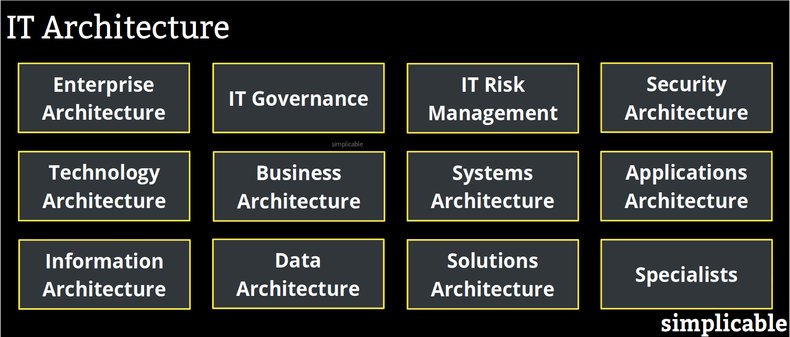
Enterprise Architecture
The top level structure of information technology. Defines foundational principles, platforms, models and standards to be used by the entire organization. This requires a great deal of authority and/or influence and is typically an executive role.IT Governance
Oversight of IT strategy and change. Aligns change to business strategy and enterprise architecture. Typically reviews the architecture of major projects with authority to stop funding.IT Risk Management
The process of identifying and managing IT risk. This requires architectural analysis and solutions for treating risk.Information Security Architecture
Analysis of information security at the structural level. Outputs include principles, models, controls, policies, processes, procedures and standards to address information security.Technology Architecture
The design of technology infrastructure such as networks and computing facilities.Business Architecture
Analysis and design of business structures. For example, an analysis of current business capabilities, gaps between capabilities and strategy and a roadmap for future capabilities.Systems Architecture
Designing systems that automate work.Applications Architecture
Designing applications that are used by people.Information Architecture
Designing information structures for people to use.Data Architecture
Designing data models, structures and integrations for machine use.Solutions Architecture
A generic term for architecture at the implementation level including systems, applications, data, information security and technology architecture.Specialists
It is common to address architecture in terms of specialized domains or technologies. For example, a cloud architect.| Overview: IT Architecture | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The structural design of information technology. | |
Related Concepts | ||