|
| |
Fine particulate air pollution, causes about 3% of mortality from cardiopulmonary disease, about 5% of mortality from cancer of the trachea, bronchus, and lung, and about 1% of mortality from acute respiratory infections in children under 5 years, worldwide.- World Health Organization, 2005 Particulate matter is a soup of microscopic particles suspended in the air that includes sea salt, dust, cement dust, fly ash, oil smoke, smog, tobacco smoke and soot. It occurs as a result of natural processes such as volcanoes, forest fires and sea spray. Human processes such as burning fossil fuels and factory emissions also create significant amounts of particulate matter. Health ImpactParticulate matter has a variety of impacts on human health and was estimated to cause 3.22 million deaths globally in 2010 as reported in the global burden of disease collaboration1. The health effects of particulate matter can be highly localized. For example, exposure to traffic exhaust causes around 7.4% of heart attacks according to one 2011 study2. The amount of particular matter in the air differ widely from one area to the next based on factors such as national and local environmental regulations.|
Type | | Definition | A soup of microscopic particles suspended in the air due to both natural processes such as volcanoes and human processes such as burning fossil fuels. | Also Known As | Atmospheric particulate matterParticulates PMPM2.5PM10 | Related Concepts | |
Sustainability
This is the complete list of articles we have written about sustainability.
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
A few examples of environmental issues.
An overview of greenwashing.
A definition and brief overview of global warming.
The definition of environmental justice with examples.
A list of countries ranked by CO2 emissions per capita.
Nations ranked by total CO2 emissions
A list of major social issues.
A list of common local issues.
A list of common community problems.
A list of common environmental problems.
An overview of existential risk.
An overview of the precautionary principle.
A definition of comparative risk with examples.
The common types of energy efficiency.
The definition of external stakeholder with examples.
Common examples of an economic bad.
The definition of win-lose with examples.
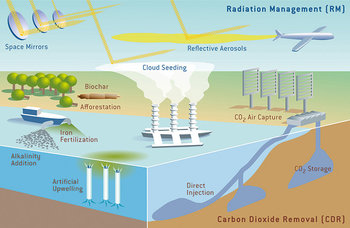
An overview of climate engineering.
Why carbon soil is important.
TrendingThe most popular articles on Simplicable in the past day.
Recent posts or updates on Simplicable.
Site Map
References(1)A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010.(2) Nawrot, Tim S; Laura Perez; Nino Künzli; Elke Munters; Benoit Nemery, 2011. "Public health importance of triggers of myocardial infarction: a comparative risk assessment"
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|