
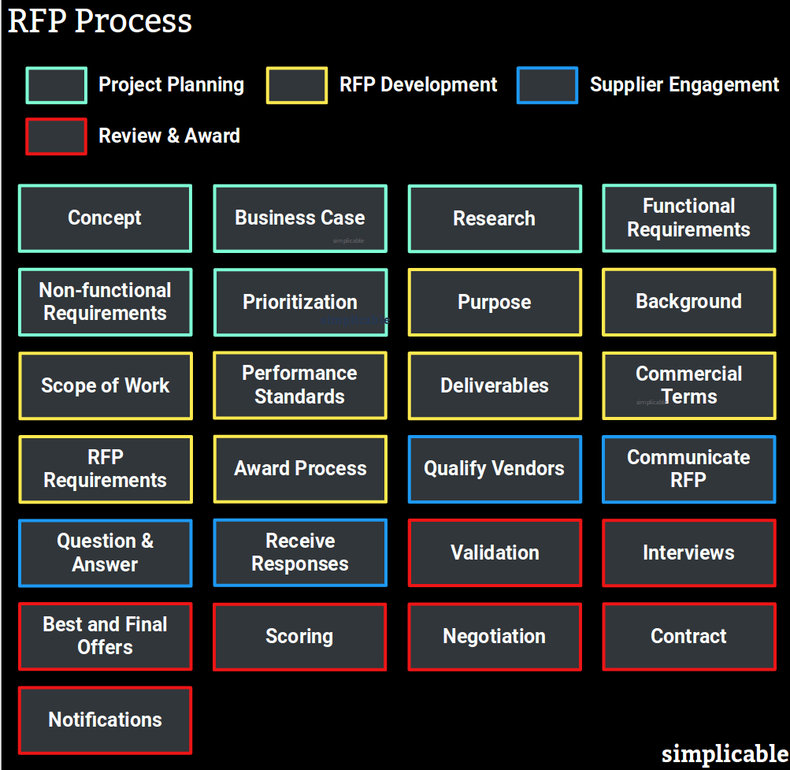
Project Planning
Project planning is the process of developing a strategy, business plan and requirements. This defines your business needs from which you may identify a list of supply contracts that require an RFP or RFQ.Developing the foundational idea for a project. | |
Building a case to invest in a project including financial projections such as return on investment. | |
Research | Data gathering such as market research or a feasibility study. |
Developing functional requirements such as user stories. | |
Developing non-functional requirements that define the quality of deliverables. | |
Prioritization | Selecting the requirements that will be implemented and those that will go into a backlog. |
RFP Development
Drafting the RFP to document your needs and the information you are seeking from suppliers.Purpose | Summarizing what you need and why. |
Background | Provide business context for the request. |
Scope of Work | List the requirements that apply to the RFP. It is common to ask vendors to comment on each requirement to explain how it will be satisfied. |
Performance Standards | Develop supplier performance standards and define how performance will be managed. |
List the expected deliverables and define acceptance criteria for each. | |
Commercial Terms | List the commercial terms being offered including details of payments, incentives and penalties. An initial contract may be attached to the RFP. |
RFP Requirements | Specify what is to be included in RFP responses. |
Award Process | Develop the award process such as a system of scoring responses and a schedule. |
Supplier Engagement
Communicate the RFP to vendors and clear up any questions and issues.Qualify Vendors | Seek out vendors and perform an initial evaluation to qualify those who wish to participate in the RFP. |
Communicate RFP | Send the RFP out. Some organizations, such as government departments, may be required to publish RFPs to the public. In other cases, an RFP is confidential. Security measures and legal agreements may be required to ensure confidentiality. |
Question & Answer | Hold Q&A sessions with each vendor. |
Receive Responses | The process of receiving responses from vendors. |
Review & Award
Evaluate RFP responses, select a preferred vendor, negotiate a contract and inform the other vendors that the contract has been awarded. If a contract can't be negotiated with the preferred vendor, the process may be repeated with the vendor in second place.Validation | A review of each RFP to confirm it is at an acceptable level of quality. |
Interviews | Interviews with each vendor to obtain any information that is unclear or missing from the RFP. |
Best and Final Offers | Ask vendors to submit their best and final price. |
Scoring | Score each RFP using the scorecard or criteria defined in your award process. Select a preferred vendor and rank all others. |
Negotiation | Negotiate terms and price with the preferred vendor. If a contract can't be negotiated you may open up negotiations with other vendors in your ranked list. |
Contract | Finalize the contract. |
Notifications | Notify other vendors that the contract has been awarded. |
| Overview: RFP Process | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The process of defining business needs, requesting detailed bids from suppliers and awarding a contract. | |
Related Concepts | ||




























