Manufacturing | Assembly |
Textile production | Paper production |
Chemical production | Food processing |
Beverage production | Shipbuilding |
Printing & publishing | Craft production |
Construction | Bakeries |
Pharmaceutical production | Artisanal production |
Microchip fabrication | Materials production |
Energy production | Aerospace manufacturing |
Manufacturing
The production of physical products such as vehicles, furniture and housewares. Manufacturing is often done at scale in large, highly automated factories that are able to deliver a low unit cost.Fast Moving Consumer Goods
The production and marketing of goods that are quickly consumed such that people need to buy regularly such as food, cosmetics, toiletries and candy. The fast moving consumer goods industry is dominated by large brands with extensive manufacturing and logistics capabilities.Construction
The construction of houses, buildings and other structures such as transportation infrastructure.Materials
The production of raw materials that are finished enough to be used. For example, production of wood products such as 2x4s that are directly purchased by contractors and consumers.Heavy Industry
Heavy industry is the construction of large facilities such as a hydroelectric dam and the manufacturing of large products such as aircraft.Food Industry
The production of food and beverage products such as a bakery or brewery.Fashion
The design, production and marketing of clothing, footwear and other items that people wear.Craft
Production by hand such as a craftsperson who produces handmade traditional jewelry.Advanced Manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing such as 3d printing and mass customization.Three Levels
The three basic levels of the economy:Primary Industry
The production of basic materials including mining, forestry and fishing.
Secondary Industry
Production of a finished product including manufacturing, craft and construction.
Service Industry
The delivery of intangible value such as service, entertainment and education.
Types
The following are the basic types of secondary industry.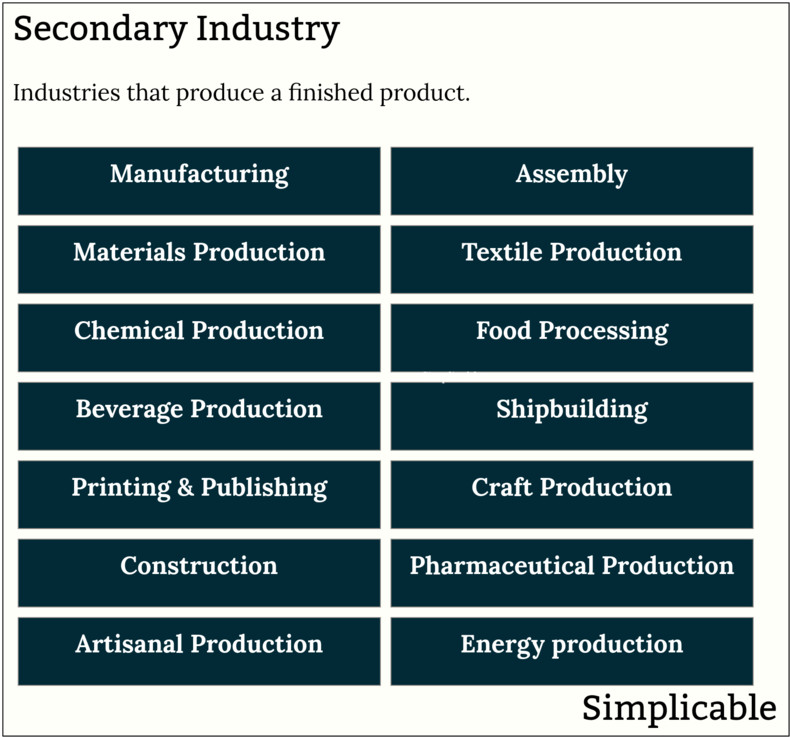
Summary
Industries such as manufacturing and construction that take materials as inputs and create finished products that are ready for consumption.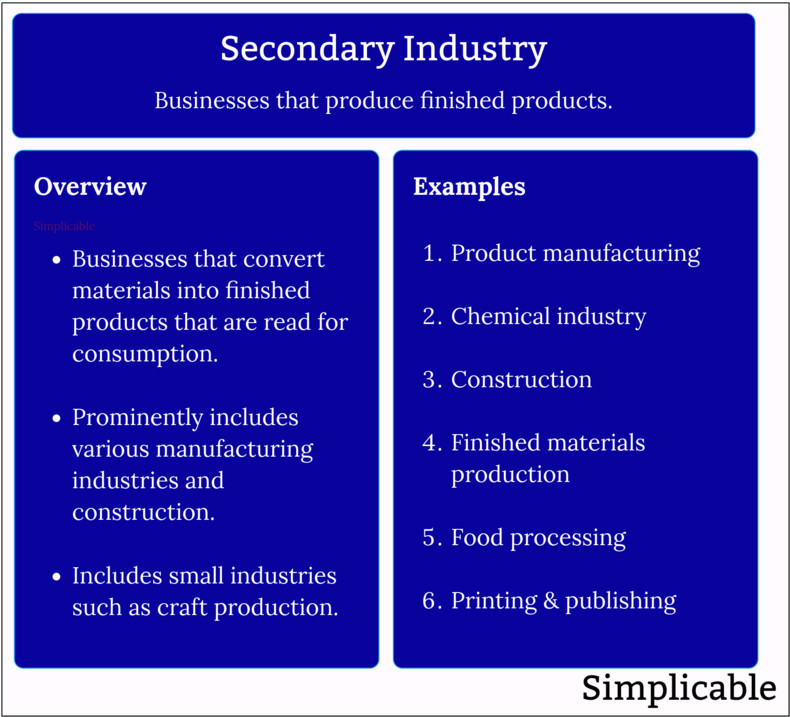
| Overview: Secondary Industry | ||
Type | ||
Definition | An industry that takes raw materials as an input and creates finished products as an output. | |
Also Known As | Secondary Sector | |
Related Concepts | ||