Client & Server
Keep alives are used in networking to maintain connections between a client and a server. Establishing a connection involves overhead such as a handshake protocol. As such, reestablishing a connection for every message can be extremely expensive and slow. Leaving connections open generally results in faster networking but this eats up resources such as memory. For this reason, it is common for operating systems to be configured to limit the total number of connections that can be opened at one time. In order to clean up underutilized connections, a timeout is set. A keep alive is used to prevent this timeout by informing the server that the client is still planning to send more messages. For example, a web browser may send a keep alive to a web server as long as a web page remains open.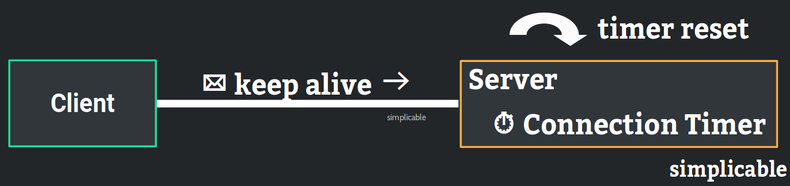
Network Layers
Networks operate on 7 layers known as the application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link and physical layer. Each layer builds functionality on top of the layers below it. It is possible for communication over a network to occur at each layer and for each layer to maintain a connection that may be persisted. Timeouts and keep alives may apply to these connections at each layer.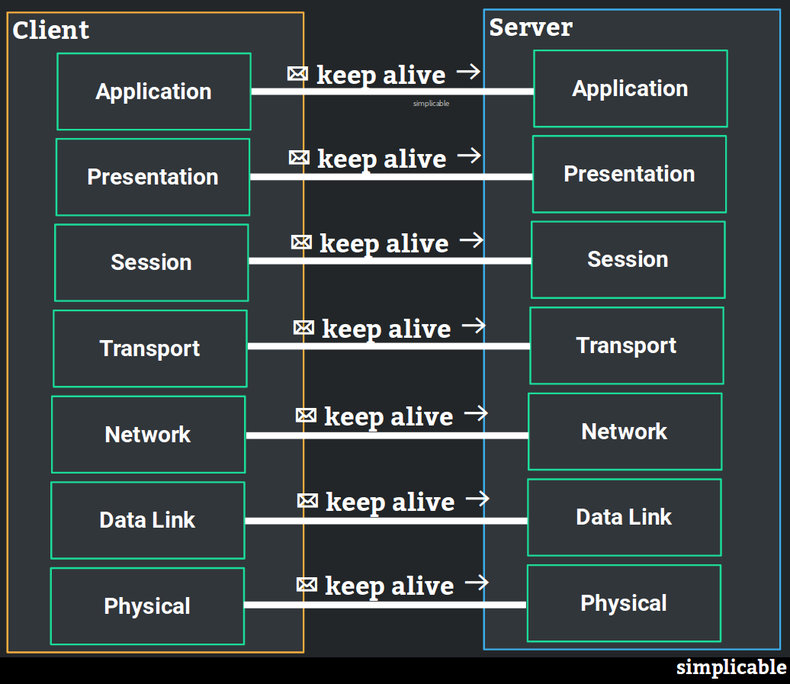
Web Layers
In practice, every layer may not have connections that expire that require a keep alive mechanism. For example, it is common for keep alives to occur at two layers between a web browser and web server: the session layer (TSL or SSL encryption) and the transport layer (TCP).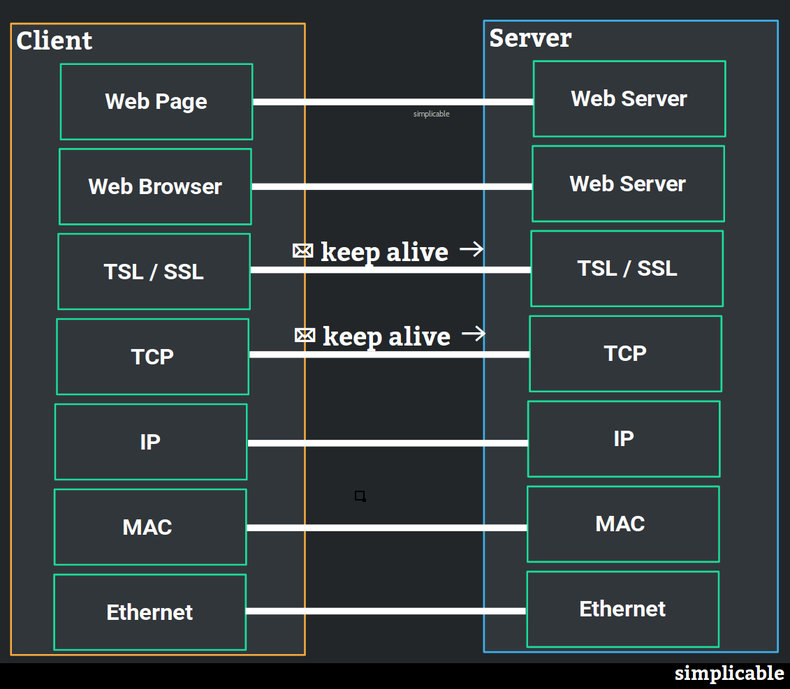
Proxies
A proxy is a service that act as intermediary between a client and server. For example, a VPN service is a proxy that establishes an encrypted connection with a client and then acts on behalf of the client to make network requests. Connections between a client and a proxy may be set to expire and the client may send keep alives to prevent this from occurring. In the case of a VPN client, ping requests may be sent to indicate to the server that the client is still present.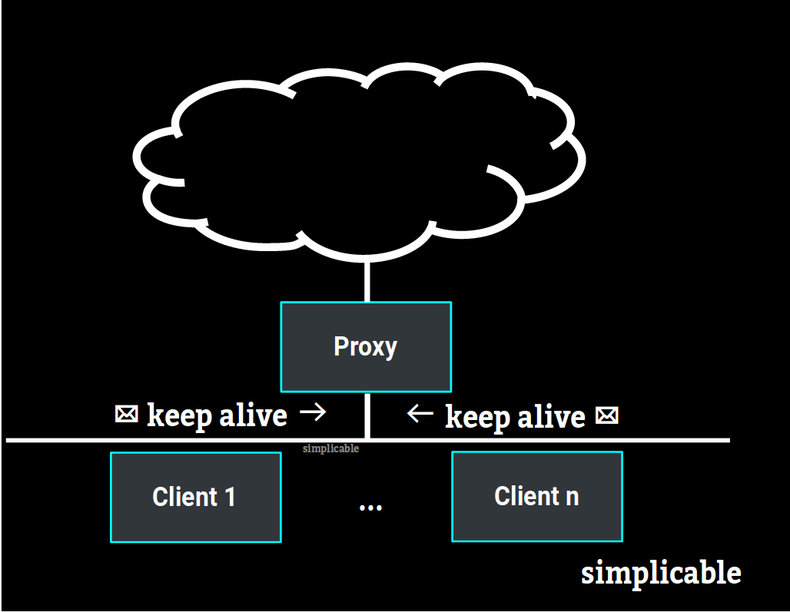
Reverse Proxies
A reverse proxy acts as an intermediary between a server and a client. For example, a load balancer handles connections with clients on behalf of servers. Such devices may maintain both connections with clients and servers with timeouts and keep alives on each connection.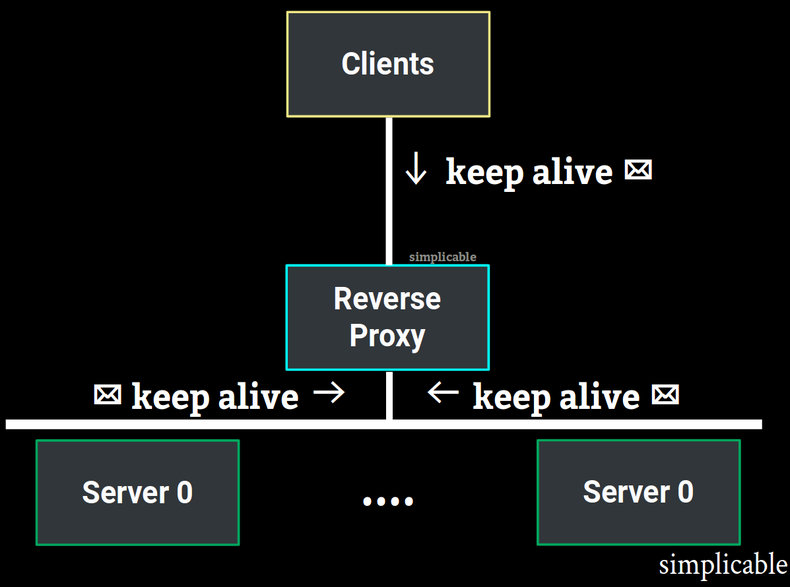
Other Keep Alives
Keep alives may be used to keep other computing resources from being released. For example, a keep alive may be used to prevent hardware from going to sleep due to power management features of a device.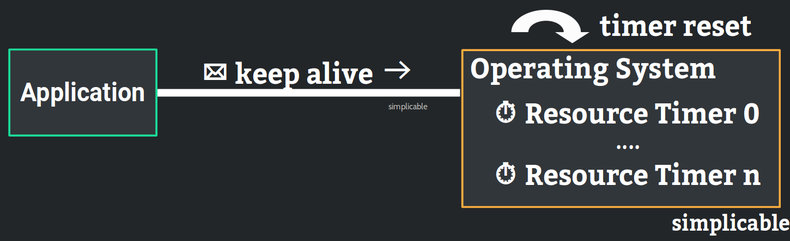
| Overview: Keep Alive | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An event that prevents a timeout. | |
Related Concepts | ||