies and network you are using. Bandwidth is important for downloading large files quickly. Latency is important for transferring small amounts of data and getting a quick response back. For example, a connection needs both high bandwidth and low latency to stream an HD video feed of a live event in real time. However, if the event isn't live latency doesn't matter much because the video can be cached before it begins to play. In other words, on a high bandwidth and high latency connection a video might be slow to start but should work once it begins to play. It should be noted that "high bandwidth" is good and "high latency" is bad.Bandwidth vs Throughput
Throughput is the actual bandwidth of a connection at a point in time. For example, a connection may have a bandwidth of 100 Mbps but an actual throughput of 5 Mbps during peak usage hours.Proximity
The best way to reduce your latency is to have a high speed fiber connection that is physically close to the service you want to use. For example, a bank might lease data center space that is a block away from a major stock exchange to achieve low latency trading. This typically requires that the data center have a direct link to the exchange.Edge Computing
Edge computing is the practice of deploying a service to multiple data centers to perform computation close to users. For example, a mobile app might deploy its backend services to dozens of data centers so that a user in Dubai is served from a data center in Dubai. This greatly reduces latency.Content Delivery Network
A content delivery network is a platform for delivering static files such as videos, pictures and html from data centers that are physically close to each user to reduce latency.| Overview: Latency | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The response time of a technology. | |
Related Concepts | ||