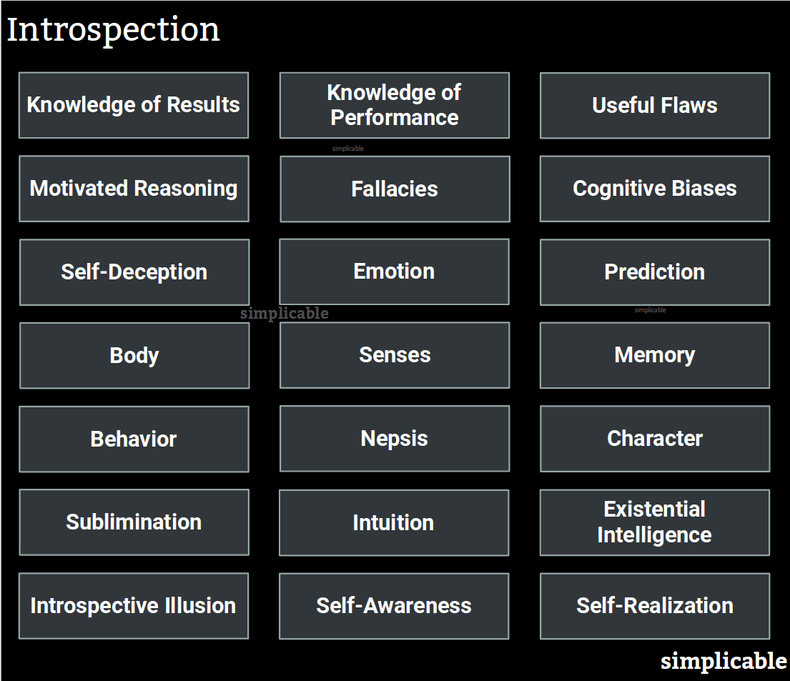
Knowledge of Results
The ability to look at the real world results of your thought processes and behavior. For example, an individual who notices that they often complain and that people appear to find this boring.Knowledge of Performance
The ability to judge your mental and emotional performance independently of real world results. Knowledge of performance is associated with being able to see positive performance despite failure and negative performance despite success. For example, being able to see that you behaved nervously in a job interview despite getting the job. Alternatively, an individual may be able to see that they performed reasonable well in a job interview that didn't progress to an offer.Useful Flaws
In many cases, an character flaws can produce positive results. For example, some individuals may find that overconfidence helps them to face stress and challenges. Recognizing your need for coping mechanisms is an element of introspection whereby you may forgive your character flaws where they are useful to you.Motivated Reasoning
Motivated reasoning is the use of logic to support arguments for what you want. Although supported by logic, motivated reasoning often produces poor choices because it is completely driven by your emotions as opposed to rational thought. For example, an individual may decline a vacation with family due to a fear of flying but rationalize the decision with the logic that they are too busy with work. Motivated reasoning is difficult to detect by introspection as it is designed to fool you into thinking you're being logical.Fallacies
The ability to spot flaws in your own logic. Fallacies can be non-obvious such that they require significant intelligence to detect.Cognitive Biases
Spotting your own cognitive biases and working to overcome them.Self-Deception
The ability to detect and foil attempts to deceive yourself. For example, a gambler who recognizes that a good luck omen is not actually going to improve their chances of winning.Emotion
Emotions are mental states that color your thoughts. Introspection involves understanding your emotions and how they are impacting your thoughts and behavior. This can also involve understanding the sources of emotion and how to overcome negative or unproductive emotion. For example, a student who feels depressed during exams who understands that this is due to the pressures of studying and that this feeling will soon pass.Prediction
Being able to predict how future events will influence your thoughts and emotions. For example, being able to predict how well you will handle a stressful situation such as a political battle at work. Accurate predictions of emotions can help you avoid taking on things you aren't yet ready to handle.Body
Developing an understanding of your own body. For example, noticing that one food appears to give you energy while other makes you feel sluggish.Senses
Being mindful and observant of your senses. For example, noticing that your eyesight is worse in the morning for some reason.Memory
Understanding your memory including factors such as reliability and rosy retrospection. For example, an individual who recognizes that a distant memory is foggy and perhaps the realities of the event differed from their recollection.Behavior
Being able to see your own behavior as a rational and independent third party would see it. For example, noticing that you came off as unfriendly towards someone.Nepsis
A state of being awake, alert and watchful of your own behavior in order to prevent poor behavior.Character
The ability to understand your mental and moral qualities that distinguish you as a person. For example, an individual who recognizes they have a quick temper who takes care to control such tendencies.Sublimination
Detecting urges that are anti-social and redirecting these energies into social pursuits. For example, redirecting anger to produce positive competitive energy.Intuition
Intuition is high speed judgement provided by the unconscious such that you can not directly understand how it was formulated. Individuals may learn to trust certain types of intuition as they find that such judgements have value. Alternatively, an individual may recognize that certain intuitive thoughts are simply motivated reasoning triggered by emotions such as fear or desire.Existential Intelligence
Developing an understanding of your self and its place in the universe. For example, meditating by silencing your internal monologue to experience your consciousness without words. Existential intelligence is also known as spiritual intelligence.Introspective Illusion
A common cognitive bias whereby people overestimate how well they know themselves. For example, an individual may predict with certainty how they will feel in a particular situation but then experience a completely unexpected series of emotions when the situation actually occurs.Self-Awareness
A state of highly developed introspective knowledge whereby you understand your character, thought processes, behavior and emotions reasonably well.Self-Realization
A state of understanding your potential and purpose as a person and taking brave steps to realize this potential.| Overview: Introspection | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An individual's ability to examine their own thoughts, emotions, motivation, behavior and character. | |
Related Concepts | ||