Hunter-gatherer | Pastoral |
Horticultural | Agricultural |
Feudal | Industrial |
Capitalist | Communist |
Modern Capitalism | Crony Capitalism |
Social Market Economy | Multicultural Societies |
Post-industrial | Consumer Societies |
Postmodern Societies | Post-scarcity Societies |
Hunter-gatherer Societies
The oldest type of society organized around small populations that move frequently in search of food and other resources. Tend to be egalitarian with little structure but strong gender roles. Traditional knowledge transmitted with spoken language plays a strong role in survival.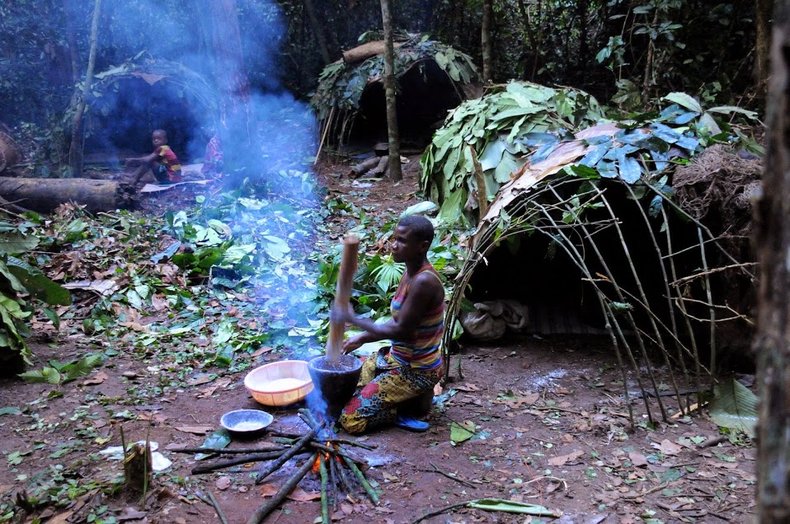
Pastoral Societies
Societies based on the domestication and herding of animals as a form of subsistence agriculture. These societies move to secure resources for animals often along seasonal routes. Strong bonds of kinship and family. Depend on trade to secure things they don't produce directly.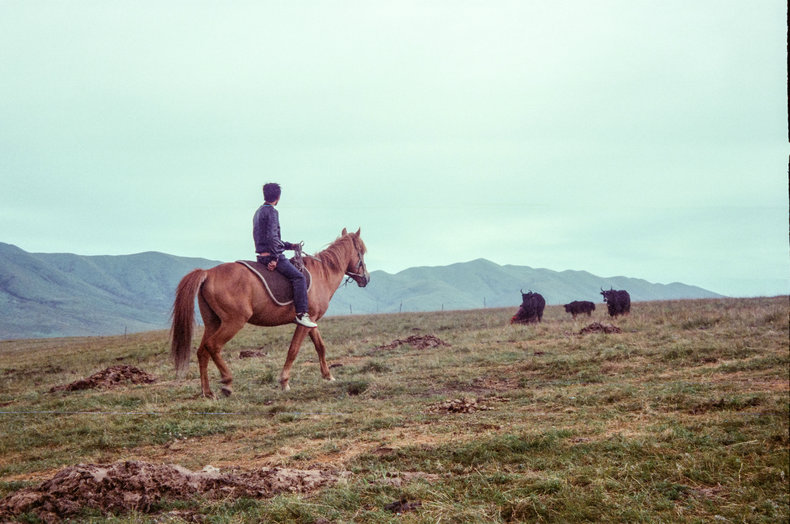
Horticultural Societies
Horticultural societies cultivate fruits, nuts and vegetables in areas where vegetation naturally thrives. This is essentially a basic type of agricultural society that has limited ability to transform the landscape to make it more fertile. For example, an tropical environment where fruits and other plants are naturally abundant such that few tools are required to thrive.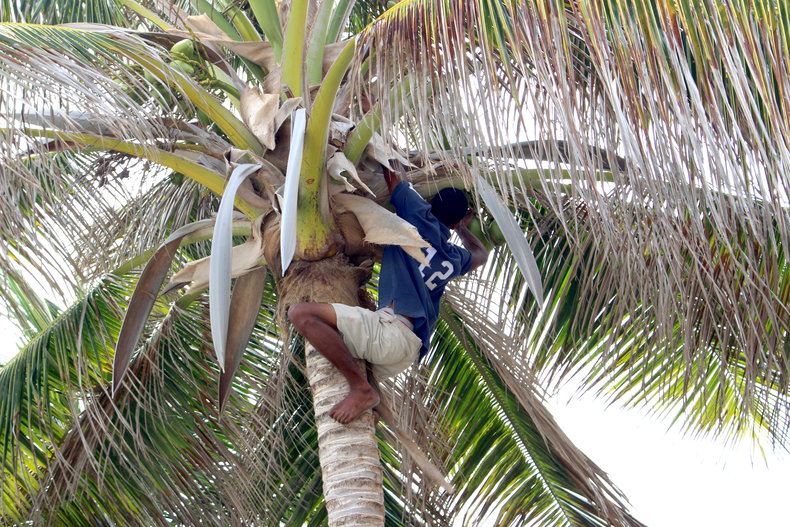
Agricultural Societies
Permanent settlements that rely on farming with the tools and knowledge required to make land more productive. Agriculture also lead to the specialization of labor and growing trade with a small merchant class. Began around 10,000 BC and was the dominant type of human society for the 5,000 years preceding the industrial-era. Living in one place creates a rich culture, strong norms and much sense of social hierarchy and status.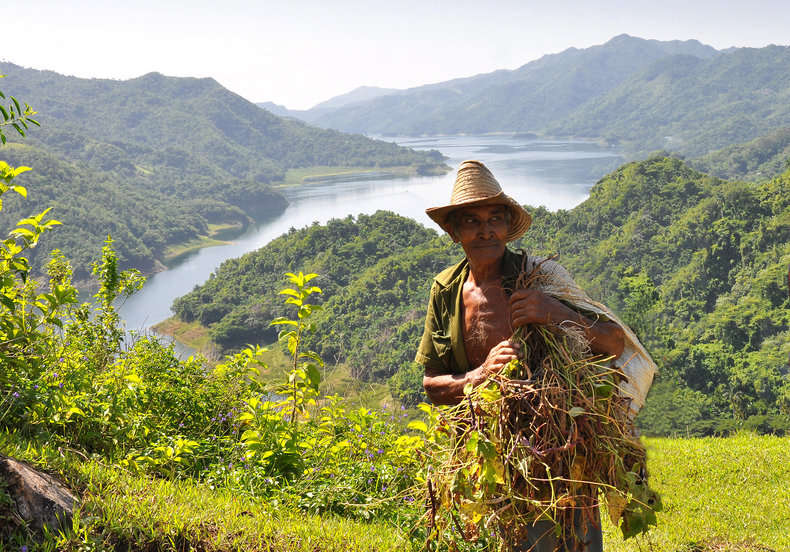
Feudal Societies
An agricultural society based on a hierarchy of land ownership whereby there is an exchange of labor for land. This included the exchange of land for military service that allowed for societies with military capabilities.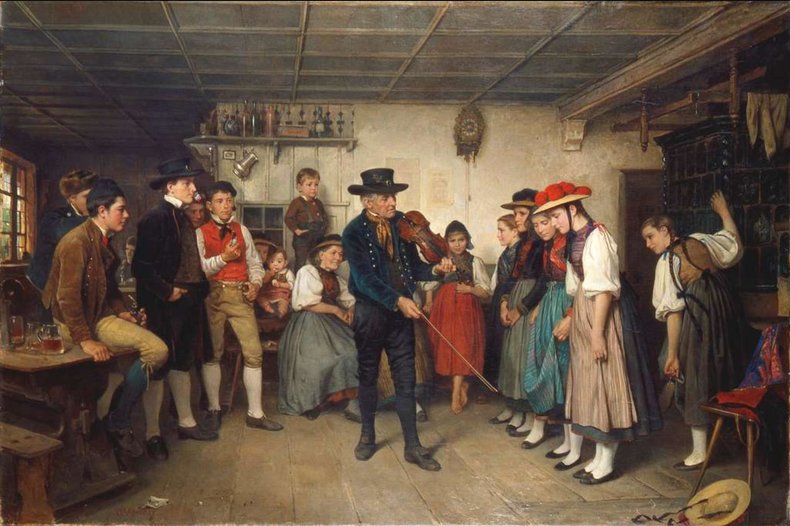
Industrial Societies
Machine based mass production and cooperation at great scale that generates significant wealth. Creates a division between the owners of capital and labor. Produces uneven improvements in quality of life and economic bads such as pollution. Drives urbanization, the formation of very large cities and a fast pace of technological and cultural change. Work in an industrial society is often toilsome and repetitive but efficient.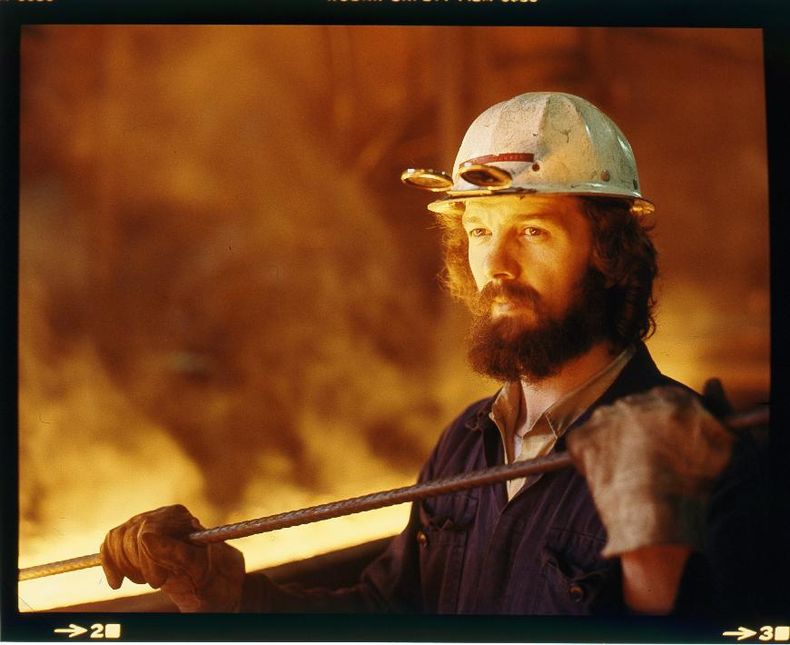
Capitalist Societies
Capitalist societies extended the exchange of labor for land under feudalism to include other types of capital such as factories under a system of private ownership and economic freedom. This is essentially a system of competition whereby people compete for jobs and to build capital. Capitalism provides strong incentives for productivity, efficiency, growth and improvement. It can generate a great deal of wealth that is unevenly distributed.
Communist Societies
The exchange of labor for access to capital except that all capital is owner by the state and total equality is enforced whereby everyone must work and no one must be allowed to profit more than anyone else. This removes the profit motive and gives no incentives for strategic prowess, invention, improvement, productivity, effort or creativity. The result is a sprawling bureaucracy, inefficiency, decline, failures, shortages and continued inequality whereby a bureaucratic elite control all resources1.
Modern Capitalism
During the cold war the quality of life of capitalist and communist industrial nations diverged. Workers in capitalist nations pushed for higher wages and better working conditions. The management layers of firms expanded and higher paying roles became available. This produced massive increases in quality of life with more disposable income and leisure time. Service industries grew and opportunities for small business increased.
Crony Capitalism
Capitalism is based on the profit motive and the efficiencies created by people pushing for a better life. This can only work where open competition is sustained. Crony capitalism is a system with a large rent seeking elite that add little value but seek wealth using relationships, institutions and systems that work against the masses. This produces monopolies, anti-competitive practices, government interference in markets, unfair systems, inefficiency and a shrinking middle class.
Social Market Economy
A social market economy is a society that preserves the profit motive, open markets and competition but uses taxation as a limited form of income redistribution often in the form of free or low cost government services in areas such as education and healthcare. Nations with a large middle class and low poverty usually fall into this category.
Multicultural Society
A multicultural society is a society where people are encouraged to retain their cultural identities. This requires a shared culture that is built on norms of tolerance. The opposite approach is a melting pot society where people are encouraged to adopt a national culture and to try to conform.
Post-industrial Societies
A post-industrial society is a society where the service sector generates more wealth than the manufacturing sector of the economy. This is an indication of an advanced economy with much economic activity in areas such as education, healthcare, technology, entertainment, travel, leisure and culture.
Consumer Society
A consumer society is a society oriented to consumer markets where firms try to meet every imaginable need with products and services. This produces an incredible variety of goods. Some argue that the consumer society represents the commoditization of the human experience whereby people become obsessed with convenience, comfort and consumption over living their lives in some fulfilling way.
Postmodern Societies
Postmodern society is a term for a society under the influence of relativism whereby people reject the notion of objectivity, fact and authority in favor of subjective reality. This calls on society to conform to each individual as opposed to the other way around. It is unclear how this could create civility as people tend to have conflicting ideas and society traditionally plays a unifying role by establishing shared understanding and common rules.
Post-scarcity Society
The theory that little labor will be required in future such that governments would need to provide a basic income and firms would still compete but things would be massively automated. This would not eliminate work but rather it would eliminate unpleasant work known as toil. People would likely still find ways to compete and to increase their share of wealth or whatever is valued such as social status. For example, you could have an economy where almost everyone is an influencer on social media. Alternatively, there may be countless hobbies, recreational pursuits, cultures, subcultures and virtual worlds where people compete in niche ways.
Historical Societies
If you take a long view, over the course of human history there have been six types of society: Hunter-gatherer societies, pastoral societies, horticultural societies, agricultural societies, feudal societies and industrial societies.
Modern Societies
If you are just looking at the modern-era, political systems become much more relevant whereby systems such as capitalism, communism and social market economy stand out as major types of society.