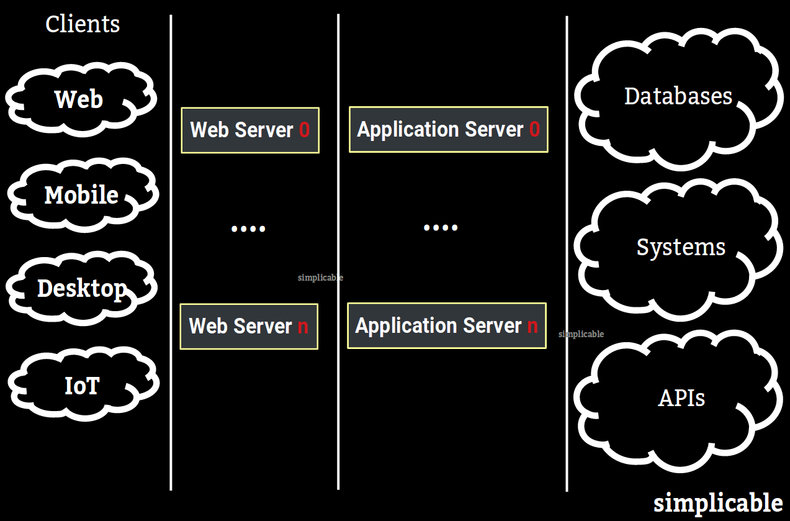
Web Server
An application server can build and serve dynamic web pages.Media
Application servers can serve static web pages and media such as images and video.Business Logic
Application servers provide an environment to run code such as Java or PHP to implement business logic such as authorization & authentication, transactions, business rules and data processing.Web Server Integration
Although application servers can serve web pages and media they aren't necessarily optimized for these functions because it is common to use a separate web server for this purpose. This is considered a best practice because this allows you to secure the application server. In other words, application servers are commonly deployed behind a firewall whereby clients can only request services through a web server. This is highly efficient as web servers can cache responses and serve static content while leaving the heavy lifting of business logic to the application server.APIs
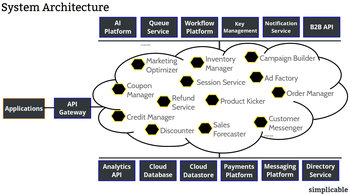
It is common to build and deploy APIs on an application server that may be used by different types of clients.Asynchronous JavaScript
In some cases, a web page includes active content whereby the page itself calls an application server using javascript. For example, a web page that serves maps may request updates to the map from an application server. When a response is received, javascript can be used to dynamically change the page.Mobile Application Server
Application servers can provide services to mobile apps. For example, an ecommerce app that calls an application server to retrieve lists of product information.Desktop Applications
In many cases, desktop software connects to an application server. For example, an MP3 player on a laptop that connects to the internet to retrieve metadata about a song.Internet of Things
Beyond web pages, mobile apps and desktop software it is common for software on any type of device to connect to an API running on an application server. For example, an electronic bicycle that connects to an API to retrieve road condition data.Systems
Although application servers are designed to provide services for applications, they are also occasionally used to implement systems. For example, an IoT device with no user interface such as a smart window may connect to services that run on application servers.Integration
It is common for a application server to integrate with a database and a wide range of backend systems. For example, an application server for a banking website that connects to its own database and services for market data, account data and transactions.High Availability
In many cases, application servers allow for load balancing, clustering and failover such that you can deploy many servers to handle load and achieve high availability.Cloud Deployment
It is increasingly common to deploy application servers to cloud infrastructure and use cloud load balancers as opposed to the high availability features of application server products themselves.Microservices
Microservices is a modern architectural technique that involves breaking down business logic into individually deployable services. Microservices are often deployed to application servers on cloud infrastructure. This produces extremely scalable and resilient applications.| Overview: Application Server | ||
Type | ||
Definition | A platform for building and running software that is used by users. | |
Also Known As | App Server | |
Related Concepts | ||