Internet
A global network of interconnected networks. The largest network on the planet with about 4 billion users.Intranet
The internal web sites of an organization deployed to a private network.Extranet
An internet website that is restricted to authorized users. For example, a site that is only for employees, partners or customers.Private Network
A network that is secured such that outside devices can't connect.GAN
A global area network, or GAN, is a network that connects multiple locations in different countries.WAN
A wide area network, or WAN, is a network that connects multiple locations in different regions of a country.MAN
A metropolitan area network, or MAN, is a network that connects multiple locations in a city.CAN
A campus area network, or CAN, is a network that connects multiple locations in the same area such as a university or corporate campus.LAN
A local area network, or LAN, is a network that connects multiple devices at the same location such as an office network.Home Network
A local area network that is shared by members of a household.Personal Area Network
A network that is established by an individual for their personal use. Typically connects electronics such as computers, mobile devices, televisions, printers, data storage and media devices.Overlay Network
A network that is build on top of the internet using encryption and specialized networking protocols.Darknet
Another term for overlay network.Deep Web
A term for any web pages that are connected to the internet but that aren't indexed by search engines, typically because they require authorization to view.VPN
A virtual private network, or VPN, is an overlay network that is used to extend a private network over the internet. For example, a VPN can allow an employee working at home to connect to an office LAN.URL
A human readable address that is used to locate resources on the internet.IP
A machine readable address that is used to locate resources on the internet.IPv4
The original format of IP addresses that includes the strings 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. This is less than 4.3 billion addresses. As such, these are in short supply.IPv6
A successor to IPv4 with a length of 128 bits. This allows for 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 addresses.DNS
A global hierarchical decentralized service that is used to map URLs to IPs.Host
A machine or device that is connected to a network.Hostname
The part of a URL that maps to an IP such as www.google.com.Domain Name
The part of a hostname that is owned by an individual or organization such as google.com.Host File
A file on most operating systems that allows you to override the IP returned by DNS. This can be used to test a service from your local machine.HTTP
Hypertext transfer protocol, or HTTP, is a data communication protocol for web content and services.Web
The web, or world wide web, is a term for the documents published on the internet that are accessed with the HTTP protocol using URLs.SMTP
Simple mail transfer protocol, or SMTP, is an internet protocol for email transmission.TCP
Transmission control protocol, or TCP, is a foundational communication protocol that underlies many internet-based networking technologies.SSL
Secure socket layer, or SSL, is a security protocol for cryptographic data communication.TLS
Transport Layer Security, or TLS, is a security protocol for cryptographic data communication. Essentially the more modern version of SSL.IPsec
A secure networking protocol for mutual authentication based on cryptographic keys.Compression
The conversion of data to a smaller format.Cryptography
Cryptography is the science of coding data to prevent unauthorized access.Encryption
The process of encoding data using cryptography.Cryptographic Key
Data that is used to lock or unlock encrypted data.Public Key
A cryptographic key that is openly published. Used to encrypt data for an entity that holds the corresponding private key.Private Key
A cryptographic key that is kept secret. In some cases, a private key has a corresponding public key that allows anyone to encrypt but only those who hold the private key to decrypt.SSL Certificate
A means of publishing the information required for SSL and TSL. Includes a public key and information about the organization that owns the corresponding private key.Certificate Authority
The services that are responsible for publishing SSL certificates. You need to trust these organizations as they are important to your security on the internet.Server
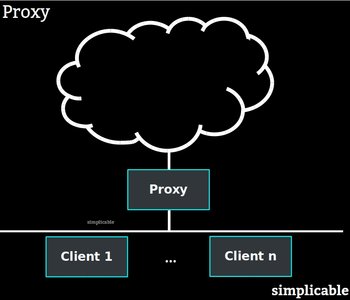
A machine that provides content or services.Client
A device that uses content or services. A device can be both a client and a server.P2P
A decentralized model of networking whereby clients interact without a central server coordinating things.Request/Response
A model of networking whereby clients make requests to servers that respond.Push
A model of networking whereby servers initiate exchanges with a client.Synchronous
A mode of communication where a client makes a request and waits for a reply on the established connection.Asynchronous
A mode of communication where a client makes a request but doesn't wait for the reply on the established connection. This is done for efficiency so that the client can work on other things while waiting for the reply.Web Browser
A client for accessing a broad array of open technologies.Mobile App
A client that is specifically constructed for a particular application to run on a particular mobile device.Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a class of technologies for using many physical machines for a single operation, service, system or application.CDN
A content delivery network, or CDN, is a service for delivering files such as video, images and static html from a location that is geographically close to each request.Edge Computing
A class of technologies for performing computation at a location that is relatively close to each client. For example, a mobile app in Tokyo that connects to a server in Tokyo.Latency
The time it takes a message to travel from origin to destination.Bandwidth
The amount of data that can be transferred in a period of time by a connection, device or technology. A theoretical limit of the technology set up.Throughput
The actual amount of data successfully transmitted in a period of time.Internet Backbone
A high capacity data route that connects large networks of the internet.Router
A device that directs traffic on a network by forwarding data to a specified address.Switch
A device that connects devices to a network by forwarding data to a specified address.Hub
A device that connects devices to a network by forwarding data to every device connected to it. This allows all devices connected to the hub to see all data. Generally speaking, this isn't as efficient or secure as a switch.Ethernet
A family of standards for wired networking.Wifi
A family of standards for wireless networking.Firewall
A network security device that monitors and controls network traffic based on a set of rules.Intrusion Detection System
A security device that monitors a network or host for malicious activity or policy violations.| Overview: Networking | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The practice of linking computing resources to provide systems, services, applications, data processing, analysis and communication. | |
Related Concepts | ||