|
| |
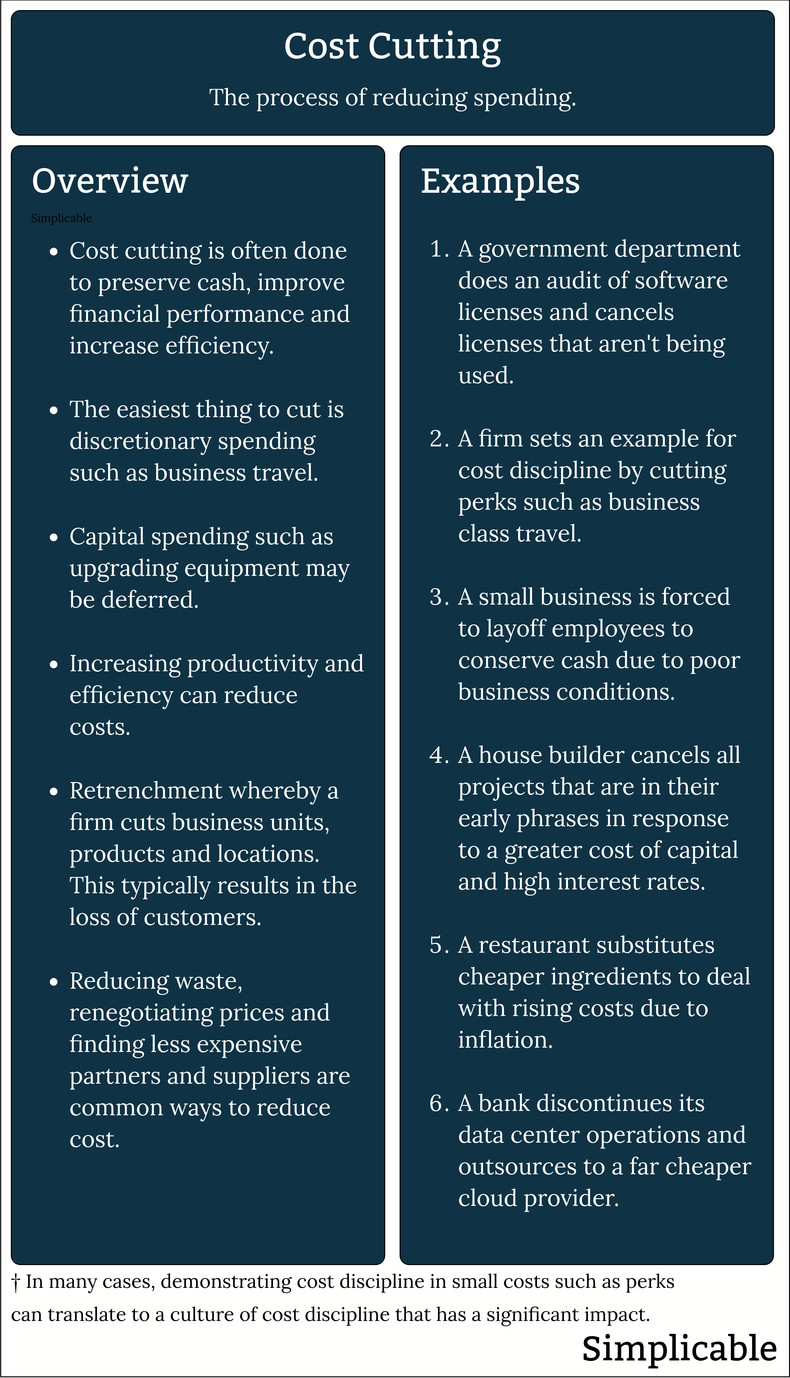
Cost cutting is the process of reducing spending. This is often done to improve net revenue or to preserve cash. Cost cutting may be implemented as a long term controlled strategy. Alternatively, cost cutting can be a sudden and urgent activity driven by changing financial conditions, prices, costs and competition. The following are common examples of cost cutting.
Discretionary SpendingDiscretionary spending is any expense that is easy to defer or avoid. Common examples include business travel, events and training. In any urgent cost cutting scenario, all discretionary spending is typically halted or carefully examined with a measure such as return on investment. For example, a firm may allow sales teams to continue to travel in economy but freeze all travel that isn't directly related to revenue generation.
Capital SpendingCapital spending such as developing new software and buying new machines is often easily deferred. For example, a firm may freeze all new IT projects, park inflight projects and restrict changes to IT systems.Productivity is the amount of value produced in an hour of labor. In the long term, productivity can be increased with automation, training and tools. In the short term, it can be increased with layoffs if an organization has employees who don't produce much value. In many cases, layoffs hit middle managers who are disconnected from the urgent revenue and operational functions of a firm. For example, a manager who mostly creates obscure documents and reports that are far from critical may be at risk of layoff in a cost cutting cycle.Efficiency is the amount of output you get for a unit of input. Improving efficiency is a basic type of cost cutting. For example, a taxi driver who spends 21% of their revenue on fuel might reduce this to 5% by leasing an electric vehicle.A firm may cut entire business capabilities to reduce overhead costs. This can include any area that doesn't directly produce revenue or deliver services that are essential to the survival of a company such as accounting. For example, a firm may cut entire business capabilities in human resources such as recruiting, career planning and diversity management in a time of severe financial constraints. In many cases, a business capability that feels critical and important produces little impact when it is cut as long as it is not directly connected to revenue and operations.Outsourcing a business function that you view as non-core can quickly reduce costs. For example, a manufacturer of organic cosmetic products finds it can dramatically reduce costs and improve quality by manufacturing at the bulk level and outsourcing packaging to a contract packaging partner.WasteReducing waste both in terms of physical waste and wasted effort. For example, an office policy of turning off air conditioning when no one is in a room. SourcingPushing suppliers for lower prices and changing to cheaper versions of things. For example, an ecommerce company that is able to reduce computing costs by 40% by switching cloud providers.Redesigning products and services to cost less. For example, a snowboard manufacturer that develops a board with a bamboo wood top and stainless steel bottom that is competitive with more expensive carbon fiber materials.Reducing product, service or customer experience quality can dramatically reduce costs in the short term but may be a terrible long term strategy. For example, a restaurant that cuts costs with lower staffing levels, smaller portions and lower quality ingredients will soon see a wave of bad reviews that impact revenue. In some cases, firms with extremely strong brand names get away with cutting quality for years such that it appears to be an effective strategy. However, this is often a reflection of how much the brand was originally worth such that the reduction in quality is destroying brand equity that is difficult to measure.Firms are often stuck paying license fees and maintenance costs for software and hardware that is beyond its useful life. This is typically due to integrations and process dependencies that make it difficult to remove anything from a technology environment. Legacy technology costs often require a little risk taking to eliminate. For example, a firm may simply announce that a legacy customer relationship management system will be fully retired in nine months and require all business and technology units to be ready for the day it is switched off by migrating integration and processes. This may cause business disruption but may be better than infinitely paying for an expensive system that no longer produces much value.Partner ReductionRemoving partners who are costly relative to their value. For example, migrating from an expensive operating system to a free one.Product DiscontinuationDiscontinuing unprofitable products and services that do not contribute to net revenue such as a fashion brand that has always failed at shoes that finally gives up on its shoe line.Closing LocationsIt is common for retailers and service businesses to close unprofitable locations in order to cut costs.Dropping CustomersA firm may drop or restrict their relationship with unprofitable customers in order to cut costs. This has reputational, compliance and strategic risks such that it is often a bad idea. Nevertheless, dropping a customer who consistently costs you more than they pay is tempting when times are hard. A better long term strategy is to shape pricing and practices to prevent such situations. For example, an outsourcing company that caps support at 30 hours a month with more support that can be purchased in increments of 10 hours. This prevents customers from consuming hundreds of hours of support that cost far more than the customer pays.DownsizingReevaluating an entire organization such that any type of cost cut is on the table. For example, a firm may cut an entire division or exit entire regions.FacilitiesReducing facility related costs. For example, moving from a large office in a high rent location to a small office in a low rent location.RelocationRelocating facilities, operations and overhead functions to a less expensive country or region. For example, a video game company that full relocates from a country with a high tax rate to a country with a low tax rate.RenegotiationRenegotiating terms with executives, partners and creditors. For example, asking the executive team to reduce their salary to $1 for a year. This may be fair if the executive team has enjoyed significant compensation in the past but has led the company to a state where it is desperate for cash. This can be accompanied with future compensation if the executive team can turn things around. If a firm is at risk of failing it is often possible to renegotiate with creditors and landlords who have an interest in keeping the firm alive.SummaryThe following are common types of cost cutting:OverviewCost cutting can start with small things that create a culture of cost discipline. Some costs such as discretionary spending and capital investment are relatively easy to cut or defer. In some cases, business and financial conditions call for drastic and immediate cuts such as retrenchment.Next: Retrenchment
More about business costs:
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|