Principles
Data architecture principles are foundational rules that guide the structure, use and management of data. For example, the principle that "data is a shared asset" can be useful for encouraging solution architects to use data repositories that already exist as opposed to replicating things.Standards
Data architecture standards are structures, practices and technologies that an organization adopts to avoid reinventing things for every system, application or analysis. For example, an organization might adopt a standard way to publish and subscribe to data.Structure
Data architecture is the structural design of information technologies for acquiring, storing, using, securing and managing data. A data architecture diagram captures the layers, interfaces, technologies and flows of data. These are typically produced at the organizational, system, application and solution level.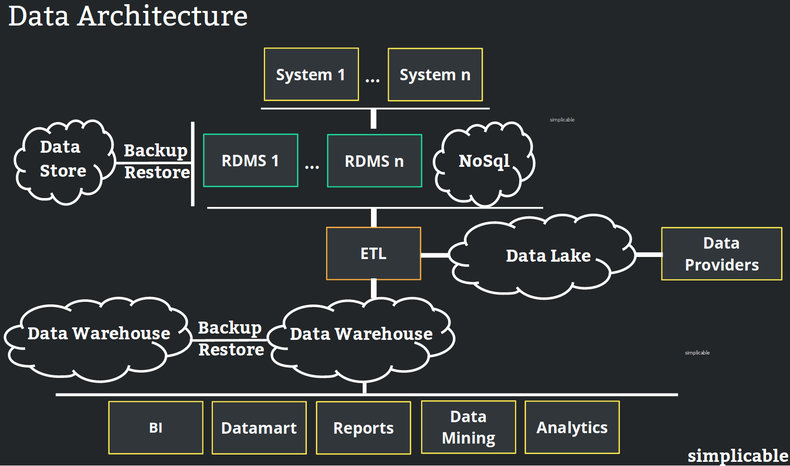
Models
A data model defines the structure of data itself. This includes data entities and relationships between entities.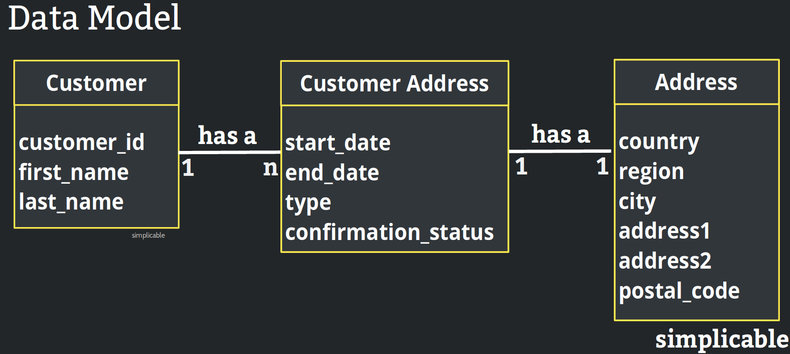
Data Dictionary
A data dictionary is a reference that provides a user friendly overview of data entities, fields, formats, validations and business context. This can be used both by software developers and users. For example, a user who wants to build a report might reference a data dictionary to see what data is available.Patterns
Patterns describe standard ways to acquire, store, transform, share, use, secure and manage data. For example, data architecture may include a sequence diagram that illustrates how to build a report from an organization's data warehouse.Controls
Data controls are roles, responsibilities, processes, procedures and systems for managing data. For example, a data architecture might define how data is encrypted in storage and the processes for managing encryption keys.Integration
Data architecture may include structures and specifications for publishing, consuming, transferring and transforming data.Master Data
Data architecture may define a single source of truth for data entities and methods for using and managing master data.Technologies
The process of defining a data architecture often involves evaluation and selection of information technologies for data storage, analysis, integration, management, security and curation. For example, a data architect may perform a product evaluation as part of the procurement of a extract, transform and load tool. A data architecture document typically provides an overview of selected technologies including their capabilities, limitations and risks.Deployment
A data architecture typically includes a diagram that captures how the architecture is physically deployed to infrastructure. This is similar to the logical data architecture diagram with details of machines, platforms, environments and technologies.| Overview: Data Architecture | ||
Type | ||
Definition (1) | ||
Definition (2) | The structural design of information technologies for acquiring, storing, using, securing and managing data. | |
Related Concepts | ||