Architecture vs Design
As information technology tends to be complex, it is often helpful to design it at both the structural level and implementation level. This is analogous to an architect designing a building and a variety of interior designers planning the interiors of the building's rooms.Types
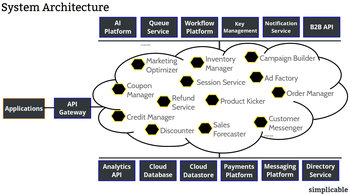
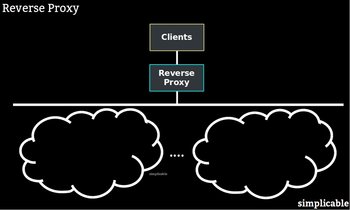
IT architecture has several common variations:Enterprise ArchitectureTop level planning of technology strategy and structures. Infrastructure ArchitecturePlanning and design of IT infrastructure. Often referred to as "technology architecture."Systems ArchitecturePlanning and design of software that automates work.Applications ArchitecturePlanning and design of software that people use.Data ArchitectureDesign of models, processes, policies and standards for managing and using data.SpecialistsIt is common for architects to specialize in a particular domain, technology or architectural approach. For example, an information security architect or cloud infrastructure architect.Output
Architects perform analysis and design to document existing structures, gaps and future structures. Typical outputs are principles, structural specifications, processes, models and standards. These may span areas such as infrastructure, integration, systems, applications, data, information security, risk management, resilience and business structures.Politics
It is a common failure of IT architecture to design worthy structures but to fail to push for their implementation. Architects are most effective when they are fully engaged in the political processes required to improve the structural design of technology. This is particularly true at the level of enterprise architecture that often requires significant authority and influence to implement.Example
An organization has customer data that is replicated in 20+ systems and applications. The data is low quality and inconsistencies between sources is common. The process of updating customer data and maintaining various integration interfaces is expensive and error prone.An enterprise architect designs a single source of truth for customer data and obtains agreement for the solution amongst major stakeholders. The architect is a key member of the project to implement the solution. Enterprise architecture also plays a governance role in making sure that future systems use the single source of truth for customer data as opposed to replicating it as anything more than a disposable cache.| Overview: It Architecture Definition | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The design of information technology at the structural level. | |
Related Concepts | ||