URL Parts
URLs can be broken down into several component parts:
Query
A query can be appended to a URL with a "?" character as follows.
Fragment
A fragment can be appended to a URL with a "#" character as follows.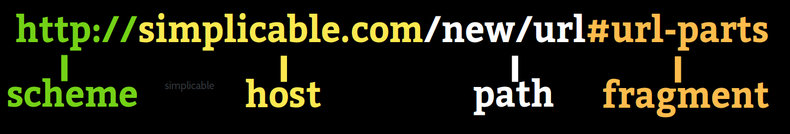
URL Normalization
There are several rules that are used to clean up unsightly URLs by mapping them to a standard version. For example, uppercase letters in a host name are mapped to lower case letters and standard port numbers are removed.
Clean URLs
As a general principle, URLs are typically designed to be human readable wherever possible. This means that URLs are guessable such that people could change them to look for information. For example, the following URL can be considered clean.https://simplicable.com/new/urlThis URL isn't particularly clean:https://simplicable.com/PageLauncher?p=6AFE8AA494844F1 Another common principle related to URLs is that information security should never rely on a complex "unguessable" URL.Relative URLs
A resource can link to itself using only the path of the URL. A query and fragment can also be specified. This is commonly done on mobile web pages to reduce the size of the page for the purposes of speed and bandwidth reduction. For example, a page on simplicable.com can link to this page with the URL: /new/url.URL Shortners
A URL shortner is a service that provides permanent short URLs such as:http://goo.gl/Z4Dzv3This is popular for sharing long URLs on social media. The provider of the short URL may collect data as they redirect each request. In some cases, the provider may share this data with the person who created the short URL. This is a way to track how many people click on a link.Hostname vs Domain Name
A domain name is an internet address that is owned by an organization or individual such as:google.comA hostname can be the same as a domain name or it can add additional strings at the front of the domain known as subdomains such as:cloud.google.comEach subdomain has a "." character after it. These can be added to many levels. However, it is a common principle to never add more than one subdomain.URL vs URI
A URL is a type of URI, or Uniform Resource Identifier. In other words, URLs are based on a standard known as URI. This standard is used to address other things such as email addresses. The following is a summary of the URI standard: scheme:[//[user[:password]@]host[:port]][/path][?query][#fragment]| Overview: Url | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An address for locating files and services on the internet. | |
Also Known As | Web Address | |
Invented By | Tim Berners-Lee | |
Related Concepts | ||