Transportation Infrastructure
The construction, maintenance and operation of transportation infrastructure such as roads, bridges, ports, canals, airports, seaports and railways.Public Transport
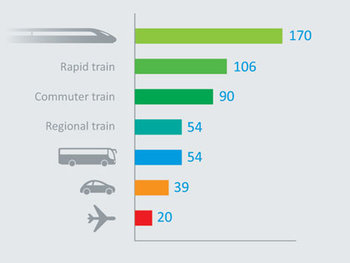
Passenger services that can be used for moving around a city and commuting such as trains, buses and ferries. For example, Japanese train companies handle around 15 billion passenger trips a year that are mostly daily commuters.Airlines & Air Cargo
Passenger services and air cargo. Airlines carry more than 4.5 billion passengers a year.Railways
Railways that offer passenger and freight services. These often resemble monopolies that may be regulated as critical public infrastructure.Maritime Shipping
Maritime freight services such as bulk carriers, container ships, tankers, refrigerated ships, general cargo ships and special cargo ships carry the bulk of world trade.Cruise Industry
Cruises offer a tour-like experience on a large ship that may offer entertainment and leisure activities. A single cruise ship can burn 150 tonnes of fuel a day and emit as much air pollution as a million cars.Trucking Industry
Another backbone for the shipping of goods that tends to be an important employer due to its smaller scale. For example, trucking employs around 2 million people in the United States alone.Logistics
Logistics related services such as trucking hubs, ports and warehouses. This includes complexities such as customs and cold chain that ensures goods remain cold over the entire supply chain.Couriers
Services that deliver to end-customers.Postal Services
Basic infrastructure for sending mail and packages to any address. Often provided as a service by governments.Taxis
Taxis and similar services that convey passengers to a location of their choice.Tours
Travel services that include an element of transport such as a bus tour.Vehicle Rentals
Rentals of vehicles including small vehicles such as bicycles.Transportation Insurance
The market for vehicle, freight and travel insurance.Shipbuilding
The construction of ships for transport. Considered a heavy industry.Vehicles
The design, manufacturing, marketing and sales of vehicles such as electric cars and buses.Aerospace Industry
The manufacturing and sales of commercial aircraft is considered part of the aerospace industry but is dependent on the transportation industry for its sales.Space Industry
The space industry is historically viewed as part of the aerospace, technology or manufacturing industry that produces products such as rockets and satellites. As the space industry evolves it may begin to resemble an element of the transportation industry as it begins to carry more passengers or freight.Summary
The transportation industry includes passenger services, services that deliver goods, transportation infrastructure and manufacturing of vehicles, ships and aircraft. This overlaps with other industries such as manufacturing and the travel industry.
| Overview: Transportation Industry | ||
Type | ||
Definition | Businesses and public services that create value by moving people and goods. | |
Related Concepts | ||