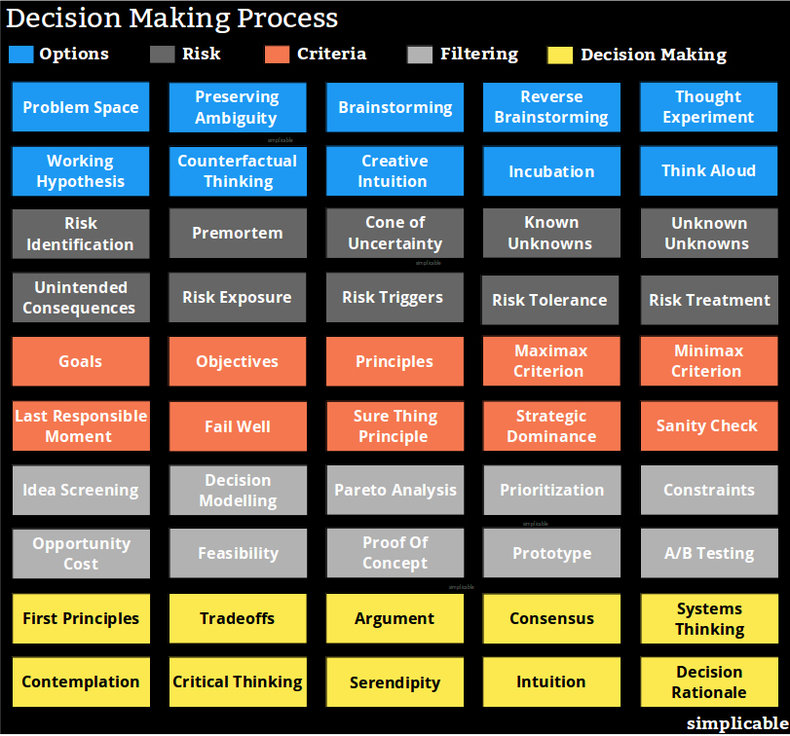
Options
Generate a list of options.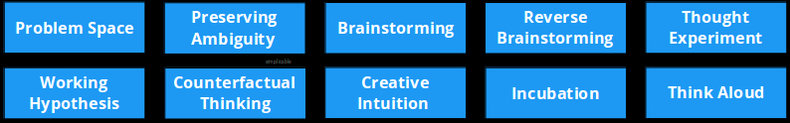
Problem Space
Define the decision in a concise statement or question. This is a delicate step as how you define the decision greatly influences the output of a decision making process. As such, if you're not satisfied with your progress in the middle of decision making, challenge the decision statement itself.Preserving Ambiguity
Preserving ambiguity is the practice of avoiding assumptions and constraints early in the decision making process. This gives creativity a chance to flourish.Brainstorming
The process of allowing ideas to flow out without validation.Reverse Brainstorming
Brainstorming based on a negative question such as "what is the worst decision we could make?" This can be done to stimulate a creative mood or to explore a solution space.Thought Experiment
Modeling complex problems with an analogy.Working Hypothesis
Start making assumptions on a temporary basis in order to explore the solution space. For example, "What if we ...?"Divergent Thinking
The process of thinking broadly and creatively as opposed to trying to find the "correct" answer.Creative Intuition
Avoiding overthinking and listening to your intuition.Incubation
Allowing time to pass while you are working on a decision. The mind appears to work on problems while you are resting or sleeping. For example, you may come up with a good idea after a nap or walk.Think Aloud
Voicing your thought processes in the context of a meeting. As with brainstorming, this allows ideas to flow out.Risk
Assessing risks associated with options.
Risk Identification
List things that could go wrong with each option and estimate their probability and impact.Premortem
Imagine that a proposed strategy has failed and list the reasons why.Cone of Uncertainty
At the onset of a strategy, there may be a great deal of uncertainty that declines with time as you make progress. Decisions can be designed to take small steps that reduce uncertainty. For example, a student considering the cost and commitment of a university education could make a decision to start the first semester to at least give it a try.Known Unknowns
Risks occur because uncertainty exists in all future endeavor. As such, listing out uncertainties is a good starting point for risk analysis.Unknown Unknowns
Things that you don't even know that you don't know. For example, if you know nothing about sailing it is difficult to identify the risks of sailing across an ocean. Unknown unknowns require information that can be difficult to obtain. As such, they should be avoided where possible. For example, an option to take certification training for sailing caries less unknown risks than sailing across an ocean.Unintended Consequences
Designing options to avoid unintended consequences. This generally involves designing options based on known approaches for which consequences are well understood. For example, solving an environmental problem by designing a new chemical to put into the ocean might have unintended consequences as you're playing with ecosystems that are too complex for anyone to fully understand.Risk Exposure
Calculating the risk exposure for decision options.Risk Triggers
Identifying the conditions that cause a risk to occur.Risk Tolerance
Thinking through your risk tolerance related to the decision. For example, are you willing to take losses or are you looking for the safest route?Risk Treatment
Developing ways to avoid, mitigate, transfer or reduce risk.Criteria
Criteria are principles, guidelines or rules that you use to make a decision.
Goals
Criteria are typically based on your goals. For example, a student considering a career choice might have criteria such as "will this make me happy?" and "will this pay my bills?"Objectives
Objectives are meaningful steps towards a goal. If the goal of a business is to achieve revenue an objective might be launching a product. Criteria are often based on objectives. For example, "can this be launched by September?"Principles
Principles are often very useful in simplifying decisions. For example, an individual who adopts the principle that they will not work for an organization that harms the environment.Maximax Criterion
Choosing the option that maximizes your potential gain without considering risk.Minimax Criterion
Minimizing the risk of a worst-case scenario. For example, an investor who establishes the criteria that they don't want to lose money on an investment.Last Responsible Moment
The criteria that you avoid doing things or committing to things too early. For example, a startup that wants to avoid any capital investments unless they are absolutely required to complete work this month.Fail Well
The principle that a decision not have any tragic consequences if it fails.Sure Thing Principle
The principle that decisions don't have to consider any risks that wouldn't impact your decision anyway. For example, a student who is considering switching from arts to engineering decides they don't care about the risk that they might struggle to pass the required math courses. This is a means of narrowing a decision to what really matters to you.Strategic Dominance
Strategic dominance is a choice that is your best option no matter what the competition might do. This is another type of simplification where you can often drop guesses about what your competition is going to do if it doesn't really matter to your choice. For example, a hockey team that is behind by one goal decides to pull their goalie for an offensive player in the last minute might decide this is their only option whatever the strengths of the other team.Sanity Check
Back to basics criteria such as "does this plan have any chance of actually working?"Filtering
Decision making is an optimistic process of generating as many options as possible followed by a pessimistic process of dropping as many options as possible.
Idea Screening
A quick process of dropping options that have obvious flaws such as being too risky or infeasible.Decision Modelling
Developing formal models for choices such as risk/reward profiles for stocks.Pareto Analysis
Pareto analysis is based on the idea that often 20% of the work you do brings 80% of your results. It might be described as a filter that removes options that involve too much work for too little reward.Prioritization
Prioritizing your decision criteria such as goals. For example, ranking the two criteria "I want to avoid stress" and "I want a promotion" can help to filter options.Constraints
Imposing constraints to filter options. For example, a job hunter who decides they don't want to relocate.Opportunity Cost
Consider the opportunity costs of options.Feasibility
Develop experiments that validate the feasibility of options.Proof Of Concept
Develop tests that validate concepts related to options. For example, a poster that depicts an idea for a product can be used to validate the idea with stakeholders.Prototype
When you are left with a handful of strong options it can be useful to start to test them in lightweight prototypes. For example, an architect that builds paper prototypes of two design options.A/B Testing
The process of testing two options against each other in the real world to gather data.Decision Making
The process of making a decision from the small list of options that survived your filters.
First Principles
Test options against things that you absolutely know to be true. For example, a design director who immediately rejects any options that aren't visually balanced.Trade-offs
List out the trade-offs for options.Argument
Social processes such as a good argument can improve the quality of your decisions.Consensus
Generally speaking, consensus results in poor quality decisions because consensus is a process of social compromise as opposed to rational thought. However, consensus is often required due to political realities and is a common way to make decisions.Systems Thinking
An approach to thinking that attempts to consider all the complexities of a situation.Contemplation
Intensive consideration by an individual who allows natural thought processes to flow.Critical Thinking
Systematic analysis of the decision.Serendipity
A sudden and seemingly spontaneous insight that occurs after a long process of thinking. Serendipity is unpredictable and can be rare.Intuition
Using your basic emotional feel about a decision.Decision Rationale
Documenting the reason for a decision. This process can be helpful to make the decision as looking at a decision rationale often leads to a change of mind.| Overview: Decision Making Process | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A set of steps that can be used to make decisions. | |
Related Concepts | ||