Inherent Risk
An inherent risk is the risk of material misstatements due to fraud or incompetence. In the context of an audit, this is a risk of misstatements in the audit itself.Control Risk
The risk that internal controls are missing or fail. For example, transactions that aren't verified.Detection Risk
The risk that misstatements aren't detected by the audit process.Governance Risk
The risk that governance bodies will fail to act upon risks and misstatements reported in an audit.Residual Risk
Residual risk is the risk that remains after you make an effort to manage risk. In the case of an audit, this is the sum of the risks above.Notes
Inherent risk is often defined in creative and indirect ways because nobody wants to mention fraud or incompetence. For example, "the risk that would occur without controls."Audit Risk
Audit risk is the potential for an audit to fail to detect issues. This is closely related to inherent risk, the potential for material misstatements in financial reporting.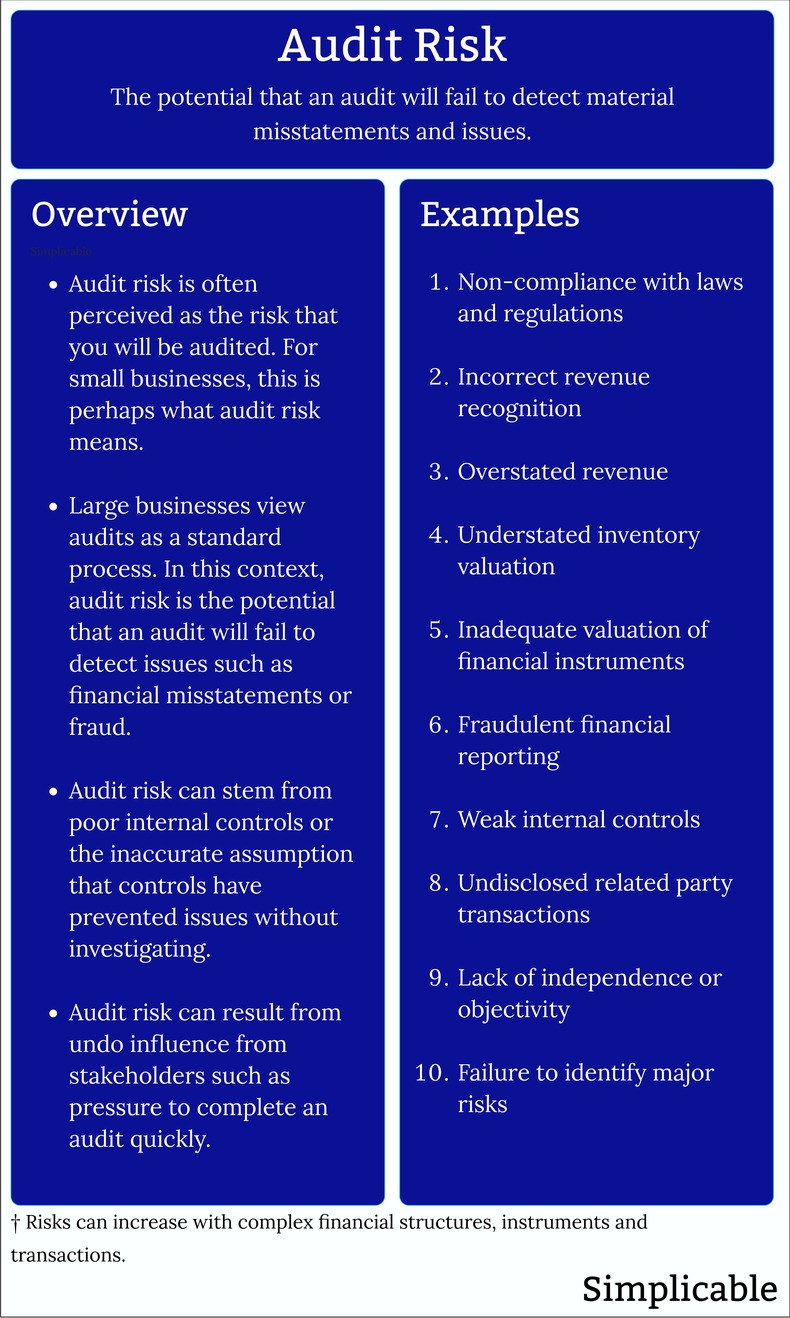
| Overview: Audit Risk | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The probability of losses due to an auditor's failure. | |
Related Concepts | ||