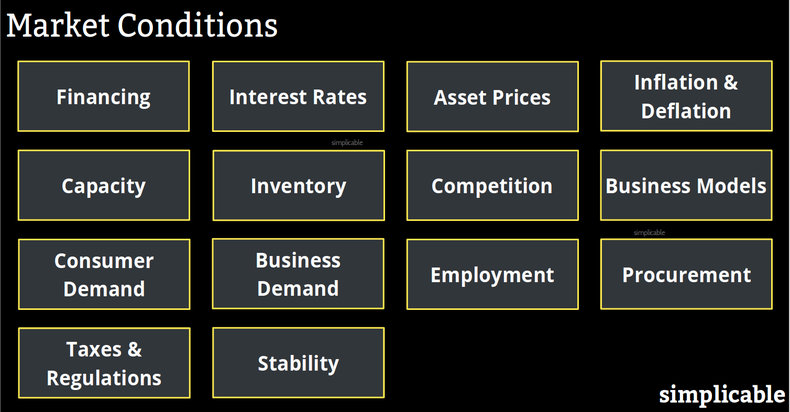
Financing
The environment for securing financing. An economy goes through periods where defaults are low and liquidity is high that encourages banks to more easily lend money. In an economic contraction, defaults increase and banks tighten their lending standards.Interest Rates
Interest rates are a fundamental type of market condition that impacts return on investment for all industries. When interest rates are low, it is easier for firms to expand profitably. A long period of excessively low interest rates can lead to irrational investments and capacity expansions.Asset Prices
The prices of assets and investments such as land and stocks. This relates to business cycles, interest rates and the enthusiasm of investors for a particular investment at a point in time. Historically, asset prices tend to go through a boom and bust cycle of dramatic increases known as bubbles and dramatic declines known as crashes.Inflation & Deflation
The rate of change in general price levels. Deflation gives buyers incentive to delay purchases as things are always getting cheaper. Excessive inflation can cause hording as producers have incentive to delay sales as the prices of goods rise. Both deflation and excessive inflation can cause a breakdown in normal economic activity that makes business and investment far more challenging.Capacity
Industries go through periods where demand is far higher than supply. Firms rush to add capacity and supply increases. This leads to a period where supply is far higher than demand. For example, a city that is experiencing an economic boom may have a shortage of restaurants. Restaurants will become unusually profitable and owners will rush to build new locations. This can lead to oversupply and a dramatic decline in profitability.Inventory
Excess capacity in an industry can lead to high inventory levels. For example, if solar panel manufacturers have more capacity than global demand they may end up with solar panels sitting in warehouses. Excess inventory leads to discounting that may make an industry unprofitable for all firms.Competition
The competitive environment in areas such as promotion, pricing, locations and product improvement. If you are able to discover a new product that customers need, you may face little competition for a short period of time. Most industries are intensely competitive such that firms need to establish and defend competitive advantages to survive.Business Models
New business models that may represent an opportunity or a challenge for an industry. For example, a trend towards offering apartments and homes as short term rentals that challenges a hotel industry to adapt.Consumer Demand
Consumer demand and related things such as customer needs, preferences and perceptions. For example, a startup fashion company that is able to capitalized on a fashion trend to grow rapidly.Business Demand
Businesses go through periods of aggressive investment in new capacity and improvements. This can be followed by periods of cutbacks. Demand can occur at the level of an individual product or service. For example, businesses may rush to invest in a trendy technology followed by a period of disillusionment as the technology fails to immediately live up to its hype.Employment
Supply and demand for employees by profession. When general employment levels are high it is far easier to find a job and more difficult to hire employees. As such, wages rise. This can also occur at the level of a particular skill set.Procurement
The environment for procuring materials, parts and equipment. For example, an industry may go through a period where an essential material or part is in short supply with rising prices. This may be followed by periods of oversupply whereby prices quickly fall.Taxes & Regulations
Governments greatly influence market conditions in areas such as trade, taxes and compliance. For example, a nation with burdensome business taxes and regulations may be less attractive to small businesses and investors. In some cases, regulations are a positive for an industry. For example, environmental regulations might benefit clean energy firms.Stability
The political stability of a nation or region. For example, a government that is predictable, reliable and reputable may be conductive to business and investment.| Overview: Market Conditions | ||
Type | ||
Definition | The economic environment for business, investing and employment. | |
Related Concepts | ||