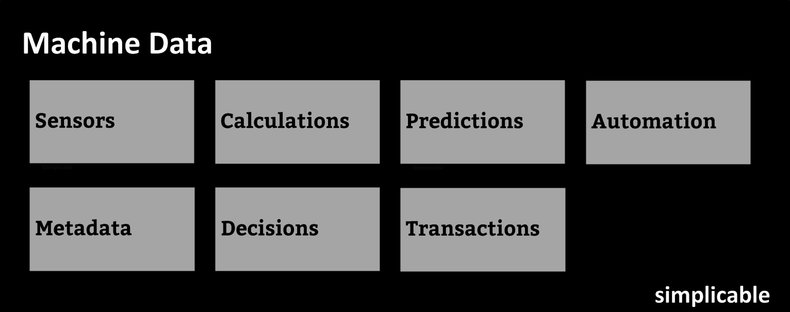
Sensors
Sensors are devices that detect physical phenomena such as light and sound and turn it into streams of data. For example, video of a street corner or temperature readings from a part in a machine.Calculations
Data that is calculated from other data. For example, an algorithm that calculates a risk estimate for an investment based on market data.Predictions
Algorithms and artificial intelligence that attempt to predict the future. For example, a robot that attempts to predict the near future direction of pedestrians as it walks down the street.Automation
Automated tasks that create data such as events, controls or commands. For example, a manufacturing control system may issue commands to a conveyor belt and create a status log.Metadata
Data about other data such as a timestamp that is added to event data.Decisions & Interpretations
Machine decisions such as an algorithm that decides to approve a customer's application for credit.Transactions
Machines may generate transactions that have commercial and legal significance for the organization that owns the machine. For example, a machine may decide to execute a stock trade for a financial institution based on rules in an algorithm.| Overview: Machine Data | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Data that is generated by machines without human involvement. | |
Related Concepts | ||