Networking Infrastructure
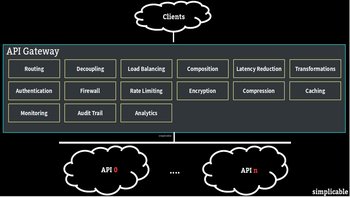
The network infrastructure devices that provide network services such as routing communications. This includes devices such as routers, switches, hubs, bridges, gateways, proxies and load balancers.Servers
Host computers that provide services on a network such as a webserver that provides web pages.Virtual Hosts
It should be noted that nodes can be virtual entities. For example, a single physical machine may host dozens of virtual machines with each acting as a server with its own network addresses.End-points
The clients that use network services that are directly connected to a network such as a laptop or mobile device.Local Nodes
Devices that aren't connected to the internet directly are not internet nodes but they may be considered nodes of your local area network. For example, a printer that isn't connected to the internet but is connected to your office or home network.Personal Nodes
A device that isn't connected to the internet directly that networks with your personal devices. For example, a Bluetooth device that you connect to a tablet. Such a device isn't an internet node but is a node within the context of your personal area network.Overlay Networks
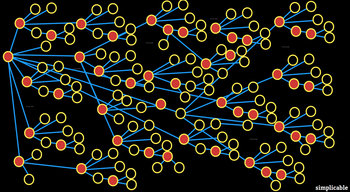
Overlay networks are virtual networks built on top of other networks, usually the internet. Every connection point that participates in an overlay network is considered a node. For example, a peer to peer network built on top of the internet using specialized encryption and networking protocols may consider each peer a node.| Overview: Node | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A connection point that participates in a network. | |
Related Concepts | ||