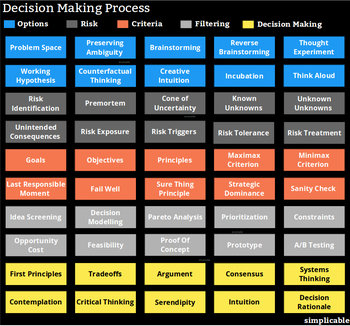
Information Technology
A consultant signs a fixed price contract to develop custom software for $1 million. The project doesn't go well and the firm has spend $1.5 million to date on the project. They consider the cost of giving up, meaning that the client will not pay the $1 million fee. They estimate the project will cost $200,000 to complete. In this decision, the $1.5 million is an irrelevant cost as it is a sunk cost that has already occurred. The relevant cost is the $200,000 required to complete the project to be paid $1 million. As such, the consultant decides to complete the project. It would be a logical error to give up on the project due to consideration of the entire $1.7 million cost.Investing
An investor buys a stock for $30 and it goes down to $3. This results in a loss of $20,000. The investor is tempted to buy more of the stock to try to recoup their losses. It is illogical to allow the cost of past losses to influence the current investment decision. The relevant cost is the current $3 price of the stock and whether this represents a value considering the risks.Innovation
A firm invests $1 billion to develop a new product. During the project it becomes clear that competitors have surpassed the product. The unit cost of the product is higher then the competition and the product can only be sold at a loss given the current pricing environment. The firm requires at least $25 million in marketing costs to launch the product. Decision makers are tempted to launch since they invested significant costs in development. However, the $25 million in marketing costs is the only relevant cost to the decision. The marketing costs will most likely be lost as the product is essentially unsellable. As such, the firm decides not to launch.| Overview: Relevant Cost | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A future cash cost that is relevant to a particular decision. | |
Related Concepts | ||