Economic Failure
The value of a free and open market is its ability to efficiently allocate resources. Economic failure is when a market allocates capital, labor and other resources inefficiently. For example, if everyone suddenly decided that volleyballs were going to be very valuable to the future and invested large scale resources into volleyball production, this could result in an oversupply of volleyballs that far exceeds demand.Irrational Exuberance
Irrational exuberance is over-investment caused by investor behavior such as a fear of missing out. This can cause money to flow to popular companies or assets quickly and then suddenly reverse. This is inefficient as causes companies to over-expand and then suddenly retract. For example, the dot com bubble of 1997 to 2001 caused large scale waste as many technology companies received excessive funding that didn't produce much value.Information Asymmetry
Markets are based on the idea that buyers and sellers have equal information. If one side knows more than the other, inefficiencies can result. For example, if a company CEO exaggerates the current capabilities of a firm or hides risks, this can cause money to flow to the firm that ends up being wasted as risks known only to insiders become expensive problems.Anti-Competitive Practices
Anti-competitive practices can cause competition to breakdown resulting in an inefficient market. For example, if all employers make employees sign restrictive agreements that make it difficult for them to change jobs, this could damage the efficiency of a labor market.Cronyism
Cronyism is the extension of unfair economic advantages to friends and allies. For example, a government that builds more infrastructure than a nation requires because construction companies fund the political campaigns of policy makers.Closed Markets
Closed markets such as transactions between insiders. For example, a company insider who buys assets from a firm with no competition.Technical Failure
Technical failures such as a digital market that is altered by an information security incident.Market Manipulation
Markets that are unfair in some way. For example, a market that gives advanced technologies an advantage over most market participants. This can discourage participation and make markets less open.Excess Burden
A market that becomes uncompetitive due to excessive taxation or administrative burden. This may affect small firms more than large, leading a lack of lively competition.Externalities
An externality is a cost or benefit that isn't reflected in market prices. For example, a factory that sells widgets for $1 that each result in $40 damage to the environment due to the manufacturing process. Reflecting the cost of environmental impact in the cost of goods can be achieved with markets such as cap and trade that places a limit on environmental damage that can be traded by firms who need to pollute to produce a good.Summary
Market failure is any situation where markets produce less value than is possible.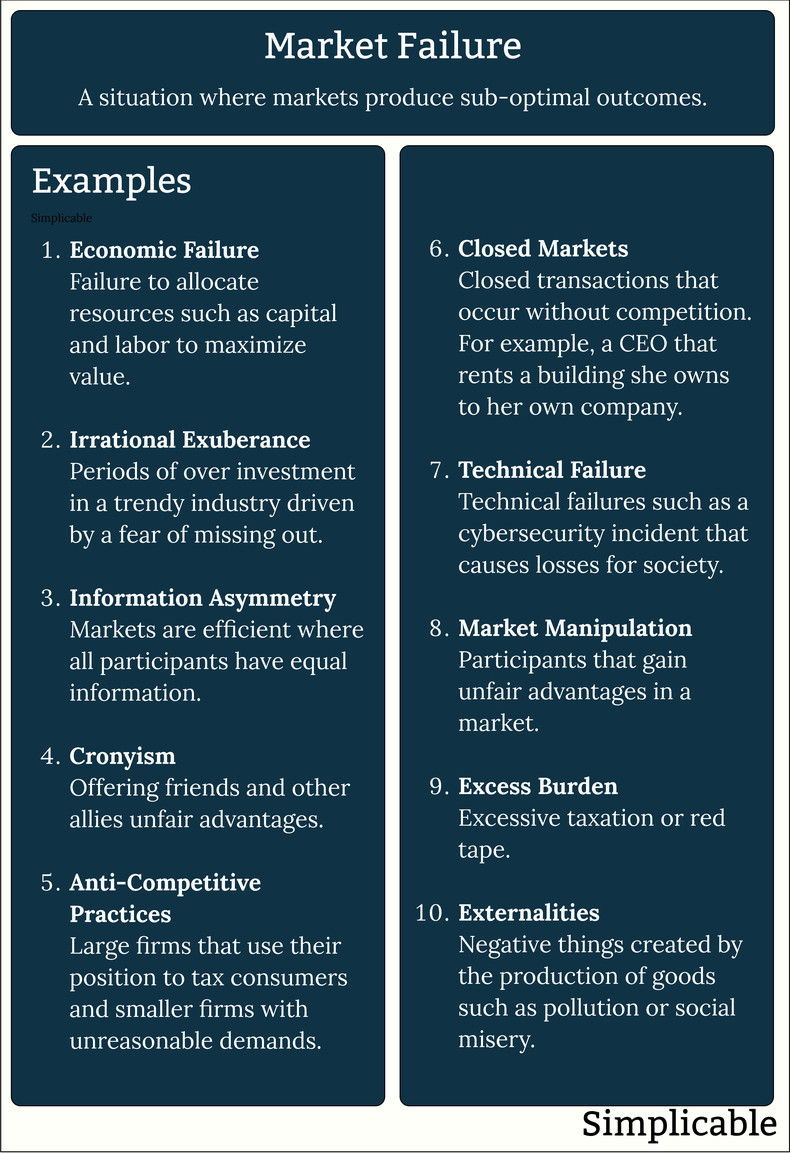
| Overview: Market Failure | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Markets that produce suboptimal outcomes on a global or national basis. | |
Related Concepts | ||