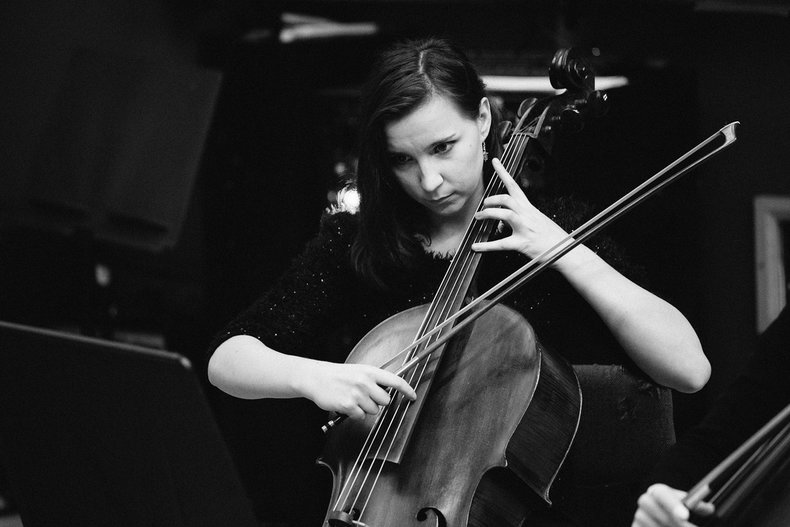
1. Music
The skill and ability required to master a musical instrument.2. Strategy
Strategy tends to be difficult to automate or document with unbreakable rules.3. Emotional Intelligence
Reading and using emotion to achieve results such as influence is a difficult to acquire skill that appears to come naturally to some people.4. Problem Solving
Problem solving techniques can be documented and taught but a vast difference in speed and ability to solve complex problems exists between people that resists knowledge transfer.5. Aesthetics
A sense of aesthetics tends to be a personal thing that is difficult to express with precision. Skills related to aesthetics such as art and design are typically considered tacit knowledge.6. Architecture
Architecture is the design of structure and form. Its mastery is thought to be largely experience-based including factors such as culture and artistic sense. It's also associated with abilities such as spatial intelligence.7. Intuition
Intuition is a type of thought process that produces analysis almost instantaneously. It is important to situations that require decisions and actions in a fast moving environment such as driving.8. Sports
Physical abilities such as sports are a type of tacit knowledge that are difficult to codify.9. Decision Making
Decision making has an art to it. It is widely accepted that years of experience in a particular area or domain tend to improve decisions.10. Language
Language skills such as intonation and pronunciation are impossible to learn from a book. Full immersion is typically required to master a language.11. Know-how
Know-how is a general term for business knowledge related to processes and practices. In many cases, know-how is remarkably difficult to transfer from one organization to another. For example, a process that is fully documented may work at one organization but not another. Such failures are commonly attributed to tacit knowledge that exists within the corporate culture and skilled employees of an organization.| Overview: Tacit Knowledge | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Knowledge that is difficult to articular, communicate and acquire. | |
Antonyms | Propositional KnowledgeEmpirical Knowledge | |
Related Concepts | ||