|
| |
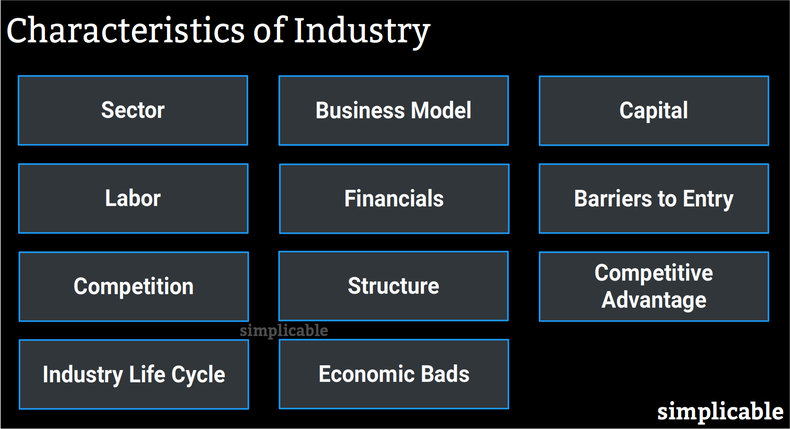
An industry is a grouping of businesses that offer similar products and services. The following are the basic characteristics that can be used to compare industries and firms within industries.SectorA sector is the level of value creation of an industry. These are as follows.| Sector | Level | Examples | | Primary | The production of raw materials. | Agriculture, Mining | | Secondary | The production of finished goods. | Manufacturing,Craft | | Tertiary | Services that add intangible value. | Restaurants, Banks, Retail |
Business ModelA business model is how a firm generates and captures value. For example, club goods is a business model used by theme parks whereby a firm offers access to expensive capital for an admissions fee.
CapitalCapital is the productive property that is required to participate in an industry including natural resources, land, buildings, infrastructure, machines, computers and vehicles.LaborThe labor requirements of an industry. For example, banks that commonly employ large numbers of knowledge workers.FinancialsFinancial metrics are typically comparable across an industry. For example, manufacturing firms in a particular region may have similar profit margins, return on invested capital and revenue per employee. Barriers to EntryBarriers to entry is how difficult it is for new competitors to enter an industry. For example, restaurants have relatively low barriers to entry such that a successful location may soon face new competitors.CompetitionThe level of competition in an industry. For example, farmers that are protected from competing with global producers by the protectionist policies of a government.StructureStructure refers to the basic type of competition in an industry. The following are the basic types.| Structure | Number of Firms | | Monopoly | A single firm mostly dominates. | | Oligopoly | Three to ten firms dominate competition. | | Pure Competition | A large number of firms compete. |
Monopolies have no competitors and typically need to be regulated to prevent abuse of their market power such as high prices, low quality and unfair practices forced on customers and partners.Competitive AdvantageWhat it takes to win competitive battles in an industry. For example, in the fast moving consumer goods industry brand recognition is a primary type of competitive advantage such that firms in this industry must spend heavily on advertising.Industry Life CycleAn industry life cycle is a stage of growth of a market for goods and services.| Stage | Growth Level | | Nascent | A newly formed industry with space for new entrants but often an uncertain future. | | Growth | An industry that is quickly growing revenue. | | Mature | An industry that is slowly growing revenue. | | Decline | An industry with falling revenues. |
Economic BadsIndustries produce economic goods that have value but may also produce economic bads such as pollution.
Industries
This is the complete list of articles we have written about industries.
If you enjoyed this page, please consider bookmarking Simplicable.
© 2010-2023 Simplicable. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction of materials found on this site, in any form, without explicit permission is prohibited.
View credits & copyrights or citation information for this page.
|